Abstract
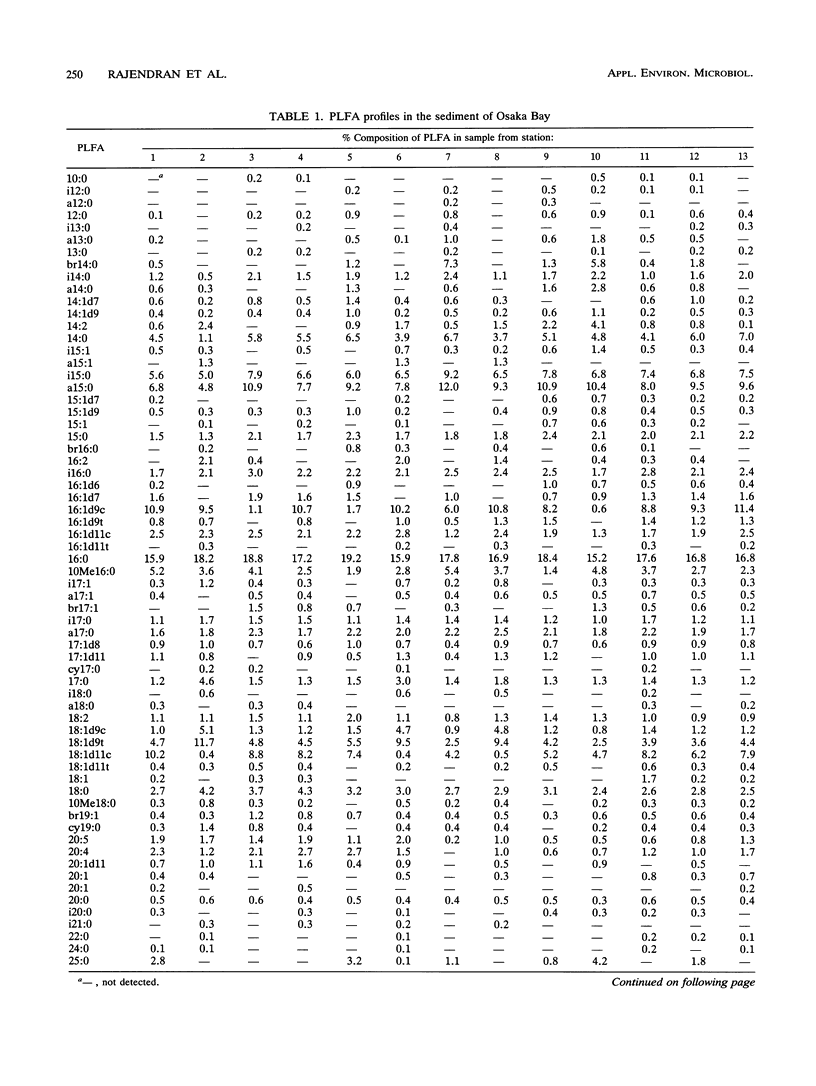
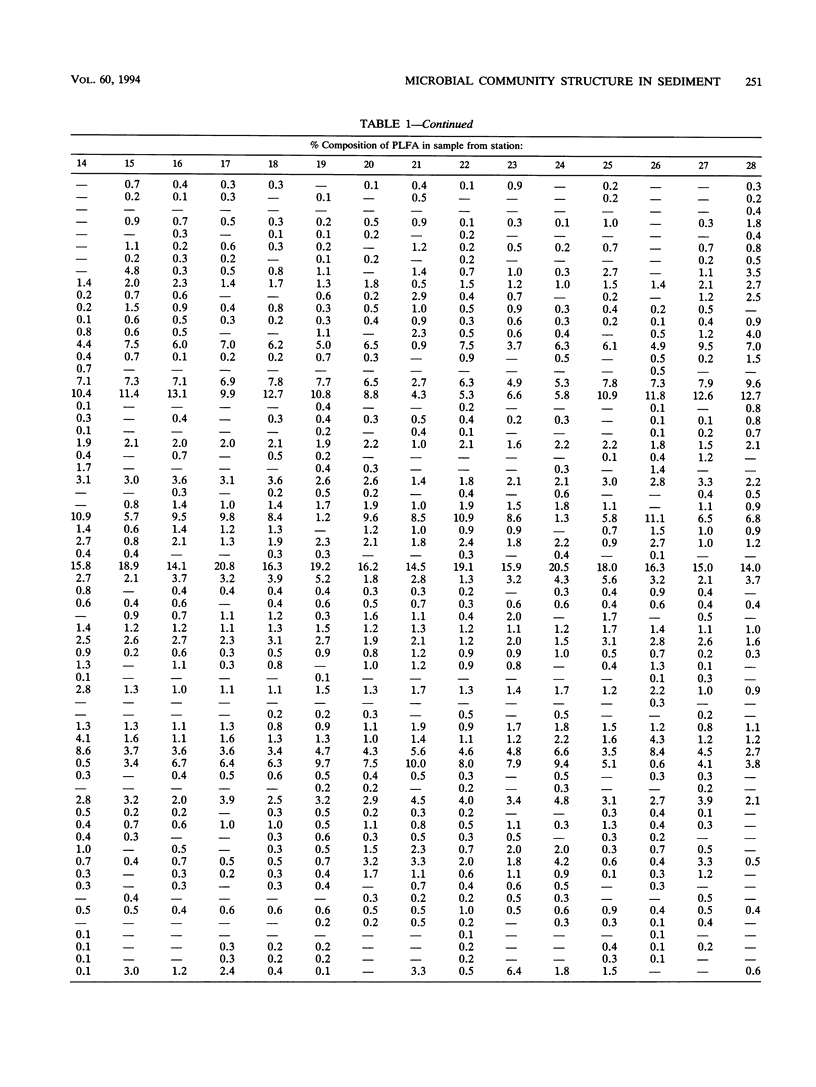
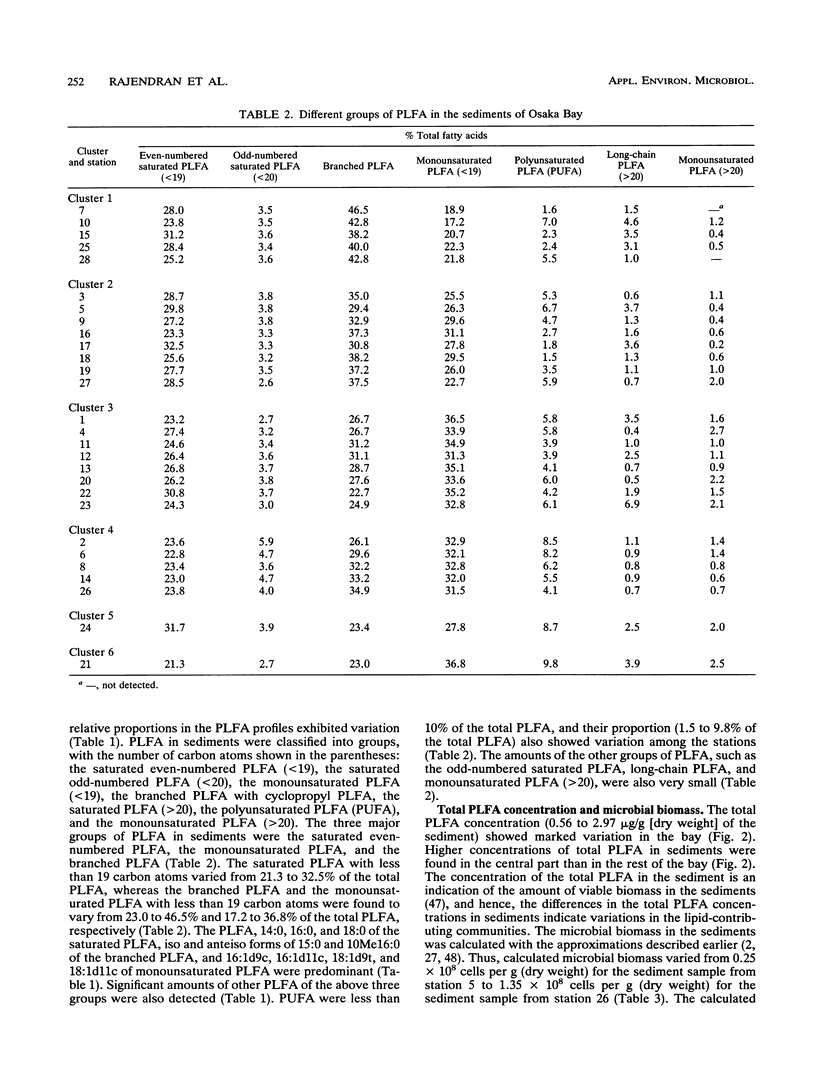
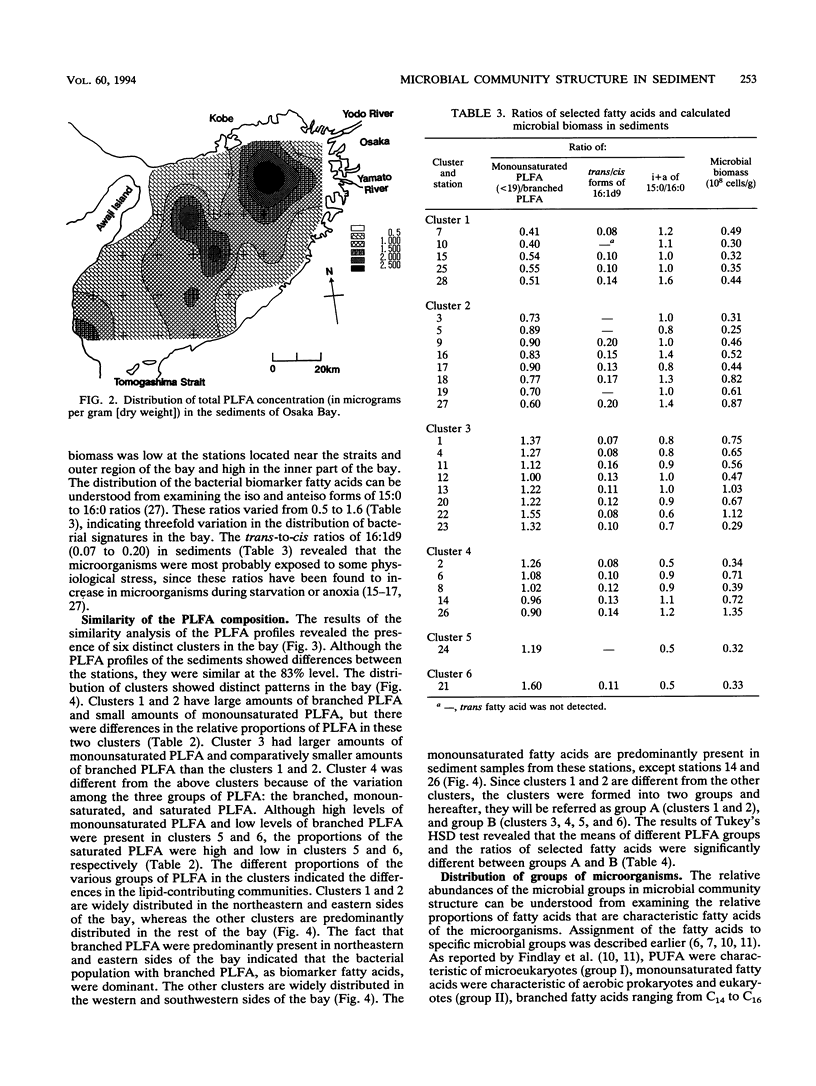
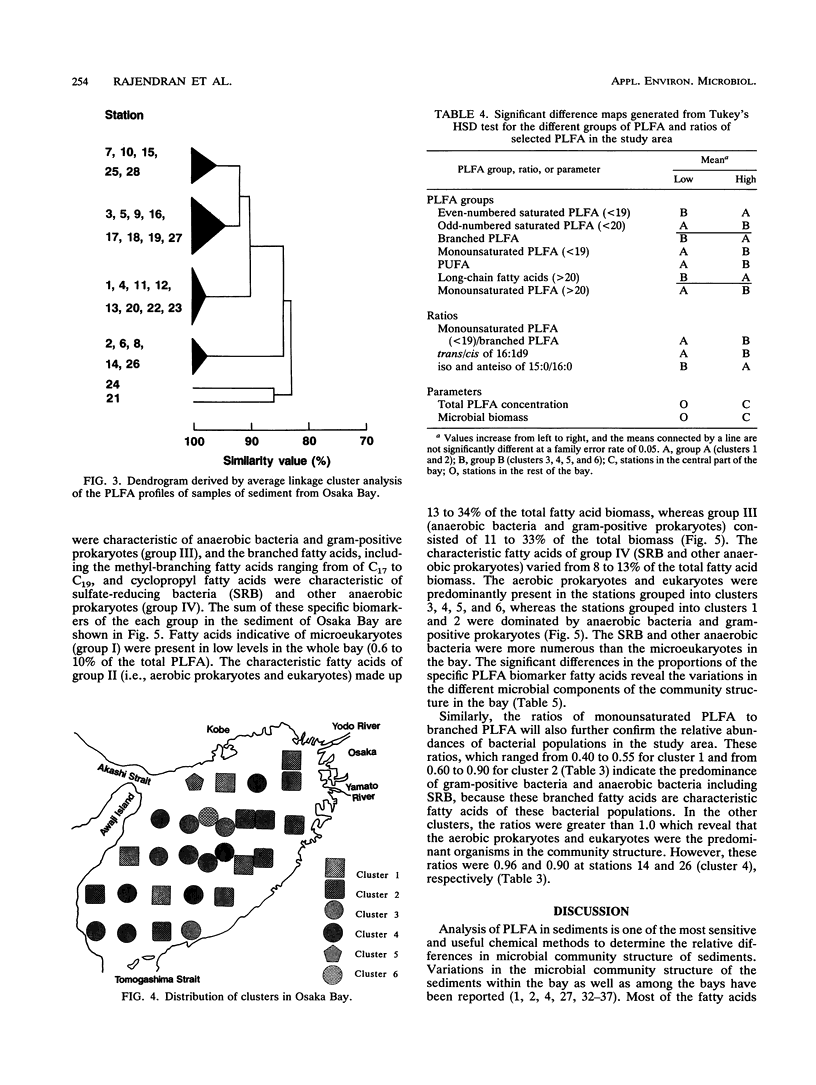
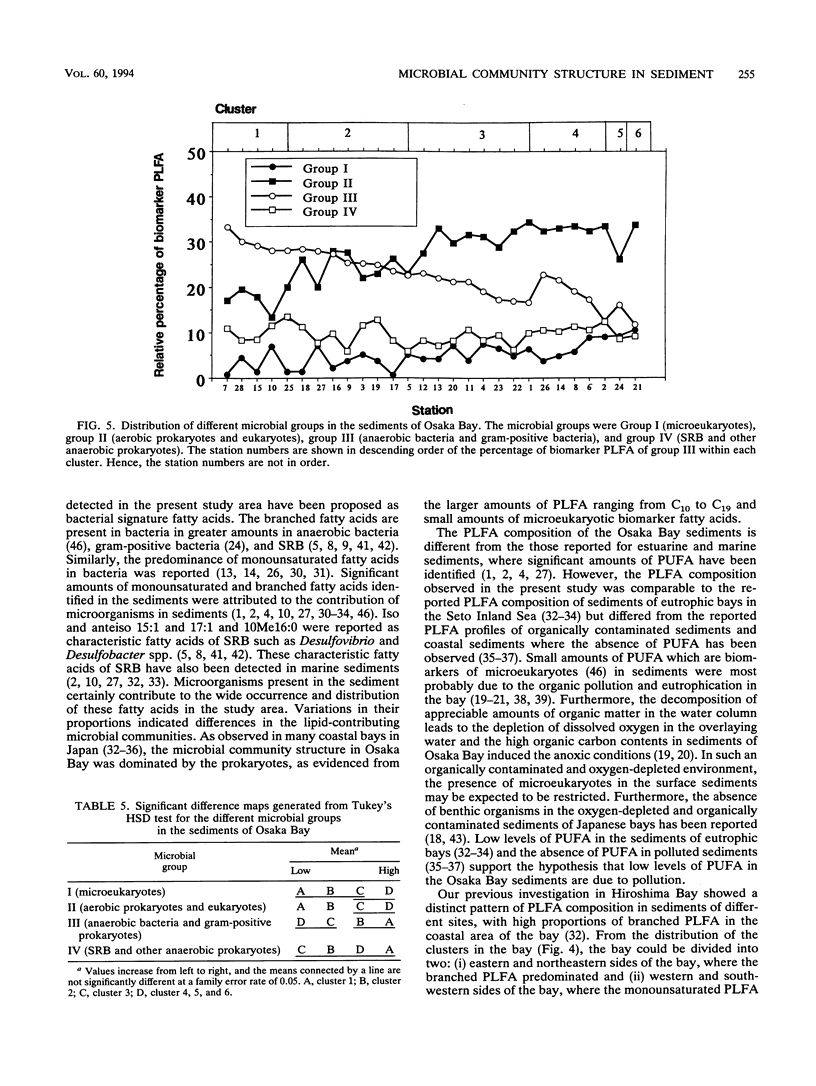
Twenty-eight sediment samples collected from Osaka Bay, Japan, were analyzed for phospholipid ester-linked fatty acids (PLFA) to determine regional differences in microbial community structure of the bay. The abundance of three major groups of C10 to C19 PLFA (saturated, branched, and monounsaturated PLFA), which accounted for 84 to 97% of the total PLFA, indicated the predominance of prokaryotes in the sediment. The distribution of six clusters obtained by similarity analysis in the bay revealed a marked regional distribution in the PLFA profiles. Total PLFA concentrations (0.56 to 2.97 μg/g [dry weight] of the sediment) in sediments also showed marked variation among the stations, with higher concentrations of total PLFA in the central part of