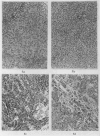
Abstract
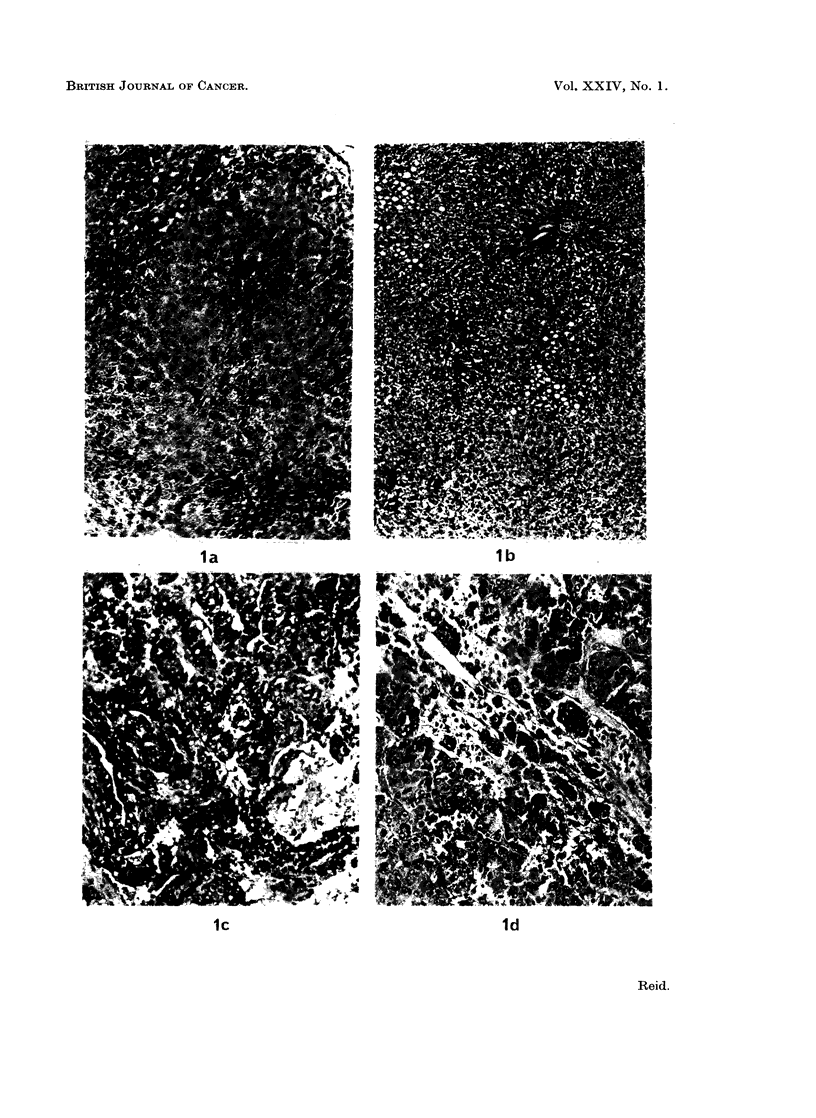
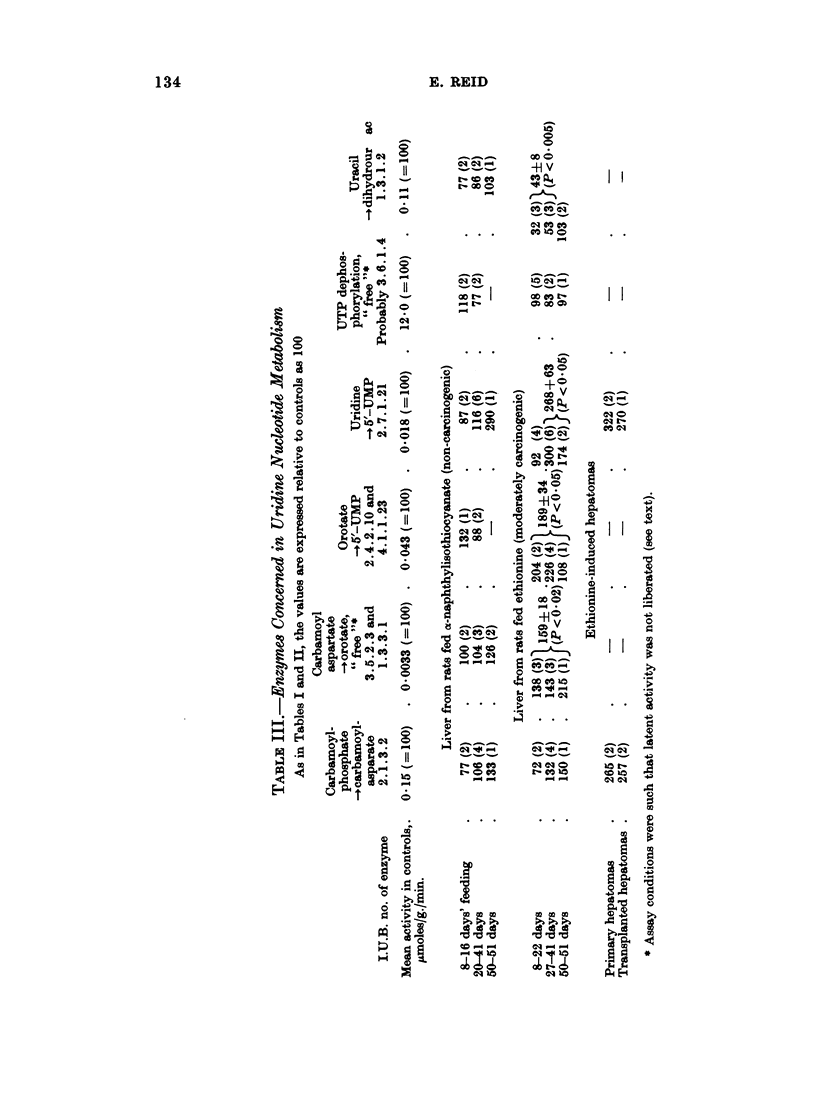
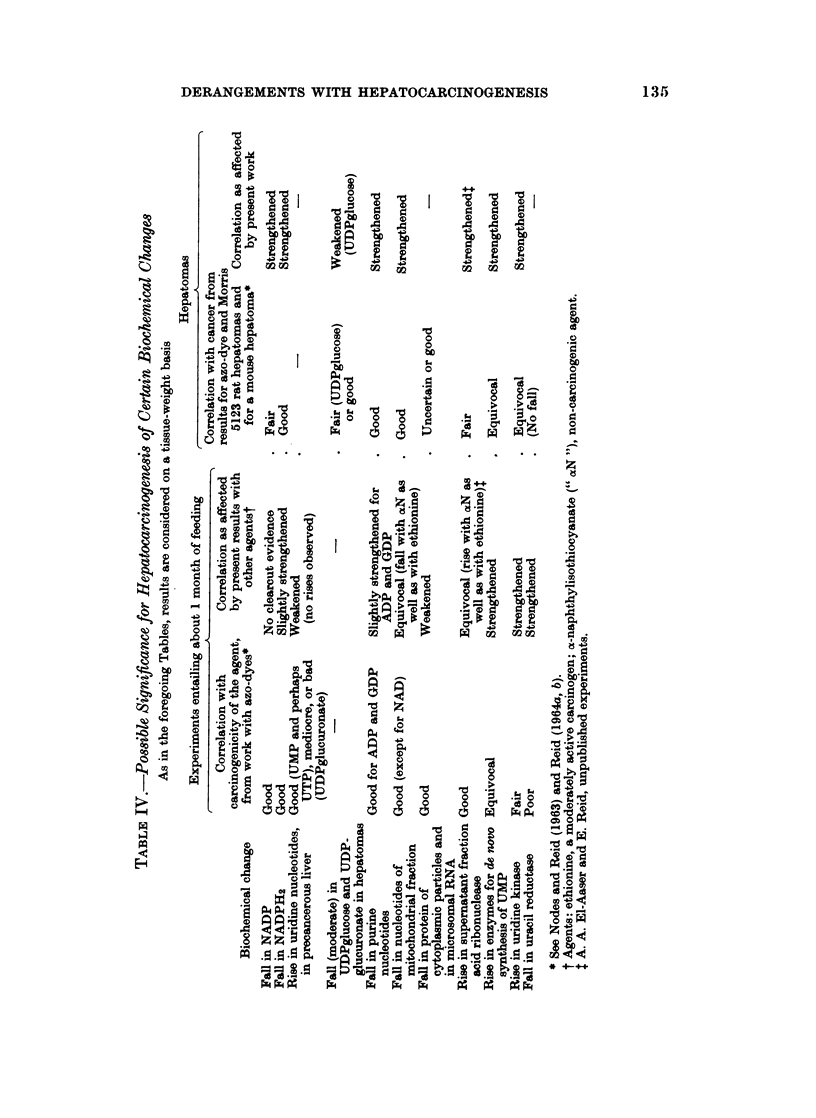
Earlier work on acid-soluble nucleotides and other liver constituents as affected by azo-dye carcinogenesis has now been extended, with trial of ethionine (weakly carcinogenic) and of α-naphthylisothiocyanate (noncarcinogenic). The effects of ethionine feeding on whole-tissue nucleotide levels were not dramatic, and were generally dissimilar to those produced by azo-dye feeding. However a fall in some or all of the purine nucleotides can still be regarded as a feature of hepatocarcinogenesis.
