Abstract
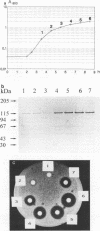
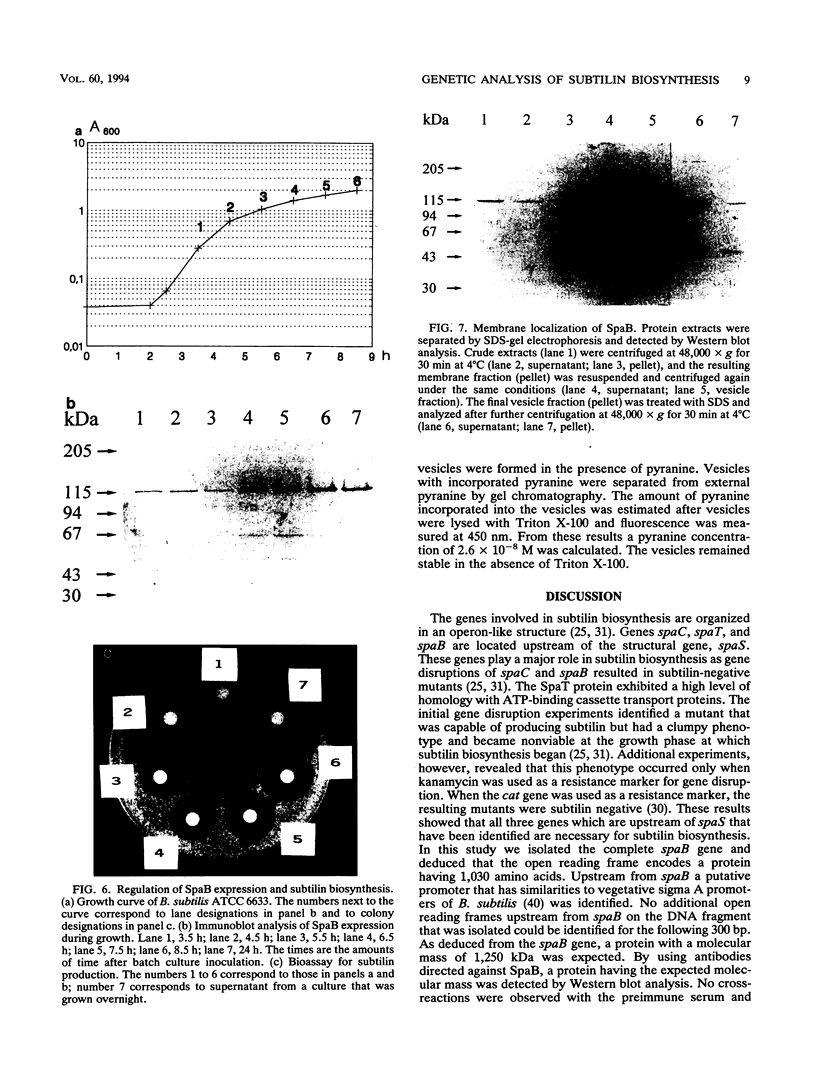
The information responsible for biosynthesis of the lantibiotic subtilin is organized in an operon-like structure that starts with the spaB gene. The spaB gene encodes an open reading frame consisting of 1,030 amino acid residues, and it was calculated that a protein having a theoretical molecular mass of 120.5 kDa could be produced from this gene. This is consistent with the apparent molecular weight for SpaB of 115,000 which was estimated after sodium dodecyl sulfate-gel electrophoresis and identification with SpaB-specific antibodies. The SpaB protein is very similar to proteins EpiB and NisB, which were identified previously as being involved in epidermin and nisin biosynthesis. Upstream from SpaB a characteristic sigma A promoter sequence was identified. An immunoblot analysis revealed that SpaB expression was strongly regulated. No SpaB protein was detected in the early logarithmic growth phase, and maximum SpaB expression was observed in the early stationary growth phase. The expression of SpaB was strongly correlated with subtilin biosynthesis. Deletion mutations in either of two recently identified regulatory genes, spaR and spaK, which act as a "two-component" regulatory system necessary for growth phase-dependent induction of subtilin biosynthesis (C. Klein, C. Kaletta, and K. D. Entian, Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59:296-303, 1993), also resulted in failure of SpaB expression. To investigate the intracellular localization of SpaB, vesicles of Bacillus subtilis were prepared. The SpaB protein cosedimented with the vesicle fraction and was released only after vigorous resuspension of the vesicles. Our results suggest that SpaB is membrane associated and that subtilin biosynthesis occurs at the cytoplasmic membrane of B. subtilis.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allgaier H., Jung G., Werner R. G., Schneider U., Zähner H. Epidermin: sequencing of a heterodetic tetracyclic 21-peptide amide antibiotic. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 1;160(1):9–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augustin J., Rosenstein R., Wieland B., Schneider U., Schnell N., Engelke G., Entian K. D., Götz F. Genetic analysis of epidermin biosynthetic genes and epidermin-negative mutants of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Mar 15;204(3):1149–1154. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee S., Hansen J. N. Structure and expression of a gene encoding the precursor of subtilin, a small protein antibiotic. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9508–9514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman G. W., Banerjee S., Hansen J. N. Structure, expression, and evolution of a gene encoding the precursor of nisin, a small protein antibiotic. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16260–16266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung Y. J., Hansen J. N. Determination of the sequence of spaE and identification of a promoter in the subtilin (spa) operon in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6699–6702. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6699-6702.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement N. R., Gould J. M. Pyranine (8-hydroxy-1,3,6-pyrenetrisulfonate) as a probe of internal aqueous hydrogen ion concentration in phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 17;20(6):1534–1538. doi: 10.1021/bi00509a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd H. M., Horn N., Gasson M. J. Analysis of the genetic determinant for production of the peptide antibiotic nisin. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Mar;136(3):555–566. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-3-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke G., Gutowski-Eckel Z., Hammelmann M., Entian K. D. Biosynthesis of the lantibiotic nisin: genomic organization and membrane localization of the NisB protein. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Nov;58(11):3730–3743. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.11.3730-3743.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredenhagen A., Fendrich G., Märki F., Märki W., Gruner J., Raschdorf F., Peter H. H. Duramycins B and C, two new lanthionine containing antibiotics as inhibitors of phospholipase A2. Structural revision of duramycin and cinnamycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1990 Nov;43(11):1403–1412. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.43.1403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross E., Kiltz H. H. The number and nature of , -unsaturated amino acids in subtilin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jan 23;50(2):559–565. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90876-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock K., Tsang V. C. India ink staining of proteins on nitrocellulose paper. Anal Biochem. 1983 Aug;133(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L. C. Synthesis of the antibiotic nisin: formation of lanthionine and beta-methyl-lanthionine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 17;184(1):216–219. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L. A ribosomal mechanism for synthesis of peptides related to nisin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 12;224(1):263–265. