Abstract
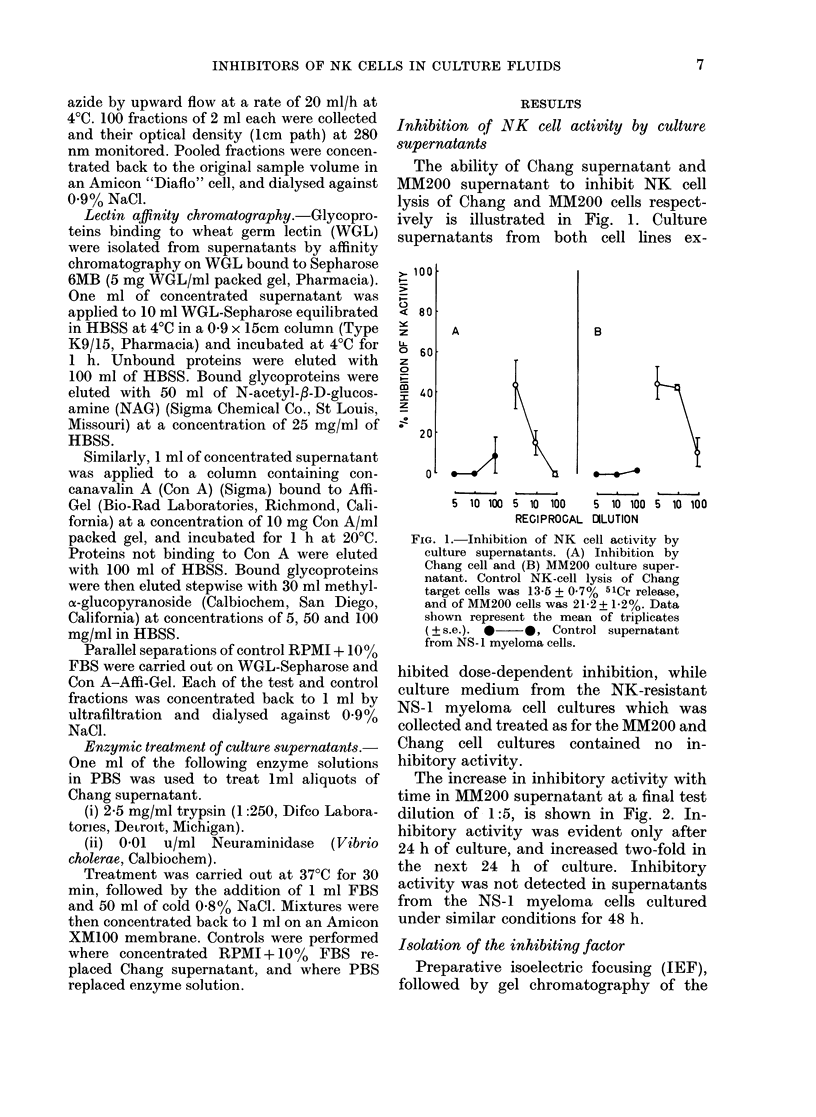
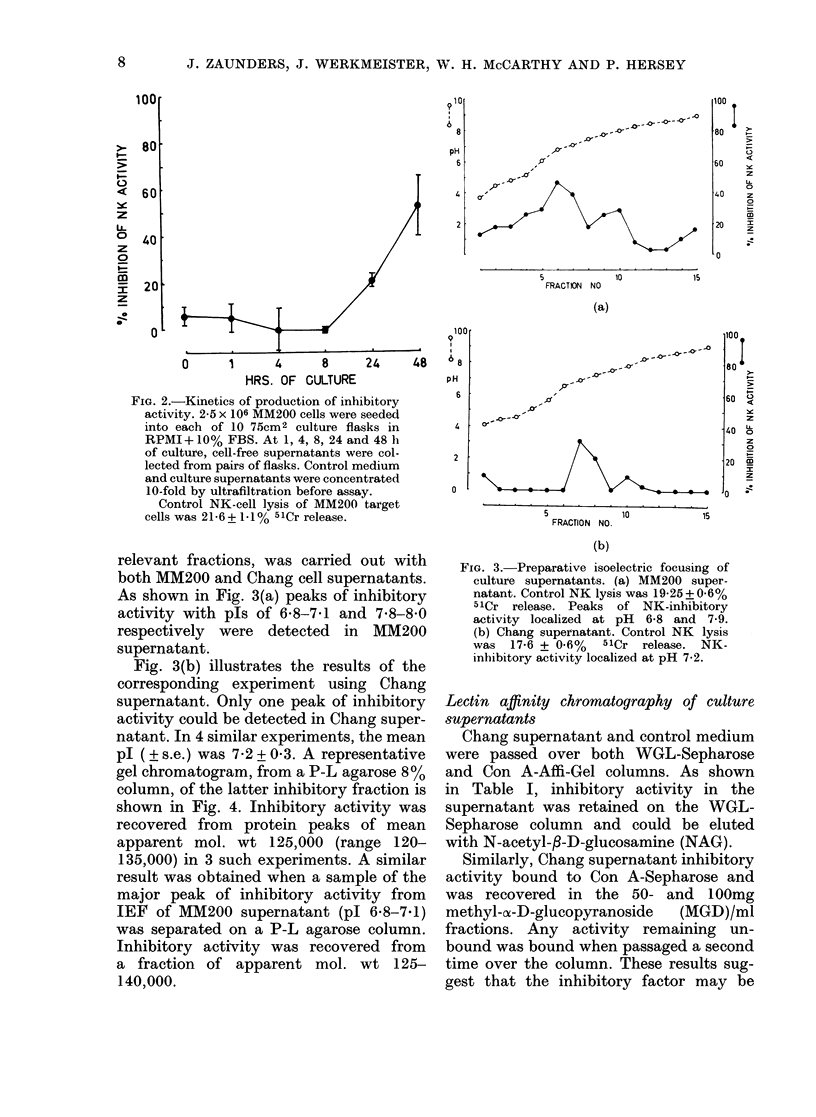
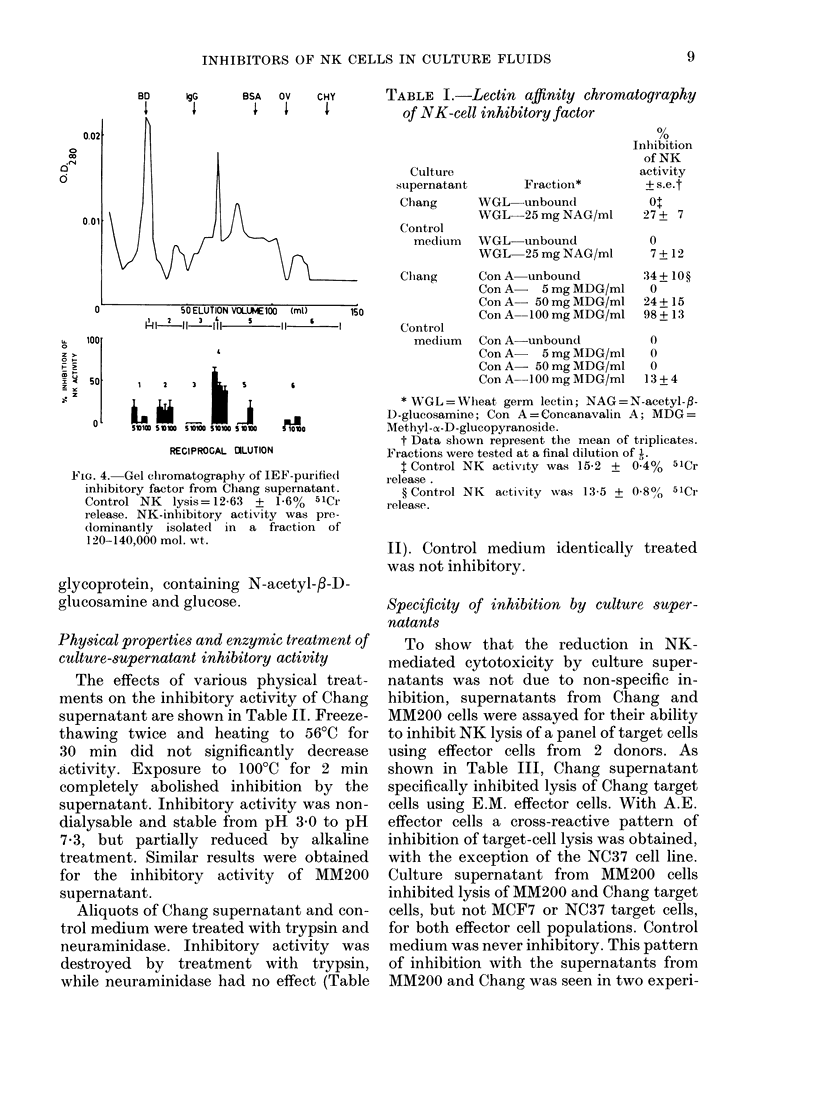
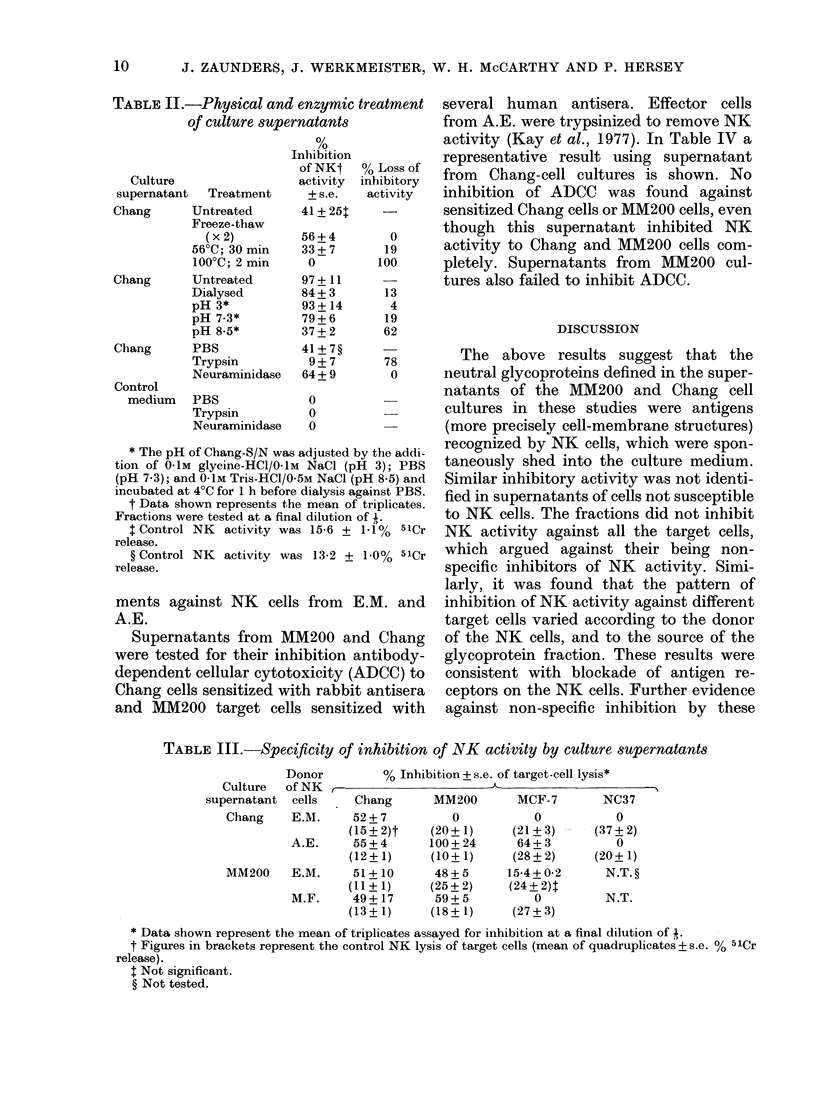
Inhibitors of natural killer (NK) cell activity in cell-culture supernatants, believed to be antigens recognized by NK cells, were defined by their ability to inhibit NK cells in 51Cr-release cytotoxic assays. Supernatants from cultures of melanoma cells and Chang cells were used as the source of the antigen. Partial characterization by a number of sequential separation procedures suggested that the antigens were glycoproteins in the size range 120-140,000 daltons which had affinity for both concanavalin A and wheat germ lectin. Inhibitory activity was destroyed by trypsin digestion, but was resistant to neuraminidase and a number of physical procedures. Addition of supernatants to NK assays against a number of different target cells indicated that inhibition was restricted to certain target cells. This indicated that the inhibition of NK cells was not non-specific, and that the antigens were not expressed on all target cells. These studies provide a basis for further analysis of antigens recognized by NK cells, and allow investigation of their role in vivo in tumour-bearing hosts.