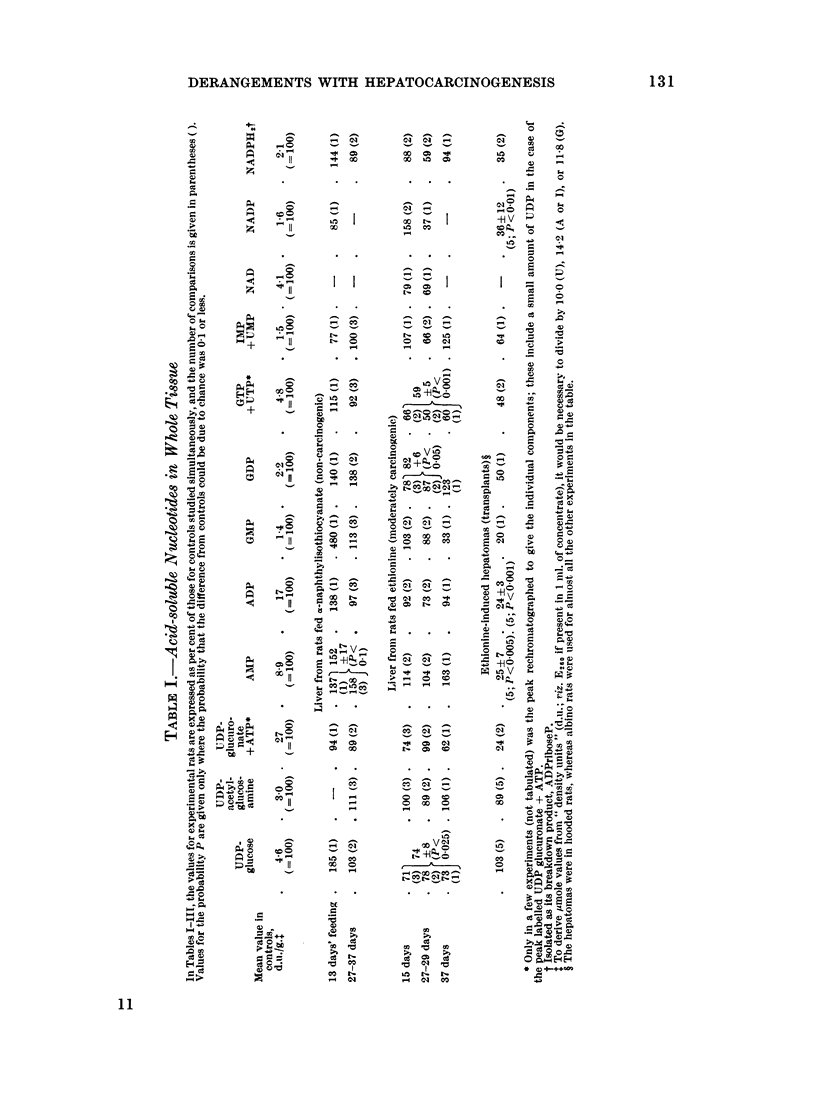
A fall in mitochondrial nucleotides, as previously found in azo-dye experiments, likewise occurs with ethionine feeding, but also with α-naphthylisothiocyanate. It is suggested that the latter warrants testing as a co-carcinogen. Unlike azo-dyes, ethionine is without adverse effect on the yield of protein in cytoplasmic particles and (in common with α-naphthylisothiocyanate) it raises the yield of RNA in the supernatant fraction.
In liver from ethionine-fed rats and in ethionine-induced hepatomas, the activity of enzymes concerned in UMP synthesis showed a rise more striking than that found with azo-dyes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CALDARERA C. M., BUDINI R., BARBIROLI B., RABBI A. The effect of ethionine on the free nucleotides in rat liver. Cancer Res. 1962 Oct;22:1026–1030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dessev G. N., Mullock B. M., Reid E., Turner M. K. Ribonucleic acid as affected by hepatocarcinogenesis. Br J Cancer. 1969 Sep;23(3):597–615. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1969.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORRIS H. P. SOME GROWTH, MORPHOLOGICAL AND BIOCHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF HEPATOMA 5123 AND OTHER NEW TRANSPLANTABLE HEPATOMAS. Prog Exp Tumor Res. 1963;3:370–411. doi: 10.1159/000385968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NODES J. T., REID E. AZO-DYE CARCINOGENESIS: RIBONUCLEOTIDES AND RIBONUCLEASES. Br J Cancer. 1963 Dec;17:745–774. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1963.96. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REID E. Significant biochemical effects of hepatocarcinogens in the rat: a review. Cancer Res. 1962 May;22:398–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEKOL J. A., BEDRAK E., MODY U., BURNETTE N., SOMERVILLE C. Inhibition of the synthesis of diphosphopyridine nucleotide by ethionine administration in the liver of rats and mice. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:469–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. C., Salmon W. D. Formation of S-adenosylethionine by ethionine-treated rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Jul;111(1):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90339-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneider T. W., Potter V. R. Deoxycytidylate deaminase and related enzymes of thymidine triphosphate metabolism in hepatomas and precancerous rat liver. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1969;7:375–394. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(69)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNGAR H., MORAN E., EISNER M., ELIAKIM M. Rat intrahepatic biliary tract lesions from alpha-naphthyl isothiocyanate. Arch Pathol. 1962 May;73:427–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]