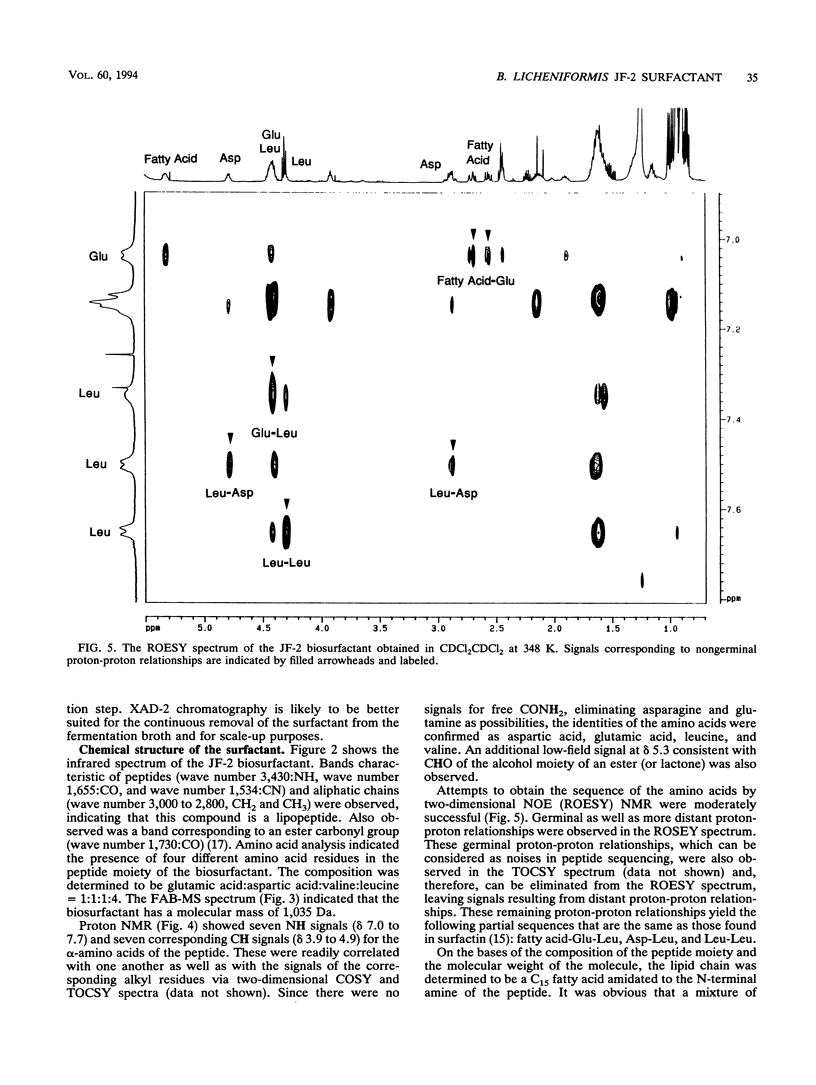
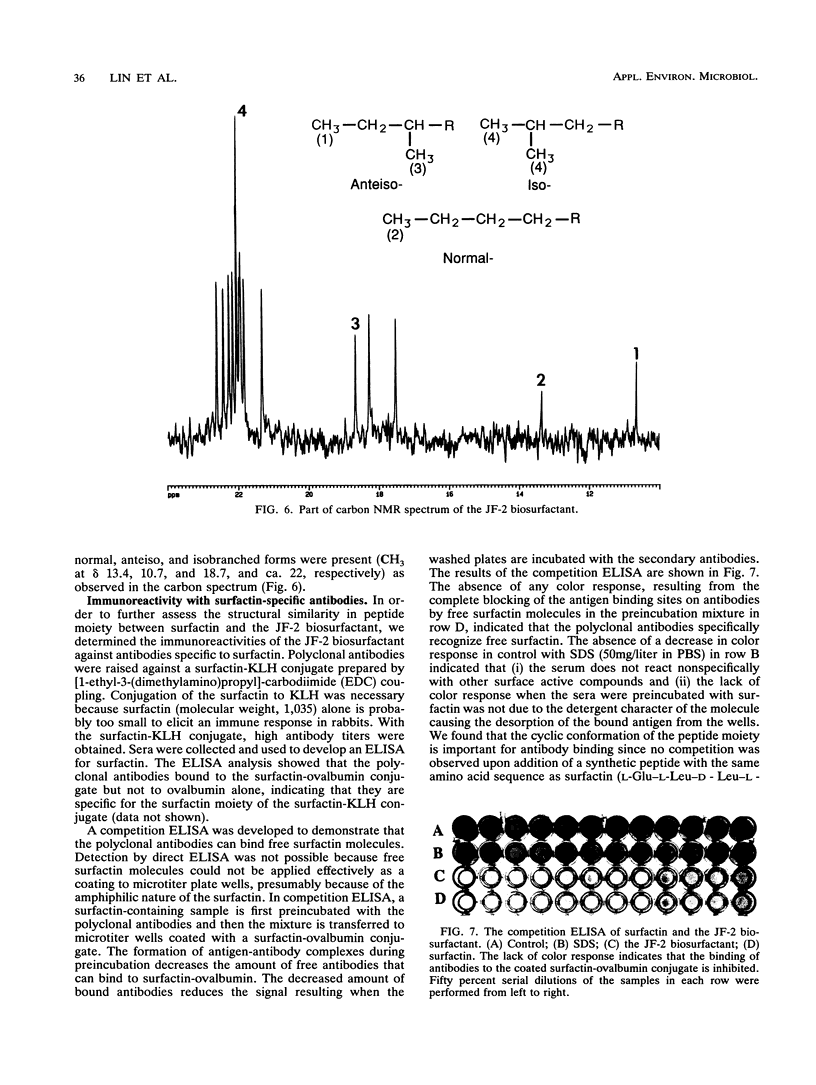
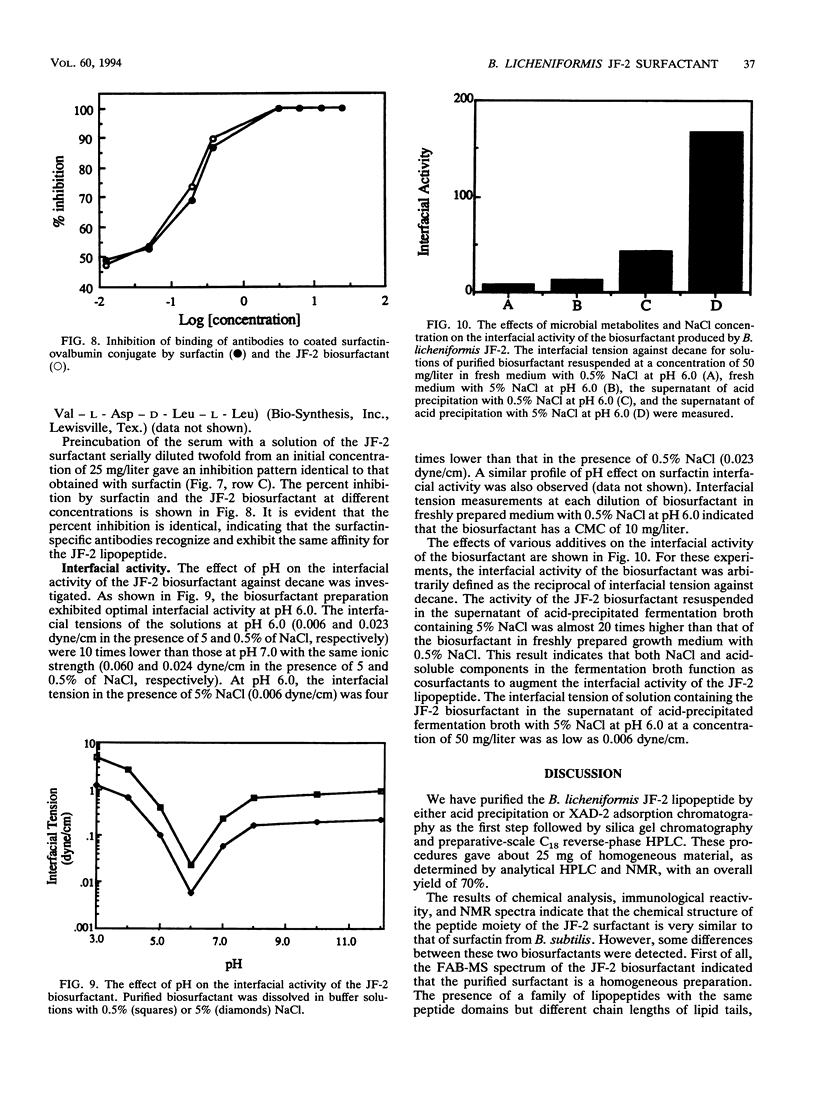
Abstract
Bacillus licheniformis JF-2 produces a very active biosurfactant under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. We purified the surface-active compound to homogeneity by reverse-phase C18 high-performance liquid chromatography and showed that it is a lipopeptide with a molecular weight of 1,035. Amino acid analysis, fast atom mass and infrared spectroscopy, and, finally, 1H, 13C, and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance demonstrated that the biosurfactant consists of a heterogeneous C15 fatty acid tail linked to a peptide moiety very similar to that of surfactin, a lipopeptide produced by Bacillus subtilis. Polyclonal antibodies were raised against surfactin and shown to exhibit identical reactivity towards purified JF-2 lipopeptide in competition enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, thus providing further evidence for the structural similarity of these two compounds. Under optimal conditions, the B. licheniformis JF-2 biosurfactant exhibits a critical micelle concentration of 10 mg/liter and reduces the interfacial tension against decane to 6 x 10(-3) dyne/cm, which is one of the lowest interfacial tensions ever reported for a microbial surfactant.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arima K., Kakinuma A., Tamura G. Surfactin, a crystalline peptidelipid surfactant produced by Bacillus subtilis: isolation, characterization and its inhibition of fibrin clot formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 May 10;31(3):488–494. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90503-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Avigad L. S. Nature and properties of a cytolytic agent produced by Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Jun;61(3):361–369. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-3-361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. G., Macdonald C. R., Duff S. J., Kosaric N. Enhanced Production of Surfactin from Bacillus subtilis by Continuous Product Removal and Metal Cation Additions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Sep;42(3):408–412. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.3.408-412.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiou G., Lin S. C., Sharma M. M. Surface-active compounds from microorganisms. Biotechnology (N Y) 1992 Jan;10(1):60–65. doi: 10.1038/nbt0192-60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S., Elashvili I., Valdes J. J., Kamely D., Chakrabarty A. M. Enhanced removal of Exxon Valdez spilled oil from Alaskan gravel by a microbial surfactant. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Mar;8(3):228–230. doi: 10.1038/nbt0390-228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S., Griffin W. M. Structural analysis of Bacillus licheniformis 86 surfactant. J Ind Microbiol. 1991 Jan;7(1):45–52. doi: 10.1007/BF01575602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosono K., Suzuki H. Acylpeptides, the inhibitors of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1983 Feb;36(2):194–196. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.36.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaheri M., Jenneman G. E., McInerney M. J., Knapp R. M. Anaerobic Production of a Biosurfactant by Bacillus licheniformis JF-2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Sep;50(3):698–700. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.3.698-700.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenny K., Käppeli O., Fiechter A. Biosurfactants from Bacillus licheniformis: structural analysis and characterization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1991 Oct;36(1):5–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00164690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInerney M. J., Javaheri M., Nagle D. P., Jr Properties of the biosurfactant produced by Bacillus licheniformis strain JF-2. J Ind Microbiol. 1990 Apr-May;5(2-3):95–101. doi: 10.1007/BF01573858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberbremer A., Müller-Hurtig R., Wagner F. Effect of the addition of microbial surfactants on hydrocarbon degradation in a soil population in a stirred reactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1990 Jan;32(4):485–489. doi: 10.1007/BF00903788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. I., Lee H., Trevors J. T. Applications of microbial surfactants. Biotechnol Adv. 1991;9(2):241–252. doi: 10.1016/0734-9750(91)90006-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wylie D. E., Lu D., Carlson L. D., Carlson R., Babacan K. F., Schuster S. M., Wagner F. W. Monoclonal antibodies specific for mercuric ions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):4104–4108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.4104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]