Abstract
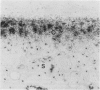
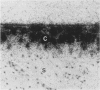
Anatomically intact, murine patellar cartilage was exposed to human polymorphonuclear leucocytes (PMN) stimulated with formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine or Ca-ionophore A-23187. This resulted in an inhibition of chondrocyte proteoglycan synthesis and breakdown of cartilage matrix proteoglycans as shown with 35S-incorporation and autoradiography. These effects could not be inhibited by catalase or superoxide dismutase. A serine protease inhibitor and a specific elastase inhibitor prevented both proteoglycan degradation and chondrocyte damage, indicating that PMN-elastase is the causative agent. It was shown that elastase shed by PMN in close contact with the articular cartilage, can escape from complexing with alpha-1 proteinase inhibitor. We would hypothesize that the elastase owing to its dual action (matrix breakdown and inhibition of chondrocyte metabolism) is a major contributor to enzymatic cartilage destruction in inflammatory disorders.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartholomew J. S., Lowther D. A., Handley C. J. Changes in proteoglycan biosynthesis following leukocyte elastase treatment of bovine articular cartilage in culture. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Aug;27(8):905–912. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates E. J., Johnson C. C., Lowther D. A. Inhibition of proteoglycan synthesis by hydrogen peroxide in cultured bovine articular cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 15;838(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90082-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castillo M. J., Nakajima K., Zimmerman M., Powers J. C. Sensitive substrates for human leukocyte and porcine pancreatic elastase: a study of the merits of various chromophoric and fluorogenic leaving groups in assays for serine proteases. Anal Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;99(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keiser H., Greenwald R. A., Feinstein G., Janoff A. Degradation of cartilage proteoglycan by human leukocyte granule neutral proteases--a model of joint injury. II. Degradation of isolated bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):625–632. doi: 10.1172/JCI108318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J. The degradation of cartilage proteoglycans by tissue proteinases. Proteoglycan heterogeneity and the pathway of proteolytic degradation. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 1;167(3):639–646. doi: 10.1042/bj1670639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandy J. D., Lowther D. A., Brown H. L. Antigen-induced arthritis. Studies on the inhibition of proteoglycan synthesis observed in articular cartilage during short-term joint inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Apr;23(4):433–447. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalkwijk J., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B., Joosten L. A. Hydrogen peroxide suppresses the proteoglycan synthesis of intact articular cartilage. J Rheumatol. 1985 Apr;12(2):205–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalkwijk J., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B., Joosten L. A., van den Bersselaar L. Cationization of catalase, peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase. Effect of improved intraarticular retention on experimental arthritis in mice. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):198–205. doi: 10.1172/JCI111946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar L. A., McNeil V. M., Jesaitis A. J., Painter R. G., Cochrane C. G. A continuous, spectroscopic analysis of the kinetics of elastase secretion by neutrophils. The dependence of secretion upon receptor occupancy. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5471–5475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries B. J., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B. Salicylate-induced depletion of endogenous inorganic sulfate. Potential role in the suppression of sulfated glycosaminoglycan synthesis in murine articular cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Aug;28(8):922–929. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., Kruijsen M. W., van de Putte L. B., van Beusekom H. J., van der Sluis-van der Pol M., Zwarts W. A. Antigen-induced and zymosan-induced arthritis in mice: studies on in vivo cartilage proteoglycan synthesis and chondrocyte death. Br J Exp Pathol. 1981 Jun;62(3):308–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]