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaletta C., Entian K. D., Jung G. Prepeptide sequence of cinnamycin (Ro 09-0198): the first structural gene of a duramycin-type lantibiotic. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jul 15;199(2):411–415. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaletta C., Entian K. D., Kellner R., Jung G., Reis M., Sahl H. G. Pep5, a new lantibiotic: structural gene isolation and prepeptide sequence. Arch Microbiol. 1989;152(1):16–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00447005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaletta C., Entian K. D. Nisin, a peptide antibiotic: cloning and sequencing of the nisA gene and posttranslational processing of its peptide product. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1597–1601. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1597-1601.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellner R., Jung G., Hörner T., Zähner H., Schnell N., Entian K. D., Götz F. Gallidermin: a new lanthionine-containing polypeptide antibiotic. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 15;177(1):53–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. S., Datta P. Chemical characterization of biodegradative threonine dehydratases from two enteric bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Aug 23;706(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90371-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C., Kaletta C., Entian K. D. Biosynthesis of the lantibiotic subtilin is regulated by a histidine kinase/response regulator system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jan;59(1):296–303. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.296-303.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C., Kaletta C., Schnell N., Entian K. D. Analysis of genes involved in biosynthesis of the lantibiotic subtilin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):132–142. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.132-142.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. J., Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. High-expression vectors with multiple cloning sites for construction of trpE fusion genes: pATH vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:477–490. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94036-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konings W. N., Bisschop A., Veenhuis M., Vermeulen C. A. New procedure for the isolation of membrane vesicles of Bacillus subtilis and an electron microscopy study of their ultrastructure. J Bacteriol. 1973 Dec;116(3):1456–1465. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.3.1456-1465.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawther R. P., Wek R. C., Lopes J. M., Pereira R., Taillon B. E., Hatfield G. W. The complete nucleotide sequence of the ilvGMEDA operon of Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2137–2155. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naruse N., Tenmyo O., Tomita K., Konishi M., Miyaki T., Kawaguchi H., Fukase K., Wakamiya T., Shiba T. Lanthiopeptin, a new peptide antibiotic. Production, isolation and properties of lanthiopeptin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1989 Jun;42(6):837–845. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.42.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahl H. G., Brandis H. Production, purification and chemical properties of an antistaphylococcal agent produced by Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Gen Microbiol. 1981 Dec;127(2):377–384. doi: 10.1099/00221287-127-2-377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell N., Engelke G., Augustin J., Rosenstein R., Ungermann V., Götz F., Entian K. D. Analysis of genes involved in the biosynthesis of lantibiotic epidermin. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Feb 15;204(1):57–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16605.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell N., Entian K. D., Götz F., Hörner T., Kellner R., Jung G. Structural gene isolation and prepeptide sequence of gallidermin, a new lanthionine containing antibiotic. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Apr;49(2-3):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell N., Entian K. D., Schneider U., Götz F., Zähner H., Kellner R., Jung G. Prepeptide sequence of epidermin, a ribosomally synthesized antibiotic with four sulphide-rings. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):276–278. doi: 10.1038/333276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil H. P., Beck-Sickinger A. G., Metzger J., Stevanovic S., Jung G., Josten M., Sahl H. G. Biosynthesis of the lantibiotic Pep5. Isolation and characterization of a prepeptide containing dehydroamino acids. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 26;194(1):217–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19446.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer J. R., Polman J., Beerthuyzen M. M., Siezen R. J., Kuipers O. P., De Vos W. M. Characterization of the Lactococcus lactis nisin A operon genes nisP, encoding a subtilisin-like serine protease involved in precursor processing, and nisR, encoding a regulatory protein involved in nisin biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2578–2588. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2578-2588.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]