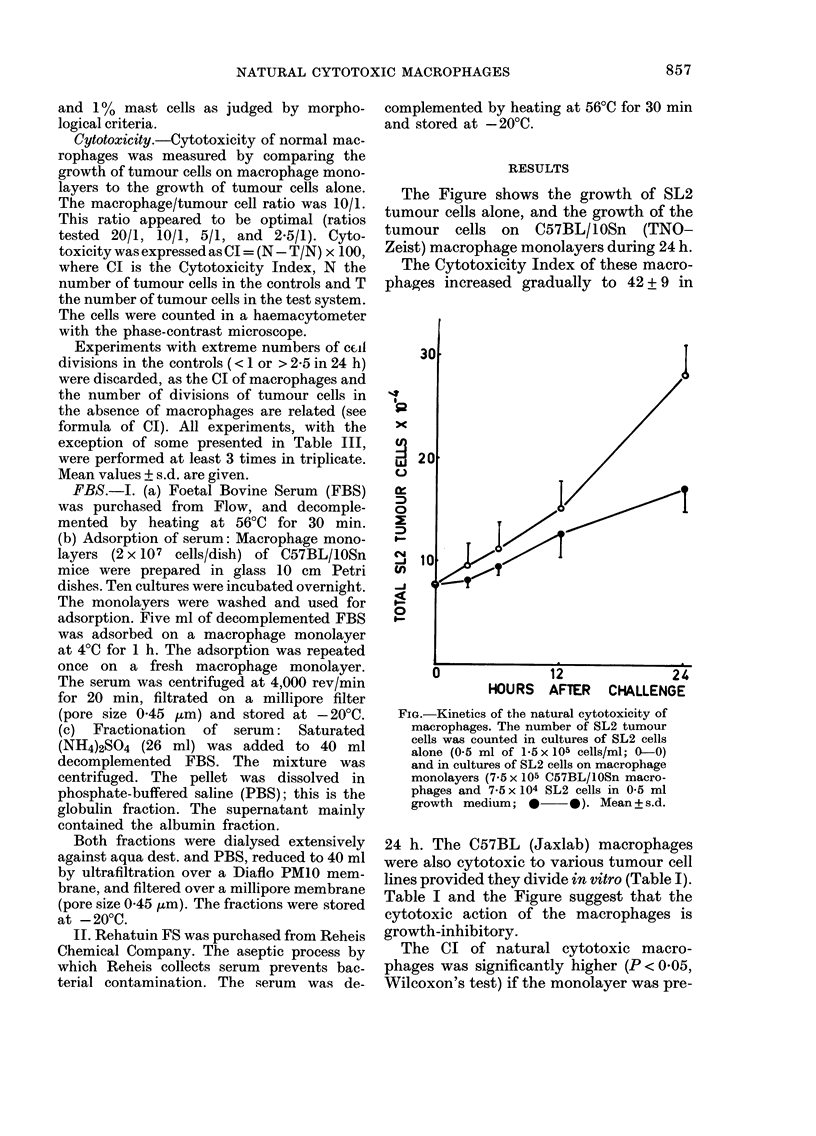
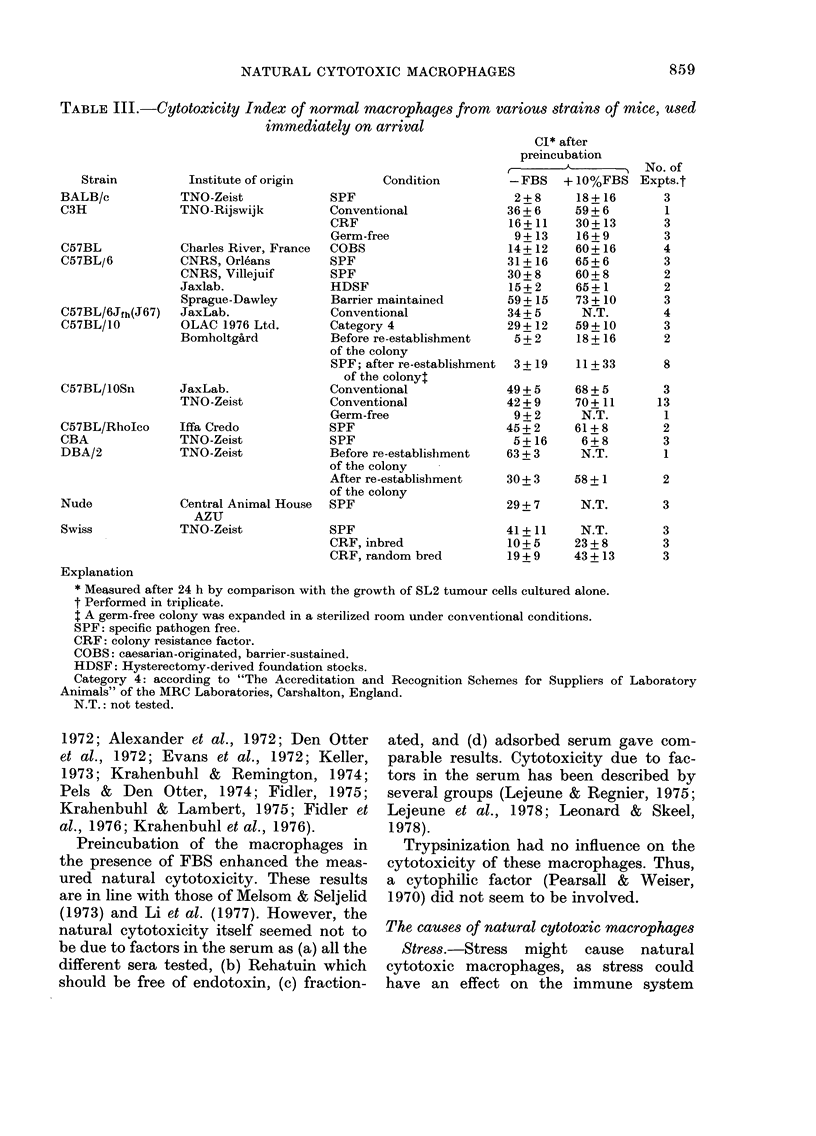
Abstract
Many strains of mice from various breeding institutes have natural cytotoxic macrophages. These macrophages can also be present in nude mice, suggesting that this cytotoxicity can be acquired without invovlvement of T cells. The natural cytotoxicity was non-specific for tumour cells, was not sensitive to trypsin treatment, was lost after 5 days incubation, but could be enhanced by foetal bovine serum. The presence of cytotoxic macrophages in the peritoneal cavity was not genetically or age controlled. Natural cytotoxic macrophages did not occur in germ-free mice. The possible causes of natural cytotoxicity are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander P., Evans R., Grant C. K. The interplay of lymphoid cells and macrophages in tumour immunity. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1972 Apr;122(4):645–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOCH H., TOBACH E. Effect of stress by crowding prior to and following tuberculous infection. Am J Physiol. 1956 Nov;187(2):399–402. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.2.399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Den Otter W., Evans R., Alexander P. Cytotoxicity of murine peritoneal macrophages in tumour allograft immunity. Transplantation. 1972 Aug;14(2):220–226. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197208000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R., Alexander P. Mechanism of immunologically specific killing of tumour cells by macrophages. Nature. 1972 Mar 24;236(5343):168–170. doi: 10.1038/236168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R., Alexander P. Rendering macrophages specifically cytotoxic by a factor released from immune lymphoid cells. Transplantation. 1971 Sep;12(3):227–229. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197109000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R., Grant C. K., Cox H., Steele K., Alexander P. Thymus-derived lymphocytes produce an immunologically specific macrophage-arming factor. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1318–1322. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Activation in vitro of mouse macrophages by syngeneic, allogeneic, or xenogeneic lymphocyte supernatants. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Nov;55(5):1159–1163. doi: 10.1093/jnci/55.5.1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Darnell J. H., Budmen M. B. In vitro activation of mouse macrophages by rat lymphocyte mediators. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):666–673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Holden H. T. Natural cell-mediated immunity. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;27:305–377. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joasoo A., McKenzie J. M. Stress and the immune response in rats. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1976;50(6):659–663. doi: 10.1159/000231544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. Cytostatic elimination of syngeneic rat tumor cells in vitro by nonspecifically activated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):625–644. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. Macrophage-mediated natrual cytotoxicity against various target cells in vitro. I. Macrophages from diverse anatomical sites and different strains of rats and mice. Br J Cancer. 1978 May;37(5):732–741. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1978.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. Macrophage-mediated natural cytotoxicity against various target cells in vitro. II. Macrophages from rats of different ages. Br J Cancer. 