Abstract
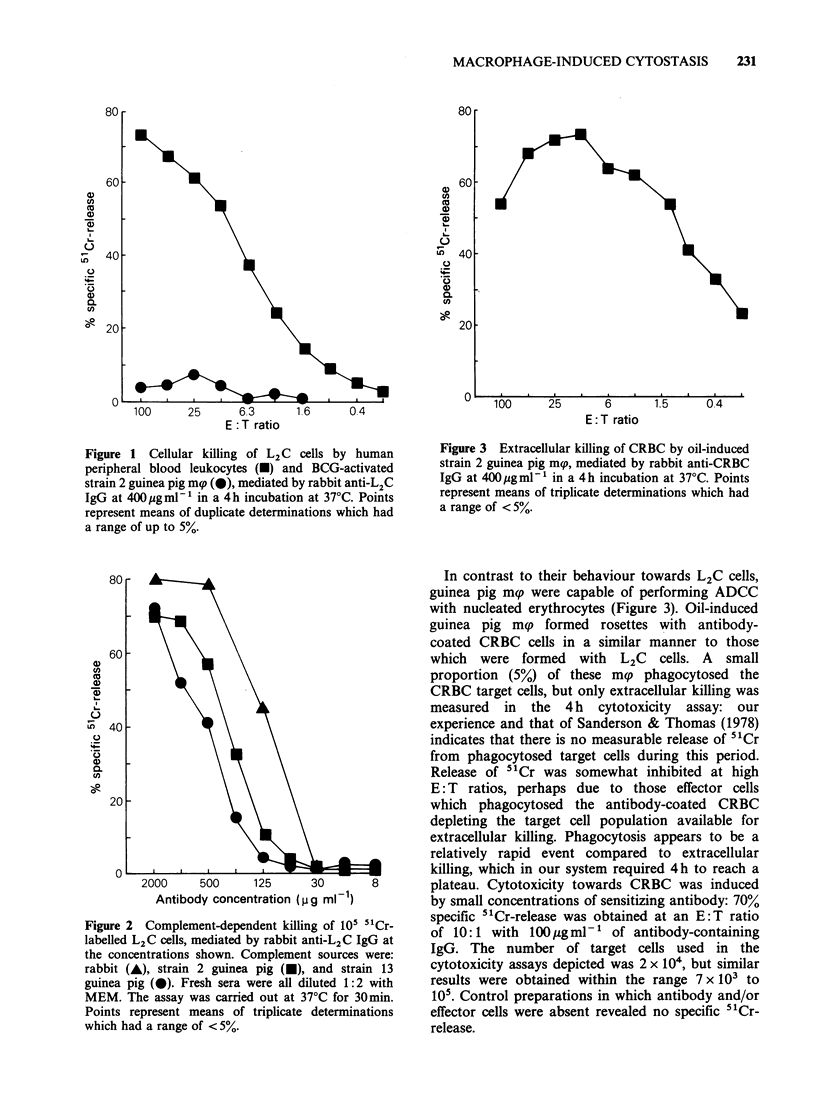
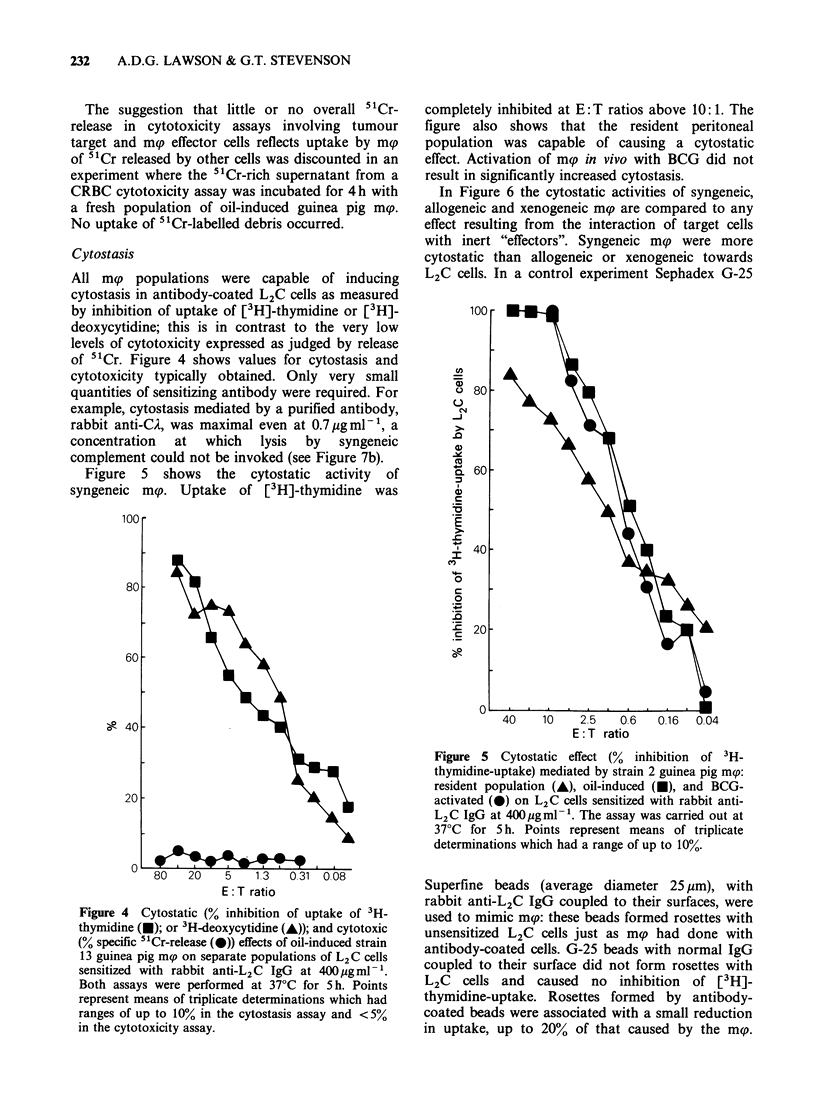
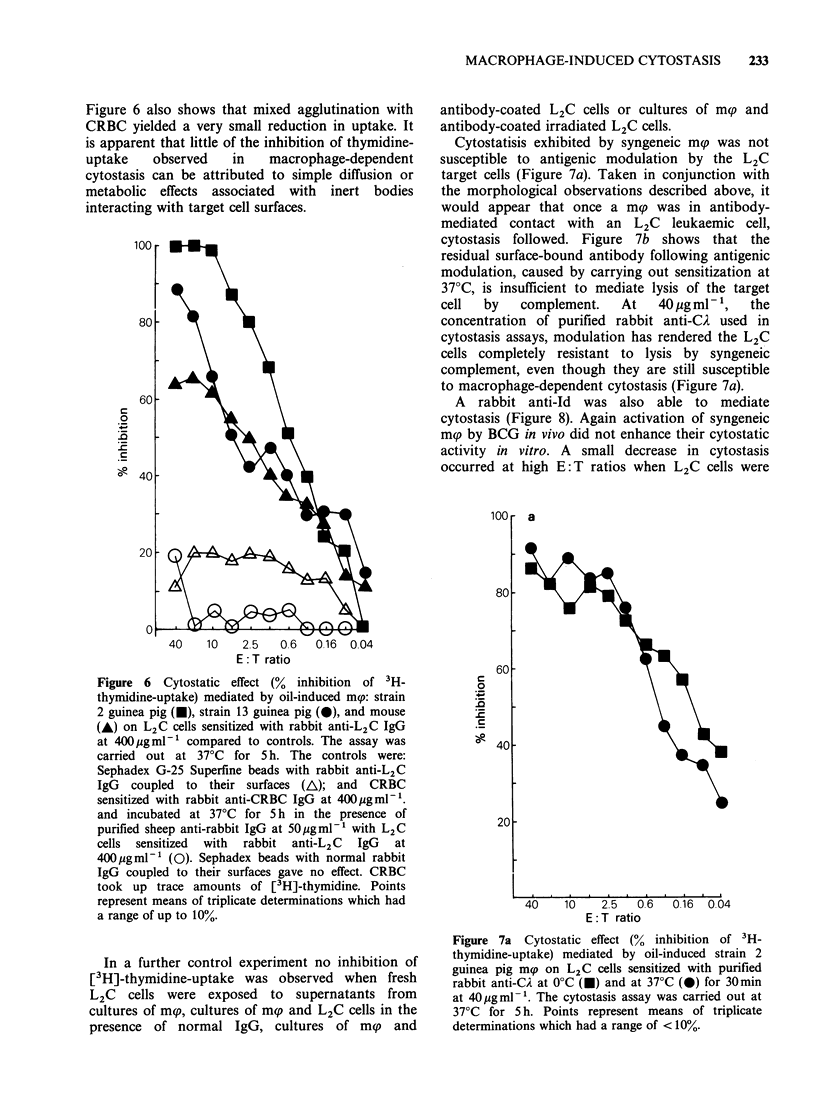
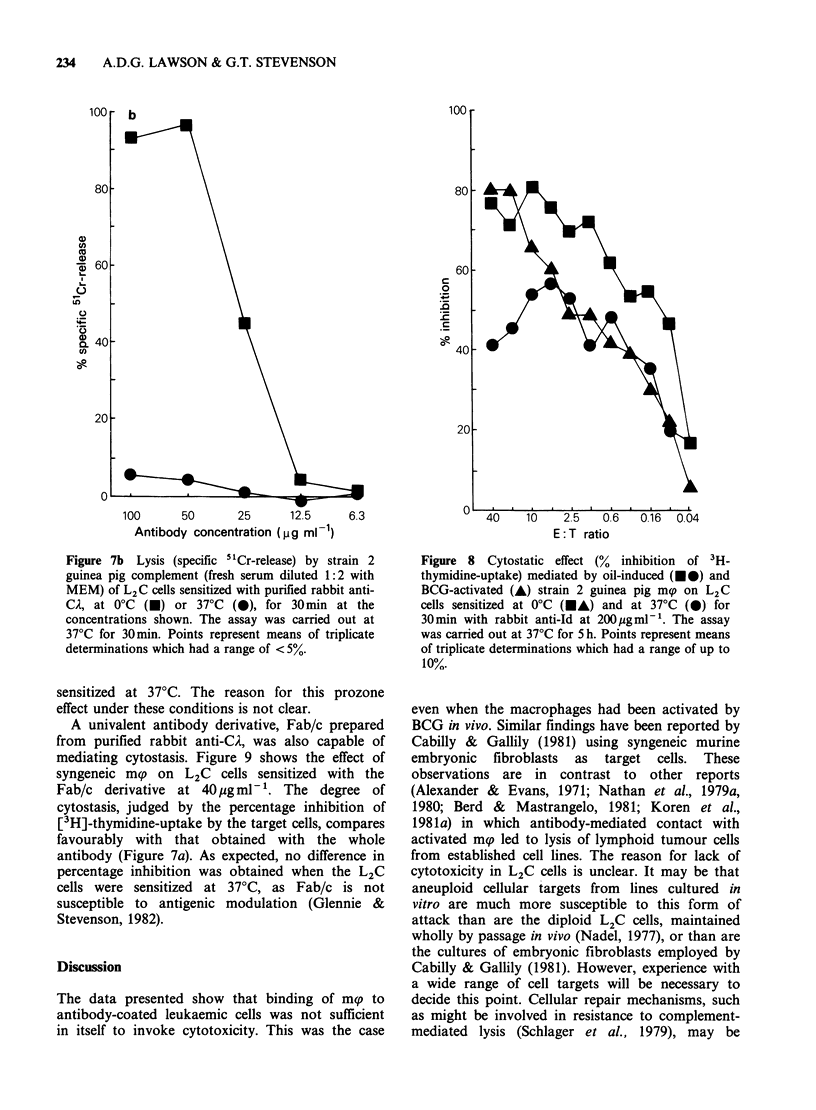
Guinea pig and mouse peritoneal macrophages formed antibody-dependent rosettes with guinea pig L2C leukaemic cells, but were unable either to phagocytose the cells or to kill them extracellularly as judged by the retention of 51Cr. Macrophages previously activated by BCG in vivo also failed to exhibit phagocytosis or cytoxicity towards the antibody-coated cells. These failures could not be attributed to deficient function of the macrophages nor to antigenic modulation of the L2C cells. The antibodies involved were capable of mediating lysis by complement, and ADCC by human leukocytes. However macrophages were cytostatic to antibody-coated L2C cells in that uptake of 3H-thymidine or 3H-deoxycytidine was abruptly and in some cases completely inhibited upon cell contact being established. Antigenic modulation which had proceeded sufficiently to protect against lysis by complement did not protect against cytostasis. Syngeneic macrophages had greater cytostatic activity than did allogeneic or xenogeneic. Macrophage activation by BCG did not result in significantly increased cytostasis. A univalent antibody derivative Fab/c was also capable of mediating cytostatis by the macrophages.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. O., Marino P. A. Evidence for a multistep mechanism of cytolysis by BCG-activated macrophages: the interrelationship between the capacity for cytolysis, target binding, and secretion of cytolytic factor. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):981–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENNETT B., OLD L. J., BOYSE E. A. Opsonization of cells by isoantibody in vitro. Nature. 1963 Apr 6;198:10–12. doi: 10.1038/198010a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandlow G., Gröner R. Cytostatic effect of macrophages from non-immunised mice on mastocytoma P-815 cells in vitro. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1979 Jul 27;94(3):225–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00419282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berd D., Mastrangelo M. J. Differential sensitivity of two murine leukaemia sublines to cytolysis by Corynebacterium parvum-activated macrophages. Br J Cancer. 