Abstract
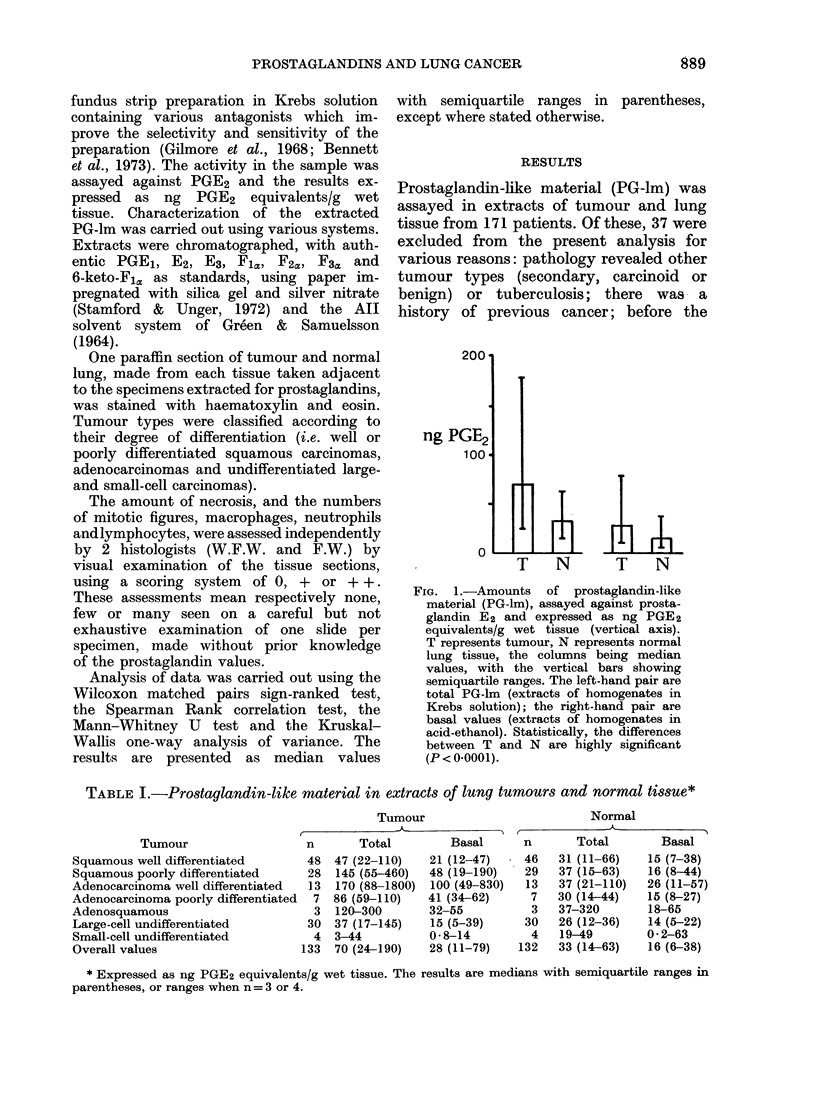
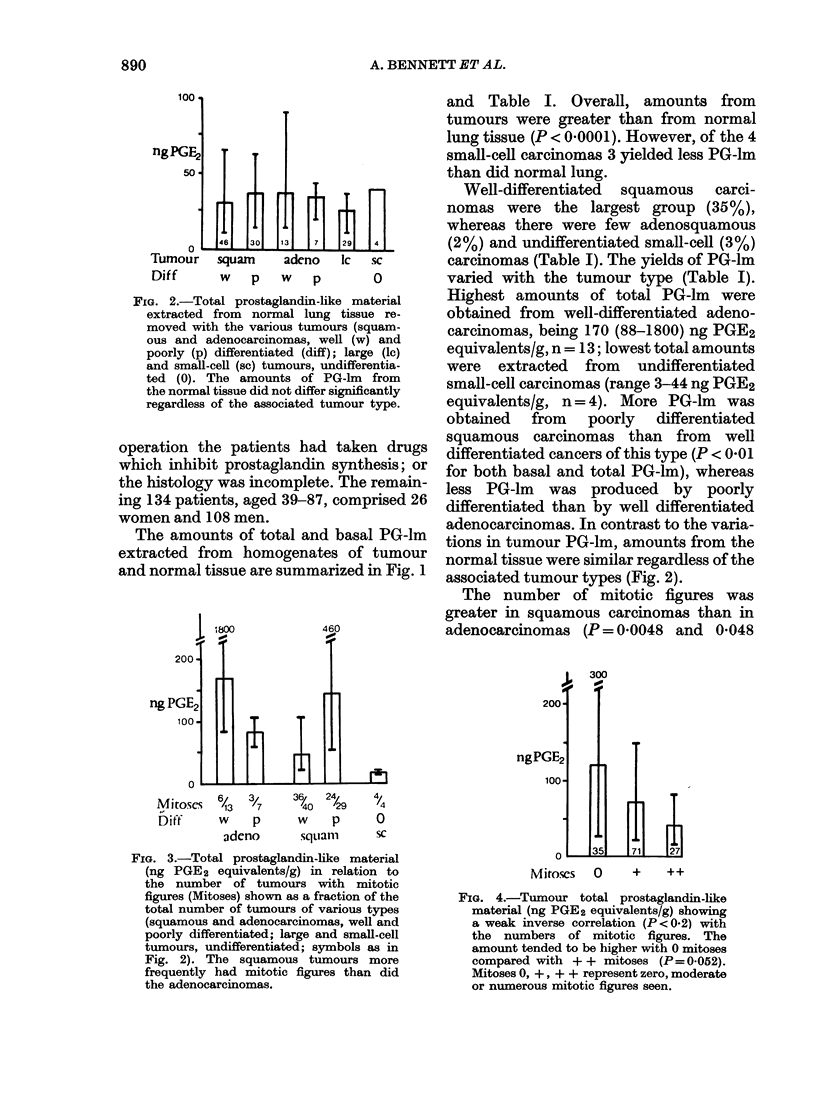
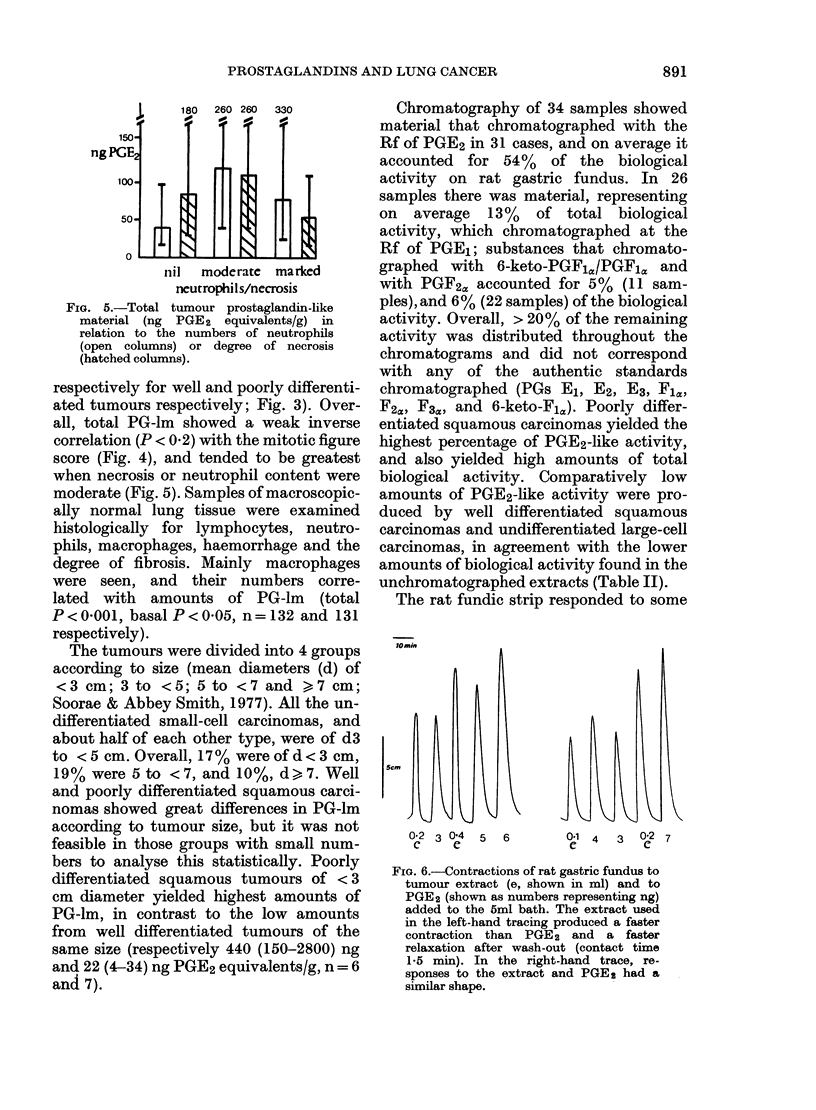
Lung primary carcinomas and normal tissue from 136 patients have been extracted for prostaglandins, and the findings examined in relation to histology. In most cases, tumours yielded more prostaglandin-like material (PG-lm), as judged by bioassay, than did normal tissue from the same lungs. Amounts varied with tumour types, in the following ascending order: small-cell carcinomas, large-cell undifferentiated carcinomas, well-differentiated squamous carcinomas, poorly-differentiated adenocarcinomas, poorly differentiated squamous carcinomas, and well-differentiated adenocarcinomas. Tumour PG-lm was highest when necrosis or the neutrophil content of the tumours were moderate, whereas PG-lm from normal lung tissue correlated with the number of macrophages. Chromatography indicated the presence of various prostaglandins, in agreement with our recent findings using gas chromatography--mass spectrometry.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett A., Charlier E. M., McDonald A. M., Simpson J. S., Stamford I. F., Zebro T. Prostaglandins and breast cancer. Lancet. 1977 Sep 24;2(8039):624–626. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92496-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A., Stamford I. F., Unger W. G. Prostaglandin E2 and gastric acid secretion in man. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(2):349–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN K., SAMUELSSON B. PROSTAGLANDINS AND RELATED FACTORS: XIX. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF PROSTAGLANDINS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:117–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore N., Vane J. R., Wyllie J. H. Prostaglandins released by the spleen. Nature. 1968 Jun 22;218(5147):1135–1140. doi: 10.1038/2181135a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. S., Pastan I. Change in growth and morphology of fibroblasts by prostaglandins. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Dec;47(6):1357–1364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolland P. H., Martin P. M., Jacquemier J., Rolland A. M., Toga M. Prostaglandin in human breast cancer: Evidence suggesting that an elevated prostaglandin production is a marker of high metastatic potential for neoplastic cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 May;64(5):1061–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler M., Karim S. M., Williams E. D. Prostaglandins in amine-peptide-secreting tumours. Lancet. 1968 Nov 16;2(7577):1053–1054. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91528-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamford I. F., Unger W. G. Improved purification and chromatography of extracts containing prostaglandins. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(2):4P–5P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger W. G., Stamford I. F., Bennett A. Extraction of prostaglandins from human blood. Nature. 1971 Oct 1;233(5318):336–337. doi: 10.1038/233336b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss W. The mitotic index in bronchogenic carcinoma. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Oct;104(4):536–543. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.104.4.536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


