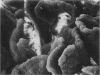Abstract
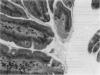
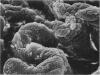
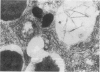
Male and female rats 8 weeks old were exposed for 360 days to a sole source of drinking water containing 0.2 g/l cadmium as the chloride salt. Control rats were exposed for the same period to deionized water. At 90, 180, 270 and 360 day intervals a proportion of the rats from both test and control groups were killed and the duodenums removed. The histopathology was assessed by both light and electron microscopy. In cadmium treated rats the duodenums were enlarged and there was a significant reduction in the percentage of crypts containing Paneth cells. Remaining Paneth cells appeared vacuolated. By both light and electron microscopy changes were noted in the epithelial cells covering the villus tips. These were swollen and protruded towards the duodenal lumen to give a 'cobblestone' appearance by scanning electron microscopy. It is suggested that these histopathological appearances will be seen in chronic dietary exposure to cadmium.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Danielson K. G., Ohi S., Huang P. C. Immunochemical detection of metallothionein in specific epithelial cells of rat organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2301–2304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostial K., Simonović I., Rabar I., Blanusa M., Landeka M. Age and intestinal retention of mercury and cadmium in rats. Environ Res. 1983 Jun;31(1):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(83)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Lewellyn J., Erlandsen S. L. Cytodifferentiation of the rat Paneth cell: an immunocytochemical investigation in suckling and weanling animals. Am J Anat. 1980 Jul;158(3):285–297. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001580305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda S., Kubota K., Yamada K., Yoshizawa S., Moriuchi S., Hosoya N. The effect of vitamin D3 and dietary calcium level on the cadmium-induced morphological and biochemical changes in rat intestinal mucosa. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 1978;24(4):405–418. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.24.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillpotts C. J. Retention of cadmium in the duodenum of the rat following oral administration. Toxicology. 1979 Nov;14(3):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(79)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillpotts C. J. The autoradiographic localisation of retained orally administered cadmium tracer within Paneth cells of rat duodenum. Toxicology. 1984 Oct;33(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(84)90016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson M. E., Fox M. R., Fry B. E., Jr Pathological changes produced in Japanese quail by ingestion of cadmium. J Nutr. 1974 Mar;104(3):323–338. doi: 10.1093/jn/104.3.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodning C. B., Erlandsen S. L., Wilson I. D., Carpenter A. M. Light microscopic morphometric analysis of rat ileal mucosa: II. Component quantitation of Paneth cells. Anat Rec. 1982 Sep;204(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092040105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stowe H. D., Wilson M., Goyer R. A. Clinical and morphologic effects of oral cadmium toxicity in rabbits. Arch Pathol. 1972 Nov;94(5):389–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbuswamy S. G. Paneth cells in diverticular disease of the colon. J Clin Pathol. 1970 May;23(4):351–353. doi: 10.1136/jcp.23.4.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valberg L. S., Haist J., Cherian M. G., Delaquerriere-Richardson L., Goyer R. A. Cadmium-induced enteropathy: comparative toxicity of cadmium chloride and cadmium-thionein. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1977 Mar;2(4):963–975. doi: 10.1080/15287397709529495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]