the bay. The biomass, calculated on the basis of total PLFA concentration, ranged from 0.25 × 108 to 1.35 × 108 cells per g (dry weight) of the sediment. The relative dominance of microbial groups in sediments was described by using the reported bacterial biomarker fatty acids. Very small amounts of the characteristic PLFA of microeukaryotes in sediments indicated the restricted distribution of microeukaryotes. By examining the distribution of clusters and groups of microorganisms in the bay, there were two characteristics of the distribution pattern: (i) the predominance of anaerobic bacteria and gram-positive prokaryotes, characterized by the high proportions of branched PLFA in the eastern and northeastern sides of the bay, where the reported concentrations of pollutants were also high, and (ii) the predominance of aerobic prokaryotes and eukaryotes, except for a few stations, in the western and southwestern sides of the bay, as evidenced by the large amounts of monounsaturated PLFA. Such significant regional differences in microbial community structure of the bay indicate shifts in microbial community structure.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird B. H., White D. C. Biomass and community structure of the abyssal microbiota determined from the ester-linked phospholipids recovered from Venezuela Basin and Puerto Rico Trench sediments. Mar Geol. 1985;68:217–231. doi: 10.1016/0025-3227(85)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobbie R. J., White D. C. Characterization of benthic microbial community structure by high-resolution gas chromatography of Fatty Acid methyl esters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jun;39(6):1212–1222. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.6.1212-1222.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon J. J., de Leeuw J. W., Hoek G. J., Vosjan J. H. Significance and taxonomic value of iso and anteiso monoenoic fatty acids and branded beta-hydroxy acids in Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1183–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1183-1191.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund A., Nichols P. D., Roffey R., White D. C. Extractable and lipopolysaccharide fatty acid and hydroxy acid profiles from Desulfovibrio species. J Lipid Res. 1985 Aug;26(8):982–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guckert J. B., Hood M. A., White D. C. Phospholipid ester-linked fatty acid profile changes during nutrient deprivation of Vibrio cholerae: increases in the trans/cis ratio and proportions of cyclopropyl fatty acids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):794–801. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.794-801.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda T. Fatty acids of the genus Bacillus: an example of branched-chain preference. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):391–418. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.391-418.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechevalier M. P. Lipids in bacterial taxonomy - a taxonomist's view. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1977;5(2):109–210. doi: 10.3109/10408417709102311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipski A., Klatte S., Bendinger B., Altendorf K. Differentiation of gram-negative, nonfermentative bacteria isolated from biofilters on the basis of Fatty Acid composition, quinone system, and physiological reaction profiles. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jun;58(6):2053–2065. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.6.2053-2065.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran N., Matsuda O., Imamura N., Urushigawa Y. Variation in microbial biomass and community structure in sediments of eutrophic bays as determined by phospholipid ester-linked Fatty acids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):562–571. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.562-571.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