1981 Dec;44(6):819–827. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1981.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabilly S., Gallily R. Artificial binding of macrophages to syngeneic cells elicits cytostasis but not cytolysis. Immunology. 1981 Jan;42(1):149–155. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. W., Sholley M. M., Miller G. A. Macrophage heterogeneity in tumor resistance: cytostatic and cytotoxic activity of Corynebacterium parvum-activated and proteose peptone-elicited rat macrophages against Moloney sarcoma tumor cells. Cell Immunol. 1980 Mar 1;50(1):153–168. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline M. J., Lehrer R. I. Phagocytosis by human monocytes. Blood. 1968 Sep;32(3):423–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R., Booth C. G. Inhibition of 125IUdR incorporation by supernatants from macrophage and lymphocyte cultures: a cautionary note. Cell Immunol. 1976 Sep;26(1):120–126. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90354-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. Host cells in transplanted murine tumors and their possible relevance to tumor growth. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1979 Oct;26(4):427–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. Phagocytosis of murine lymphoma cells by macrophages. I. Factors affecting in vitro phagocytosis. Immunology. 1971 Jan;20(1):67–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gately M. K., Martz E. Early steps in specific tumor cell lysis by sensitized mouse T lymphocytes. V. Evidence that manganese inhibits a calcium-dependent step in programming for lysis. Cell Immunol. 1981 Jun;61(1):78–89. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90355-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glennie M. J., Stevenson G. T. Univalent antibodies kill tumour cells in vitro and in vivo. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):712–714. doi: 10.1038/295712a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Robinson D. S., Stevenson G. T. Antigenic modulation of lymphocytic surface immunoglobulin yielding resistance to complement-mediated lysis. I. Characterization with syngeneic and xenogeneic complements. Immunology. 1981 Jan;42(1):7–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Stevenson G. T. Antigenic modulation of lymphocytic surface immunoglobulin yielding resistance to complement-mediated lysis. II. Relationship to redistribution of the antigen. Immunology. 1981 Jan;42(1):13–17. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin F. M., Jr, Griffin J. A., Silverstein S. C. Studies on the mechanism of phagocytosis. II. The interaction of macrophages with anti-immunoglobulin IgG-coated bone marrow-derived lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):788–809. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyöngyössy M. I., Liabeuf A., Golstein P. Cell-mediated cytostasis: a critical analysis of methodological problems. Cell Immunol. 1979 Jun;45(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90357-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N., Balkwill F. R. Species restriction in cytostatic activity of human and murine monocytes and macrophages. Immunology. 1981 May;43(1):197–204. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. Cytostatic elimination of syngeneic rat tumor cells in vitro by nonspecifically activated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1973 Sep 1;138(3):625–644. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren H. S., Anderson S. J., Adams D. O. Studies on the antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) of thioglycollate-stimulated and BCG-activated peritoneal macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1981 Jan 1;57(1):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren H. S., Meltzer M. S., Adams D. O. The ADCC capacity of macrophages from C3H/HeJ and A/J mice can be augmented by BCG. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):1013–1015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahenbuhl J. L., Lambert L. H., Jr, Remington J. S. Effects of Corynebacterium parvum treatment and Toxoplasma gondii infection on macrophage-mediated cytostasis of tumour target cells. Immunology. 