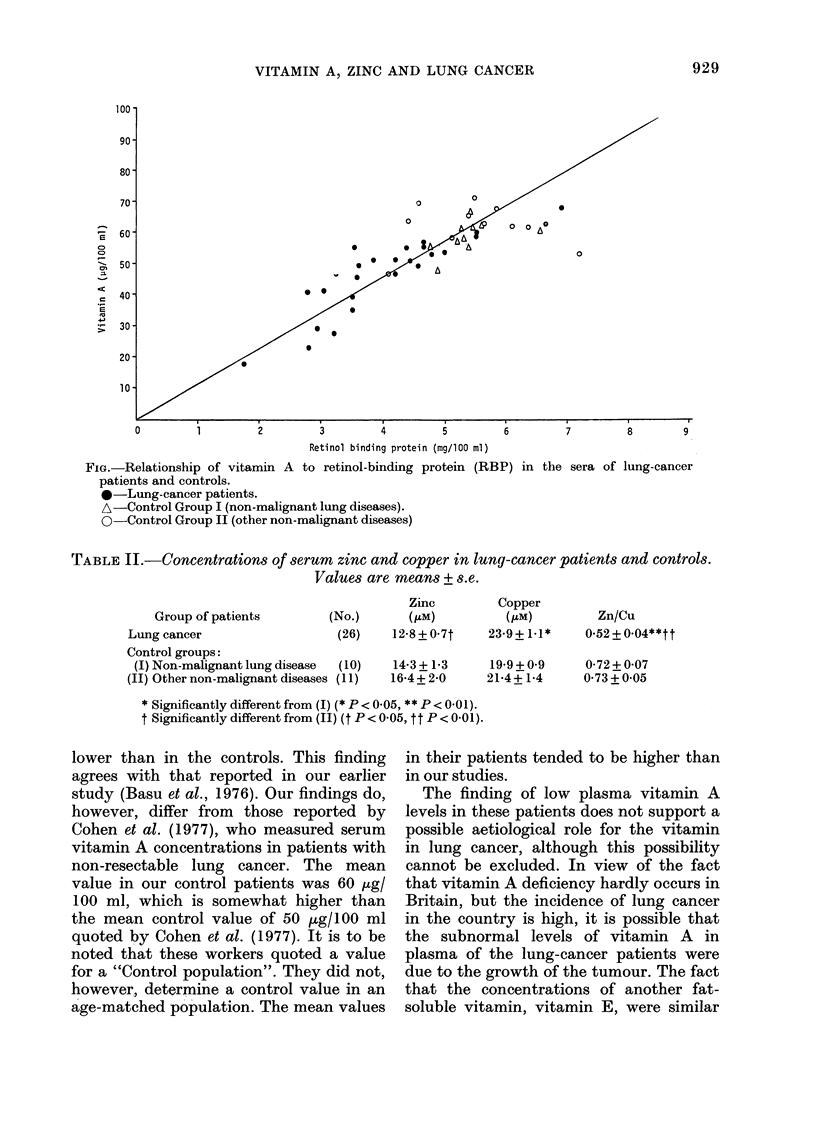
Abstract
Serum vitamin A concentration were measured in 26 newly diagnosed lung-cancer patients and found to be significantly lower than those of patients of similar age with either non-malignant lung or non-lung diseases. The levels of vitamin A in the lung-cancer patients, but not in the controls, were significantly correlated with serum concentrations of retinol-binding protein (RBP) and zinc. It is suggested that low levels of zinc might reduce the synthesis of RBP and thus reduce the mobilization of vitamin A from the liver.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames S. R. Factors affecting absorption, transport, and storage of vitamin A. Am J Clin Nutr. 1969 Jul;22(7):934–935. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/22.7.934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu T. K., Donaldson D., Jenner M., Williams D. C., Sakula A. Plasma vitamin A in patients with bronchial carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1976 Jan;33(1):119–121. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1976.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind J. C., Newmark H., Brin M. Vitamins A and E nutrition via intramuscular or oral route. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Mar;27(3):234–253. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.3.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjelke E. Dietary vitamin A and human lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 1975 Apr 15;15(4):561–565. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag W. Prophylaxis of chemically induced benign and malignant epithelial tumors by vitamin A acid (retinoic acid). Eur J Cancer. 1972 Dec;8(6):689–693. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(72)90153-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. D., Chan W., Smith J. C., Jr Vitamin A metabolism during the repletion of zinc deficient rats. J Nutr. 1976 Apr;106(4):563–568. doi: 10.1093/jn/106.4.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone M. V., Nettesheim P. Effects of vitamin A on 3-methylcholanthrene-induced squamous metaplasias and early tumors in the respiratory tract of rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Jun;50(6):1599–1606. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.6.1599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLL R., HILL A. B. MORTALITY IN RELATION TO SMOKING: TEN YEARS' OBSERVATIONS OF BRITISH DOCTORS. Br Med J. 1964 May 30;1(5395):1399–1410. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5395.1399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies I. J., Musa M., Dormandy T. L. Measurements of plasma zinc. I. In health and disease. J Clin Pathol. 1968 May;21(3):359–363. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies I. J. Plasma-zinc concentration in patients with bronchogenic carcinoma. Lancet. 1972 Jan 15;1(7742):149–149. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)90717-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ette S. I., Basu T. K., Dickerson J. W. Short-term effect of zinc sulphate on plasma and hepatic concentrations of vitamins A and E in normal weanling rats. Nutr Metab. 1979;23(1):11–16. doi: 10.1159/000176236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glover J. Retinol-binding proteins. Vitam Horm. 1973;31:1–42. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60995-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S. Vitamin A transport and retinol-binding protein metabolism. Vitam Horm. 1974;32:167–180. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim K., Jafarey N. A., Zuberi S. J. Plasma vitamin "A" and carotene levels in squamous cell carcinoma of oral cavity and oro-pharynx. Clin Oncol. 1977 Jun;3(2):203–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R. A., Sandstead H. H., Solomons N. W., Rieger C., Rothberg R. Zinc status and vitamin A transport in cystic fibrosis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1978 Apr;31(4):638–644. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/31.4.638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaëlsson G., Vahlquist A., Juhlin L. Serum zinc and retinol-binding protein in acne. Br J Dermatol. 1977 Mar;96(3):283–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1977.tb06138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A. E., Leddicotte G. W., Fink R. W., Friedman E. W. Trace elements in noraml and malignant human breast tissue. Surgery. 1974 Aug;76(2):325–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. R., Goodman D. S., Zaklama M. S., Gabr M. K., el-Maraghy S., Patwardhan V. N. Serum vitamin A, retinol-binding protein, and prealbumin concentrations in protein-calorie malnutrition. I. A functional defect in hepatic retinol release. Am J Clin Nutr. 1973 Sep;26(9):973–981. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/26.9.973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. C., Jr, McDaniel E. G., Fan F. F., Halsted J. A. Zinc: a trace element essential in vitamin A metabolism. Science. 1973 Sep 7;181(4103):954–955. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4103.954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. E., Brown E. D., Smith J. C., Jr The effect of zinc deficiency on the metabolism of retinol-binding protein in the rat. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Nov;84(5):692–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee B. L. Zinc biochemistry in normal and neoplastic growth processes. Experientia. 1977 May 15;33(5):600–601. doi: 10.1007/BF01946521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Steveninck J., de Goeij A. F. Determination of vitamin A in blood plasma of patients with carotenaemia. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Nov 23;49(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90343-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