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Grimm E. A., Silver H. K., Roth J. A., Chee D. O., Gupta R. K., Morton D. L. Detection of tumor-associated antigen in human melanoma cell line supernatants. Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):559–564. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersey P., Edwards A., Edwards J., Adams E., Milton G. W., Nelson D. S. Specificity of cell-mediated cytotoxicity against human melanoma lines: evidence for "non-specific" killing by activated T-cells. Int J Cancer. 1975 Jul 15;16(1):173–183. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay H. D., Bonnard G. D., West W. H., Herberman R. B. A functional comparison of human Fc-receptor-bearing lymphocytes active in natural cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1977 Jun;118(6):2058–2066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Klein E., Wigzell H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Feb;5(2):112–117. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong S. P., Cooperband S. R., Sutherland C. M., Krementz E. T., Deckers P. J. Detection of human melanoma antigens in cell-free supernatants. J Surg Res. 1978 Apr;24(4):245–252. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(78)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Oldham R. K., Cannon G. C., Herberman R. B. Specificity of natural cytotoxic reactivity of normal human lymphocytes against a myeloid leukemia cell line. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Jul;59(1):77–82. doi: 10.1093/jnci/59.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Ahrlund-Richter L., Jondal M. Target-effector interaction in the human and murine natural killer system: specificity and xenogeneic reactivity of the solubilized natural killer-target structure complex and its loss in a somatic cell hybrid. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):471–481. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Kiessling R. Target--effector interaction in the natural killer cell system. I. Covariance and genetic control of cytolytic and target-cell-binding subpopulations in the mouse. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(2):135–144. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00505.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasugi M., Koide D., Ramseyer A. Specificities in natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity by the cross-competition assay. Int J Cancer. 1977 Mar 15;19(3):291–297. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910190303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasugi M., Mickey M. R. Interaction analysis of selective and nonselective cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Aug;57(2):255–261. doi: 10.1093/jnci/57.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