1976 Dec;31(6):837–846. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan I. C., Loewi G., Howard A. A human serum immunoglobulin with specificity for certain homologous target cells, which induces target cell damage by normal human lymphocytes. Immunology. 1969 Dec;17(6):897–910. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunaga K., Mashiba H., Gojobori M. Cytostatic activity of in vitro activated human adherent cells against human tumor cell lines. Gan. 1980 Feb;71(1):73–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadel E. M. History and further observations (1954-1976) of the L2C leukemia in the guinea pig. Fed Proc. 1977 Aug;36(9):2249–2254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Brukner L. H., Silverstein S. C., Cohn Z. A. Extracellular cytolysis by activated macrophages and granulocytes. I. Pharmacologic triggering of effector cells and the release of hydrogen peroxide. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):84–99. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Silverstein S. C., Brukner L. H., Cohn Z. A. Extracellular cytolysis by activated macrophages and granulocytes. II. Hydrogen peroxide as a mediator of cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):100–113. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Terry W. D. Decreased phagocytosis by peritoneal macrophages from BCG-treated mice: induction of the phagocytic defect in normal macrophages with BCG in vitro. Cell Immunol. 1977 Mar 15;29(2):295–311. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90324-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Brukner L., Kaplan G., Unkeless J., Cohn Z. Role of activated macrophages in antibody-dependent lysis of tumor cells. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):183–197. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. S. Macrophages: progress and problems. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Aug;45(2):225–233. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack G. R., Johnson R. J., Shin H. S. Tumor cell cytostasis by macrophages and antibody in vitro. I. Resolution into contact-dependent and contact-independent steps. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1560–1566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Axen R., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of proteins to agarose. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1491–1492. doi: 10.1038/2151491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson C. J., Thomas J. A. A comparison of the cytotoxic activity of eosinophils and other cells by 51 chromium release and time lapse microcinematography. Immunology. 1978 Apr;34(4):771–780. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlager S. I., Ohanian S. H., Borsos T. Synthesis of specific lipids associated with the hormone-induced resistance of tumor cells to humoral immune killing. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):108–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. D., Kask A. M., Paul W. E., Shevach E. M. Structural characteristics of the alloantigens determined by the major histocompatibility complex of the guinea pig. J Exp Med. 1976 Mar 1;143(3):541–558. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.3.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadecker M. J., Unanue E. R. The regulation of thymidine secretion by macrophages. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):568–571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson F. K., Elliott E. V. Mediation of cytotoxic functions by classes and subclasses of sheep antibody reactive with cell surface immunoglobulin idiotypic and constant region determinants. Immunology. 1978 Feb;34(2):353–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson F. K., Elliott E. V., Stevenson G. T. Some effects on leukaemic B lymphocytes of antibodies to defined regions of their surface immunoglobulin. Immunology. 1977 Apr;32(4):549–557. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson G. T., Elliott E. V., Stevenson F. K. Idiotypic determinants on the surface immunoglobulin of neoplastic lymphocytes: a therapeutic target. Fed Proc. 1977 Aug;36(9):2268–2271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki M., Shinoda H., Suzuki Y., Mizuno D. Two-step mechanism of macrophage-mediated tumor lysis in vitro. Gan. 1976 Oct;67(5):741–745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


