Abstract
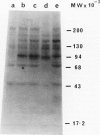
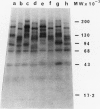
Antisera were raised in rabbits to 6 human melanoma cell lines. The cell-surface antigens recognized by these antisera were examined using cell-surface labelling with 125I, followed by immunoprecipitation of soluble extracts of the cells and polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis of the immunoprecipitates in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS). Up to 16 cell-surface antigens were recognized by these antisera, and 5 of the melanoma cell lines had a similar profile of cell-surface antigens. Digestion of labelled melanoma cells with neuraminidase before immunoprecipitation revealed that 8 of the larger antigens were sialoglycoproteins. The melanoma antisera produced haemagglutination of human erythrocytes at high dilutions, but the antigens involved could not be detected by iodination. In contrast, absorption of the melanoma sera with lymphocytes and fibroblasts revealed that these cells did contain some cell-surface glycoproteins in common with melanoma cells. The melanoma antisera contained antibodies to foetal calf serum proteins, but the amounts of these proteins on the surface of melanoma-cells were very low. Immunoprecipitation of labelled melanoma cell extracts with monospecific antiserum to β2-microglobulin produced 2 bands with mol. wts corresponding to β2-microglobulin and the HLA-determinant polypeptide chain. After absorption of melanoma antisera with cross-linked foetal calf serum, erythrocytes, lymphocytes and fibroblasts, antibodies against 10 labelled antigens remained in the absorbed antisera. However, antibodies against 8 of these antigens were still detected after absorption of the melanoma antisera with melanoma cells.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apffel C. A., Peters J. H. Regulation of antigenic expression. J Theor Biol. 1970 Jan;26(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(70)80031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badley R. A., Lloyd C. W., Woods A., Carruthers L., Allcock C., Rees D. A. Mechanisms of cellular adhesion. III. Preparation and preliminary characterisation of adhesions. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Dec;117(2):231–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Jones E. A., Crumpton M. J. Isolation, structure and genetics of HLA-A, -B, -C and -DRw (Ia) antigens. Br Med Bull. 1978 Sep;34(3):241–246. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codington J. F., Sanford B. H., Jeanloz R. W. Cell-surface glycoproteins of two sublines of the TA3 tumor. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Aug;51(2):585–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen S. E., Schwartz B. D. An improved method for isolation of H-2 and Ia alloantigens with immunoprecipitation induced by protein A-bearing staphylococci. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):136–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard A. L., Cohn Z. A. Externally disposed plasma membrane proteins. I. Enzymatic iodination of mouse L cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):438–460. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Cell surface proteins and malignant transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 30;458(1):73–107. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(76)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd K. O., Travassos L. R., Takahashi T., Old L. J. Cell surface glycoproteins of human tumor cell lines: unusual characteristics of malignant melanoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Sep;63(3):623–634. doi: 10.1093/jnci/63.3.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Trans-membrane control of the receptors on normal and tumor cells. II. Surface changes associated with transformation and malignancy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 30;458(1):1–72. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(76)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K., Andersson L. C., Gahmberg C. G., Wigzell H. Surface glycoprotein patterns of normal and malignant human lymphoid cells. II. B cells, B blasts and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive and -negative B lymphoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1977 Nov 15;20(5):708–716. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips E. R., Perdue J. F. Immunologic identification of fetal calf serum-derived proteins on the surfaces of cultured transformed and untransformed rat cells. Int J Cancer. 1977 Nov 15;20(5):798–804. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt-Rivers R., Impiombato F. S. The binding of sodium dodecyl sulphate to various proteins. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):825–830. doi: 10.1042/bj1090825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quish T. B., Lange C. F. Increased antigenicity of glycoproteins after carbohydrase treatment. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1973 Mar;5(2):473–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P. Lactoperoxidase-catalysed iodination of surface proteins on human melanoma cells. Br J Cancer. 1978 Jul;38(1):114–121. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1978.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. P., Parker J. M. Macromolecular components of the luminal fluid from the bovine uterus. J Reprod Fertil. 1974 Oct;40(2):291–303. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0400291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford B. H., Codington J. F., Jeanloz R. W., Palmer P. D. Transplantability and antigenicity of two sublines of the TA3 tumor. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1233–1237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkin M. B. The written word and cancer--some personal involvements, 1940-1977: autobiographical essay. Cancer Res. 1978 Feb;38(2):241–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D. F. Membrane anomalies of neoplastic cells. Med Hypotheses. 1976 Nov-Dec;2(6):241–256. doi: 10.1016/s0306-9877(76)80004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren L., Fuhrer J. P., Buck C. A. Surface glycoproteins of normal and transformed cells: a difference determined by sialic acid and a growth-dependent sialyl transferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1838–1842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren L., Zeidman I., Buck C. A. The surface glycoproteins of a mouse melanoma growing in culture and as a solid tumor in vivo. Cancer Res. 1975 Aug;35(8):2186–2190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead R. H. The culture of tumour cells from human tumour biopsies. Clin Oncol. 1976 Jun;2(2):131–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. S., Indiveri F., Pellegrino M. A., Ferrone S. DR (Ia-like) antigens on human melanoma cells. Serological detection and immunochemical characterization. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):658–668. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Wang C. Y., Gibofsky A., Kunkel H. G., Lloyd K. O., Old L. J. Expression of Ia-like antigens on cultured human malignant melanoma cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6235–6239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Beek W. P., Smets L. A., Emmelot P. Increased sialic acid density in surface glycoprotein of transformed and malignant cells--a general phenomenon? Cancer Res. 1973 Nov;33(11):2913–2922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]