Abstract
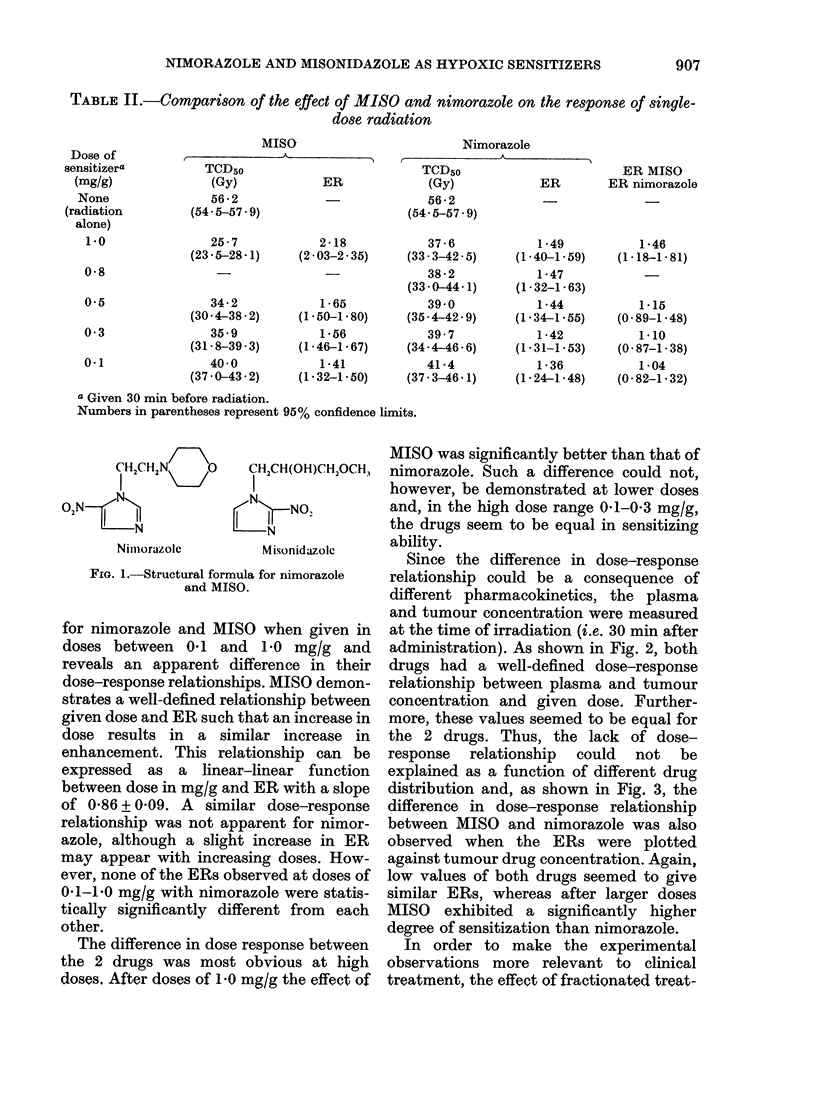
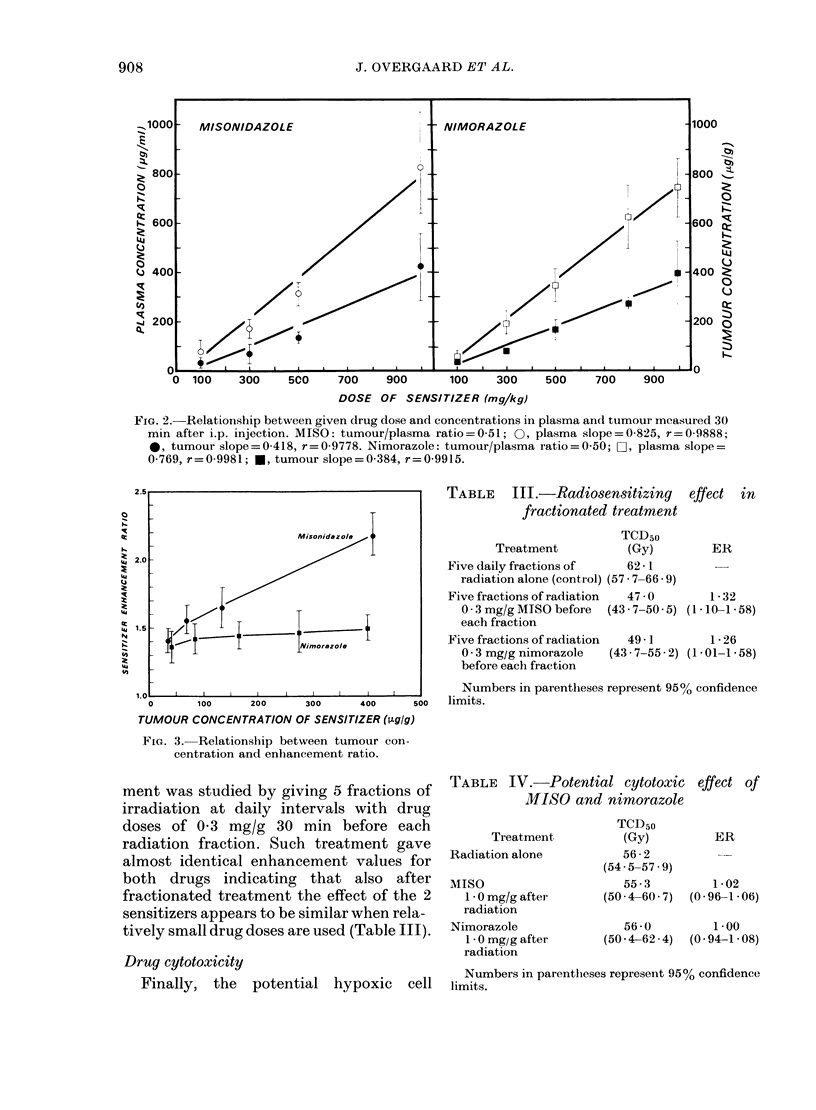
The hypoxic cell radiosensitizing properties of nimorazole have been investigated in a C3H mammary carcinoma transplanted to the feet of C3D2F1. The results have been compared with those obtained with misonidazole (MISO) in the same animal tumour system. For single-dose irradiation in air, nimorazole gives an enhancement ratio (ER) of approximately 1.4, independent of the dose of drug administered over the range 0.1-1.0 mg/g. MISO yields a similar ER at the 0.1 mg/g level but, unlike nimorazole, shows a steep dose-response curve with an ER of 2.2 when given in a concentration of 1.0 mg/g. No such dose-response relationship is seen with nimorazole despite the fact that tumour and plasma concentrations of the 2 drugs have an identical dose relationship. With irradiation given in 5 daily fractions, nimorazole and MISO at a dose of 0.3 mg/g per fraction both show an ER of approximately 1.3. The high drug doses used in single-fraction radiation experiments in animals bear little relation to those applicable to clinical practice since these would result in unacceptable toxicity. The results of the present studies are therefore of interest as nimorazole is potentially less toxic than MISO in humans but demonstrates similar radiosensitizing properties at clinically relevant dose levels.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams G. E., Clarke E. D., Flockhart I. R., Jacobs R. S., Sehmi D. S., Stratford I. J., Wardman P., Watts M. E., Parrick J., Wallace R. G. Structure-activity relationships in the development of hypoxic cell radiosensitizers. I. Sensitization efficiency. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1979 Feb;35(2):133–150. doi: 10.1080/09553007914550151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams G. E., Clarke E. D., Gray P., Jacobs R. S., Stratford I. J., Wardman P., Watts M. E., Parrick J., Wallace R. G., Smithen C. E. Structure-activity relationships in the development of hypoxic cell radiosensitizers. II. Cytotoxicity and therapeutic ratio. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1979 Feb;35(2):151–160. doi: 10.1080/09553007914550161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. M., Workman P. Partition coefficient as a guide to the development of radiosensitizers which are less toxic than misonidazole. Radiat Res. 1980 Apr;82(1):171–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. M., Yu N. Y., Workman P. Pharmacokinetic considerations in testing hypoxic cell radiosensitizers in mouse tumours. Br J Cancer. 1979 Mar;39(3):310–320. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1979.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman C. N., Wasserman T. H., Phillips T. L., Strong J. M., Urtasun R. C., Schwade J. G., Johnson R. J., Zagars G. Initial pharmacology and toxicology of intravenous desmethylmisonidazole. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1982 Mar-Apr;8(3-4):371–375. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(82)90642-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conroy P. J., McNeill T. H., Passalacqua W., Merritt J., Reich K. R., Walker S. Nitroimidazole neurotoxicity: are mouse studies predictive? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1982 Mar-Apr;8(3-4):799–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denekamp J., Michael B. D., Minchinton A. I., Smithen C. E., Stewart F. A., Stratford M. R., Terry N. H. Comparative studies of hypoxic-cell radiosensitization using artificially hypoxic skin in vivo. Br J Cancer. 1982 Feb;45(2):247–255. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1982.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dische S., Fowler J. F., Saunders M. I., Stratford M. R., Anderson P., Minchinton A. I., Lee M. E. A drug for improved radiosensitization in radiotherapy. Br J Cancer. 1980 Jul;42(1):153–155. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1980.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dische S., Saunders M. I., Anderson P., Stratford M. R., Minchinton A. Clinical experience with nitroimidazoles as radiosensitizers. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1982 Mar-Apr;8(3-4):335–338. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(82)90634-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dische S., Saunders M. I., Flockhart I. R., Lee M. E., Anderson P. Misonidazole-a drug for trial in radiotherapy and oncology. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1979 Jun;5(6):851–860. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(79)90070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazekas J. T., Goodman R. L., McLean C. J. The value of adjuvant misonidazole in the definitive irradiation of advanced head and neck squamous cancer: an RTOG pilot study (#78-02). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1981 Dec;7(12):1703–1708. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(81)90196-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler J. F., Adams G. E., Denekamp J. Radiosensitizers of hypoxic cells in solid tumors. Cancer Treat Rev. 1976 Dec;3(4):227–256. doi: 10.1016/s0305-7372(76)80012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraldi P. N., Tosolini G. P., Dradi E., Nannini G., Longo R., Meinardi G., Monti G., de Carneri I. Studies on antiprotozoans. 3. Isolation, identification and quantitative determination in humans of the metabolites of a new trichomonacidal agent. Biochem Pharmacol. 1971 Feb;20(2):339–349. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(71)90068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim A. B. Prolonged metronidazole administration with protracted radiotherapy: a pilot study on response of advanced tumours. Br J Cancer Suppl. 1978 Jun;3:299–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogelnik H. D. Clinical experience with misonidazole: high dose fractions versus daily low doses. Cancer Clin Trials. 1980 Summer;3(2):179–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overgaard J. Simultaneous and sequential hyperthermia and radiation treatment of an experimental tumor and its surrounding normal tissue in vivo. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1980 Nov;6(11):1507–1517. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(80)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips T. L., Wasserman T. H., Johnson R. J., Levin V. A., VanRaalte G. Final report on the United States Phase I Clinical Trial of the hypoxic cell radiosensitizer, misonidazole (Ro-07-0582; NSC #261037). Cancer. 1981 Oct 15;48(8):1697–1704. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19811015)48:8<1697::aid-cncr2820480802>3.0.co;2-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rofstad E. K., Brustad T. The radiosensitizing effect of metronidazole and misonidazole (Ro-07-0582) on a human malignant melanoma grown in the athymic mutant nude mouse. Br J Radiol. 1978 May;51(605):381–386. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-51-605-381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urtasun R. C., Chapman J. D., Band P., Rabin H. R., Fryer C. G., Sturmwind J. Phase 1 study of high-dose metronidazole: a specific in vivo and in vitro radiosensitizer of hypoxic cells. Radiology. 1975 Oct;117(1):129–133. doi: 10.1148/117.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman P. Analysis of the basic 5-nitroimidazole nimorazole in blood by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography, and its application to pharmacokinetic studies in individual mice. J Chromatogr. 1979 Aug 21;163(4):396–402. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81643-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman P., Bleehen N. M., Wiltshire C. R. Phenytoin shortens the half-life of the hypoxic cell radiosensitizer misonidazole in man: implications for possible reduced toxicity. Br J Cancer. 1980 Feb;41(2):302–304. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1980.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman P., Brown J. M. Structure-pharmacokinetic relationships for misonidazole analogues in mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1981;6(1):39–49. doi: 10.1007/BF00253009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman P. Pharmacokinetics of hypoxic cell radiosensitizers: a review. Cancer Clin Trials. 1980 Fall;3(3):237–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


