Abstract
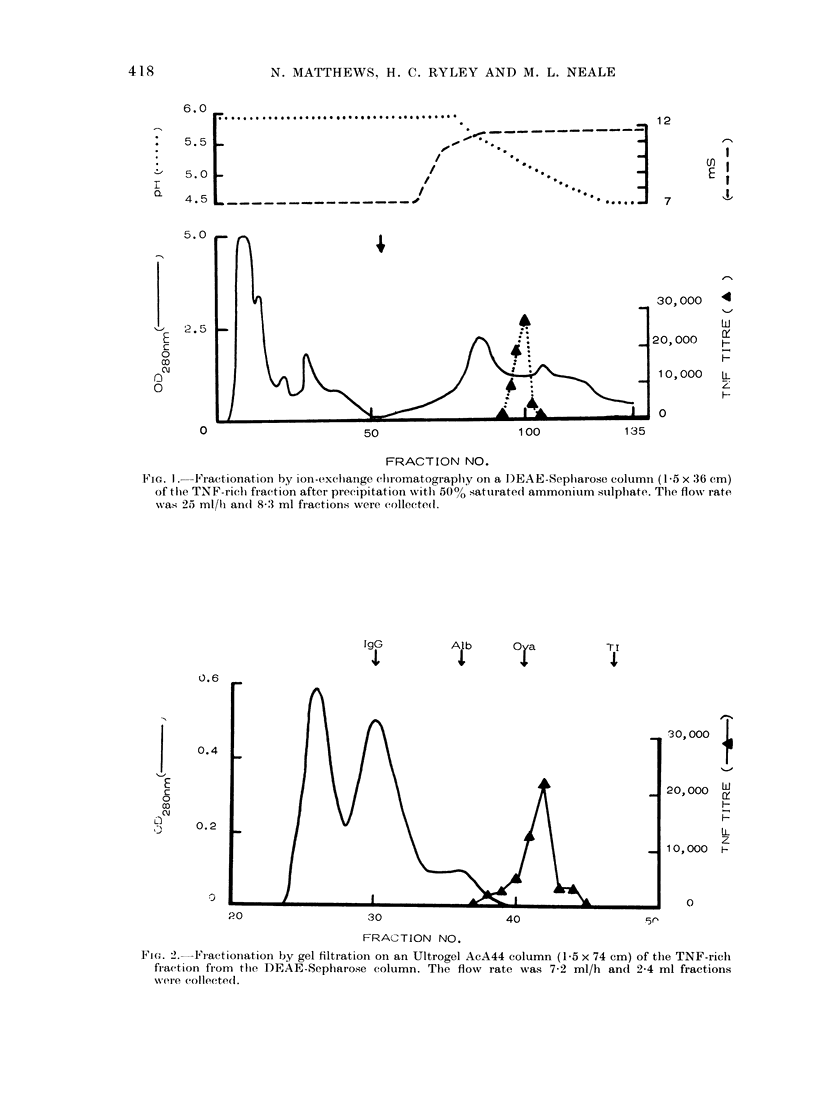
Serum from rabbits with BCG/endotoxin-induced shock is growth inhibitory or cytotoxic to a range ot tumour cell lines. The active component, tumour-necrosis factor (TNF), has been purified 1000-fold by sequential salt precipitation, ion-exchange chromatography and gel-filtration. TNF had a mol. wt of 67,000 on gradient PAGE and 39,000 on Ultrogel AcA44 gel-filtration. The isoelectric point was pH 5.1-5.2. TNF was susceptible to the proteolytic enzyme pronase, but resistant to trypsin or papain. On isopycnic ultracentrifugation it had a buoyant density of 1.27, confirming that it is protein in nature, with little or no carbohydrate. This is also suggested by its failure to bind to a range of lectins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal B. B., Goldstein I. J. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. VI. Isolation of concanavalin A by specific adsorption on cross-linked dextran gels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 23;147(2):262–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R., Sharon N. Peanut (Arachis hypogaea) agglutinin. Methods Enzymol. 1978;50:361–367. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(78)50043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis J., Kenrick K. G. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in a continuous molecular sieve gradient. Anal Biochem. 1968 Oct 24;25(1):347–362. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(68)90109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews N. Tumour-necrosis factor from the rabbit. III. Relationship to interferons. Br J Cancer. 1979 Oct;40(4):534–539. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1979.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews N., Watkins J. F. Tumour-necrosis factor from the rabbit. I. Mode of action, specificity and physicochemical properties. Br J Cancer. 1978 Aug;38(2):302–309. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1978.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Blaustein J. The interaction of Ricinus communis agglutinin with normal and tumor cell surfaces. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 9;266(2):543–547. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90109-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vretblad P. Purification of lectins by biospecific affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 20;434(1):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