1978 May;37(5):742–746. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1978.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman J. P., Janssen F. G. The suitability of an intestinal flora with colonization resistance factor for SPF mice, rats and gerbils. Z Versuchstierkd. 1974;16(2):164–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Lambert L. H., Jr Cytokinetic studies of the effects of activated macrophages on tumor target cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jun;54(6):1433–1437. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.6.1433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Lambert L. H., Jr, Remington J. S. The effects of activated macrophages on tumor target cells: escape from cytostasis. Cell Immunol. 1976 Aug;25(2):279–293. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90118-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Remington J. S. The role of activated macrophages in specific and nonspecific cytostasis of tumor cells. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):507–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lejeune F. J., Beaumont L., Garcia Y., Regnier R. Peritoneal macrophage cytotoxicity induced by serum in vitro. Biomedicine. 1978 Jan-Feb;28(1):48–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard E. J., Skeel A. H. Isolation of macrophage stimulating protein (MSP) from human serum. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jun;114(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Mansfield M., Wallace J. H. Tumoristatic effects of nonimmune BALB/c peritoneal macrophages on syngeneic lymphoma cells in vitro. Oncology. 1977;34(6):245–250. doi: 10.1159/000225234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melsom H., Seljelid R. The cytotoxic effect of mouse macrophages on syngeneic and allogeneic erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Mar 1;137(3):807–820. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.3.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S. Tumoricidal responses in vitro of peritoneal macrophages from conventionally housed and germ-free nude mice. Cell Immunol. 1976 Mar 1;22(1):176–181. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90018-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pels E., den Otter W. The role of a cytophilic factor from challenged immune peritoneal lymphocytes in specific macrophage cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. 1974 Nov;34(11):3089–3094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen A. F., Jr Emotions and immunity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1969 Oct 14;164(2):458–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1969.tb14060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensinck F., Ruseler-van Embden J. G. The intestinal flora of colonization-resistant mice. J Hyg (Lond) 1971 Sep;69(3):413–421. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400021665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler F. G., Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Fischer H. Studies on the mechanism of macrophage-mediated cytotoxicity. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1975;48(2):182–191. doi: 10.1159/000231304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Waaij D., Berghuis-de Vries J. M., Lekkerkerk Lekkerkerk-v Colonization resistance of the digestive tract in conventional and antibiotic-treated mice. J Hyg (Lond) 1971 Sep;69(3):405–411. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400021653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



