Abstract
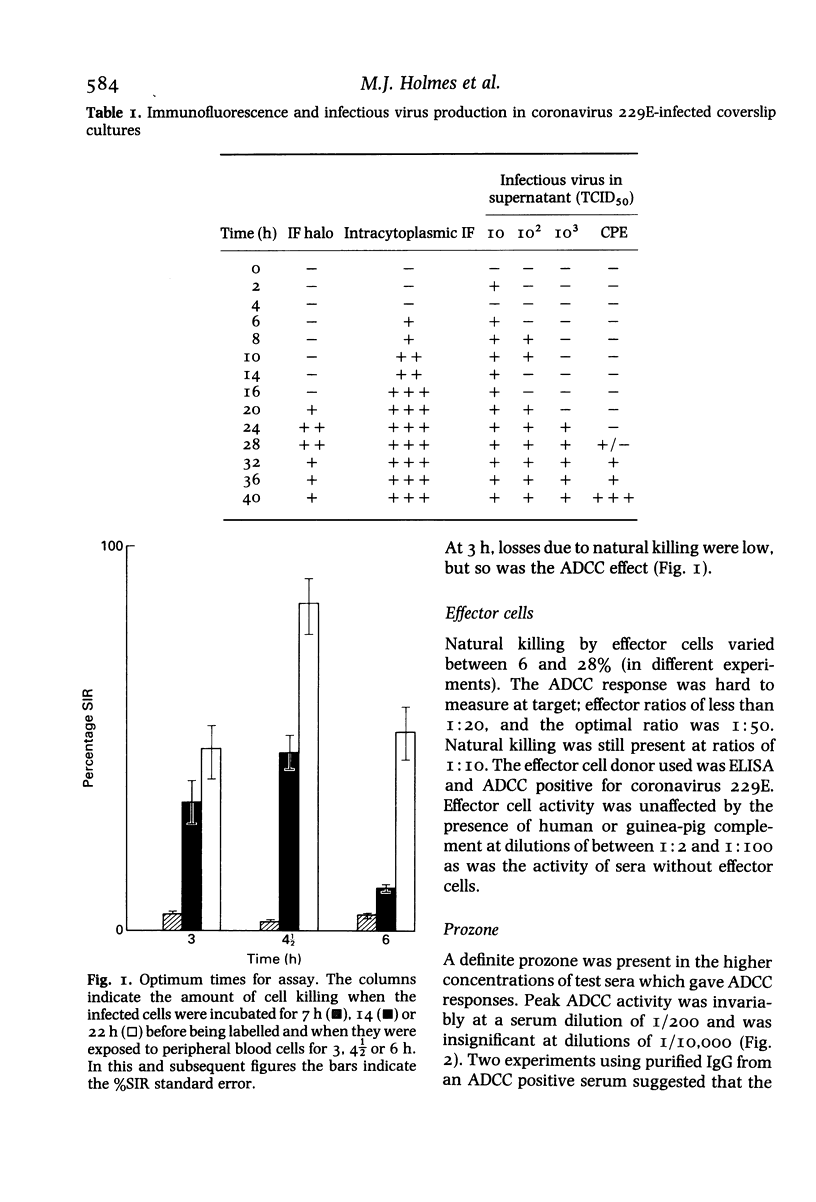
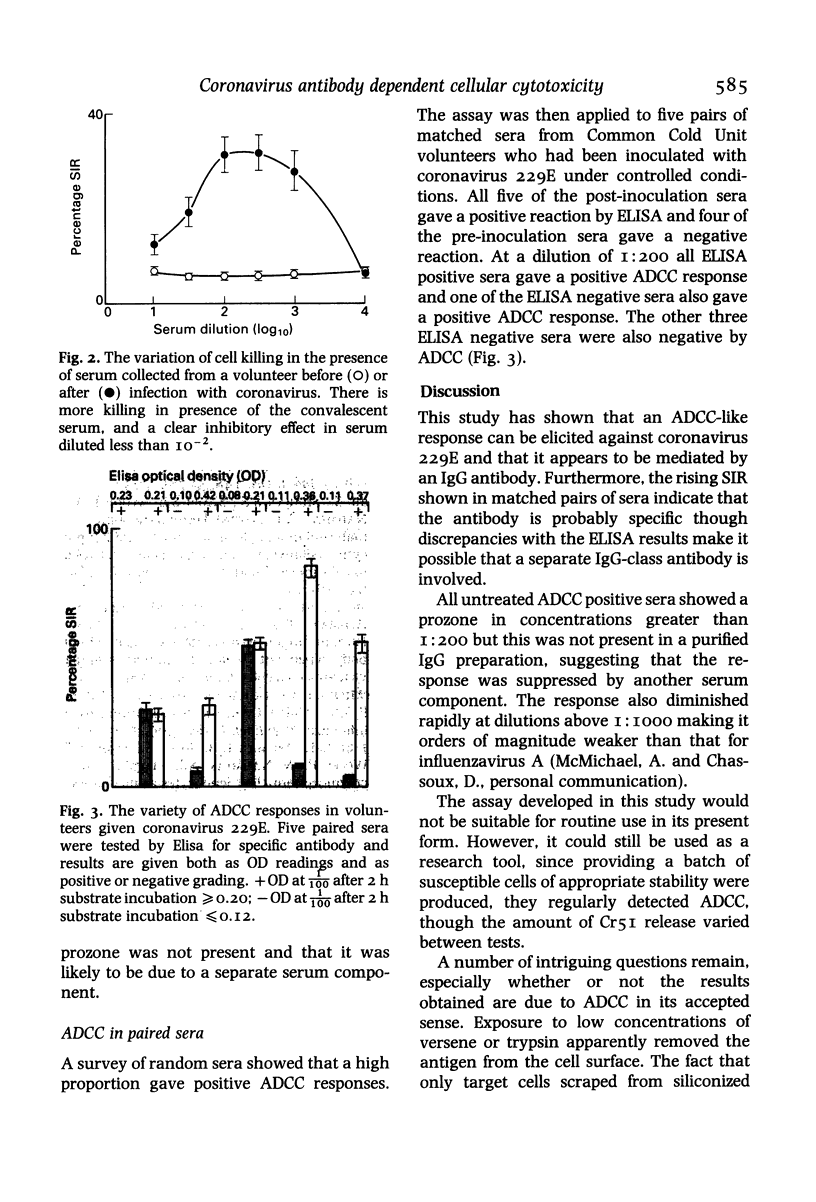
An antibody dependent cellular cytotoxic (ADCC) reaction was elicited using human mixed lymphocyte cultures against coronavirus 229E-infected C-16 cells. The response was assayed in microtitre plates by radioactive chromium release. Optimal killing of target cells was achieved using cells labelled 22 h after infection. A prozone was present and the optimal dilution of sera was invariably 1:200. The majority (70%) of sera tested gave a positive ADCC response. These included all sera judged positive by ELISA, but also some which were judged negative. Two experiments using purified IgG from serum which was ADCC and ELISA positive suggested that the response is mediated by an IgG antibody and that the prozone is due to a separate serum component.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bucknall R. A., Kalica A. R., Chanock R. M. Intracellular development and mechanism of hemadsorption of a human coronavirus, OC43. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Mar;139(3):811–817. doi: 10.3181/00379727-139-36243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callow K. A. Effect of specific humoral immunity and some non-specific factors on resistance of volunteers to respiratory coronavirus infection. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Aug;95(1):173–189. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400062410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Shaban S. S., Starr S. E., Wood P. A., Nahmias A. J. Human neonatal and maternal monocyte-macrophage and lymphocyte-mediated antibody-dependent cytotoxicity to cells infected with herpes simplex. J Pediatr. 1978 Aug;93(2):206–210. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80497-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Starr S. E., oleske J. M., Shore S. L., Ashman R. B., Nahmias A. J. Human monocyte-macrophage-mediated antibody-dependent cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):729–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleske J. M., Ashman R. B., Kohl S., Shore S. L., Starr S. E., Wood P., Nahmias A. J. Human polymorphonuclear leucocytes as mediators of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Mar;27(3):446–453. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong L., Reiser P., Coromilas J., Scherr L., Morrison J. Left ventricular function and rapid release of creatine kinase MB in acute myocardial infarction. Evidence for spontaneous reperfusion. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jul 7;309(1):1–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198307073090101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Black C. M., Melewicz F. M., Wood P. A., Nahmias A. J. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity to target cells infected with type 1 and type 2 herpes simplex virus. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):194–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


