Abstract
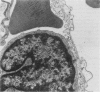
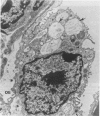
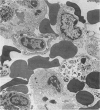
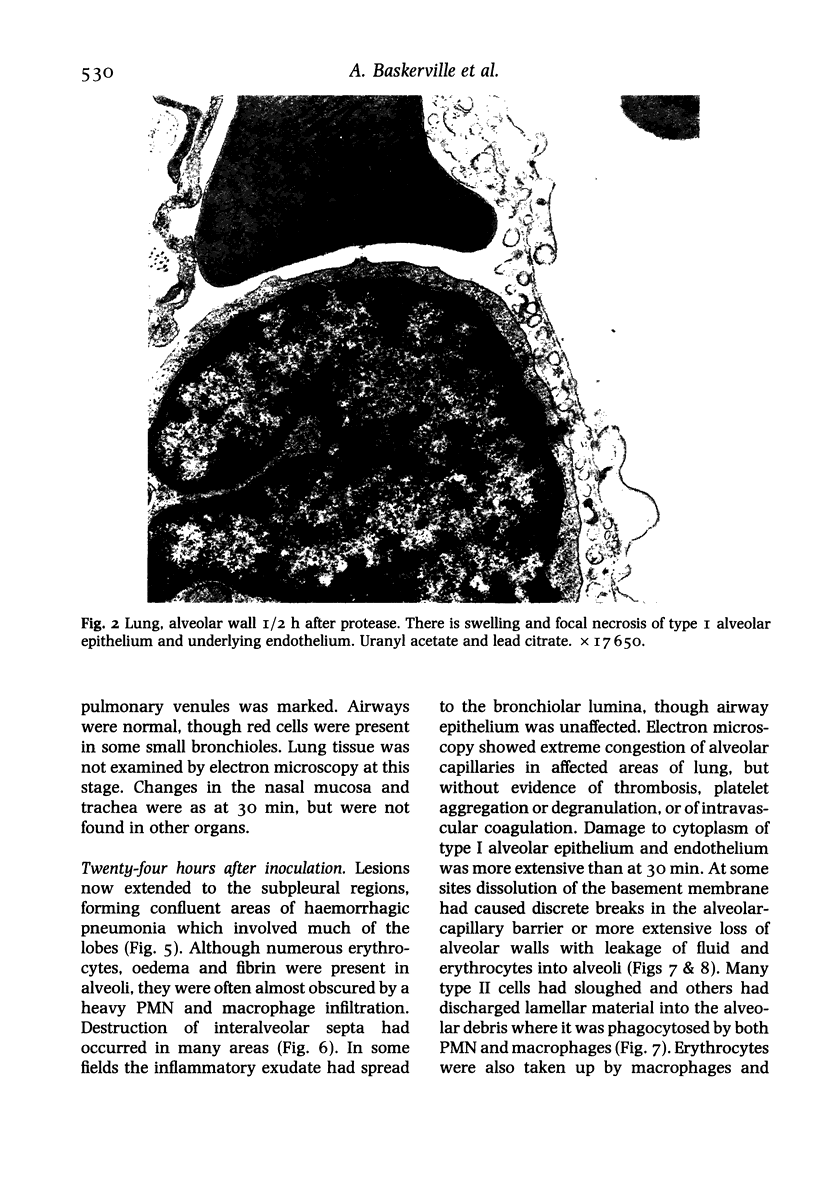
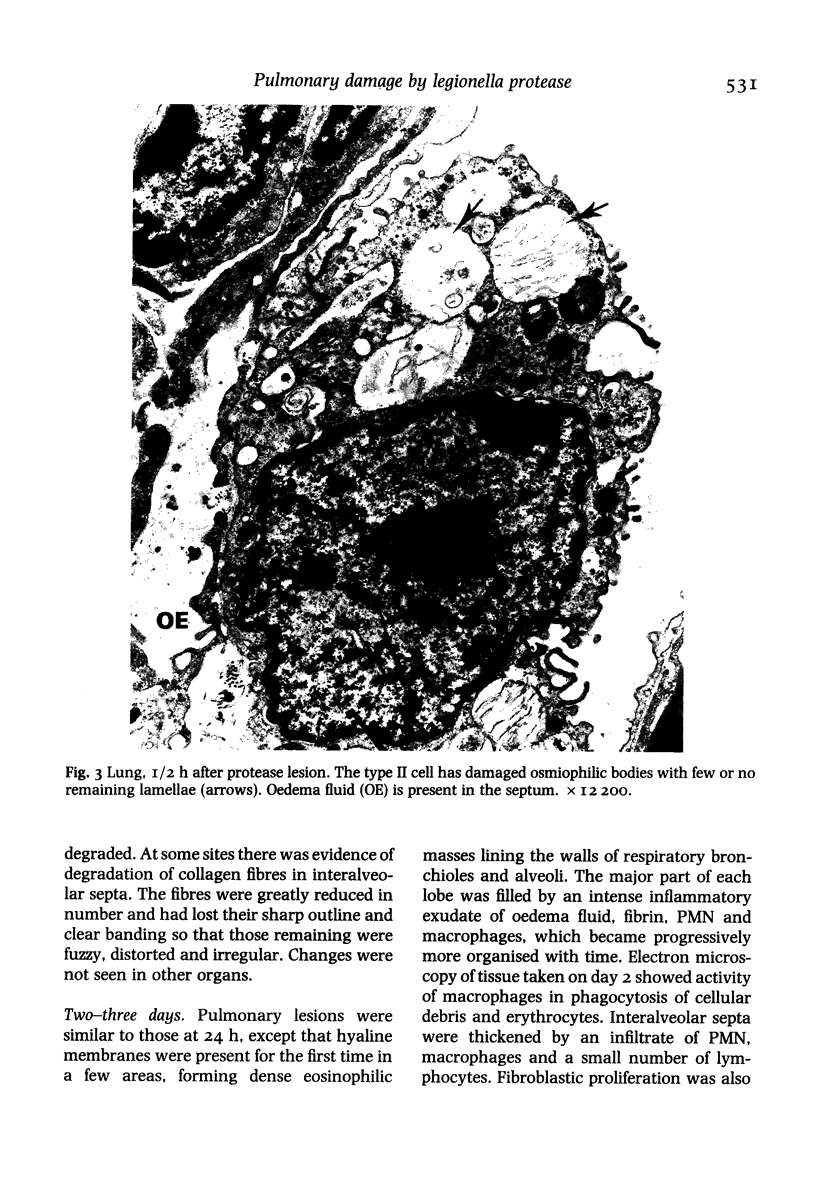
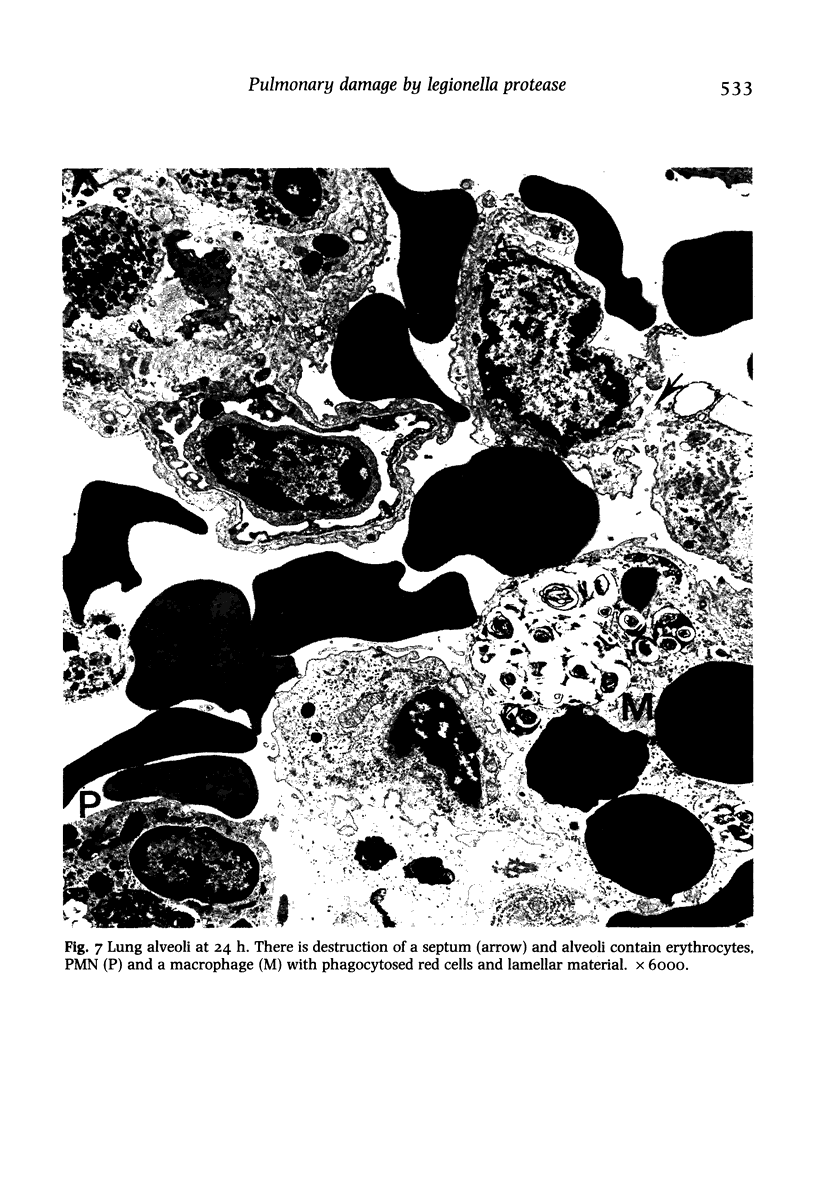
Intranasal (or intratracheal) administration of a tissue-destructive protease from Legionella pneumophila to guinea-pigs produced areas of haemorrhagic pneumonia in the lungs after 1/2 h. By 24 h there was confluent consolidation in all lobes. Histological and ultrastructural studies showed alveolar haemorrhage, vesiculation and necrosis of type I alveolar epithelium and endothelium, followed by progressive exudation of oedema fluid, fibrin, PMN and macrophages. Damage to type II cell lamellated bodies and discharge of lamellar material were significant features of the lesion. Collagenase activity was indicated by morphological degradation of collagen fibres in severely affected interalveolar septa. The pathological changes of Legionnaires' disease pneumonia can thus be reproduced experimentally by the administration of a L. pneumophila tissue-destructive protease, suggesting that production of this protease in vivo during L. pneumophila infection may play an important role in causing the pneumonia.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams W. R., Fein A. M., Kucich U., Kueppers F., Yamada H., Kuzmowycz T., Morgan L., Lippmann M., Goldberg S. K., Weinbaum G. Proteinase inhibitory function in inflammatory lung disease. I. Acute bacterial pneumonia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 May;129(5):735–741. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.5.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berdal B. P., Fossum K. Occurrence and immunogenicity of proteinases from Legionella species. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;1(1):7–11. doi: 10.1007/BF02014133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H. M. Legionnaires' disease in non-Legionnaires. A report of five cases. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Mar;88(3):294–302. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-3-294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma J. Y., Abe C., Tanamoto K., Hirao Y., Morihara K., Tsuzuki H., Yanagawa R., Honda E., Aoi Y., Fujimoto Y. Effectiveness of immunization with single and multi-component vaccines prepared from a common antigen (OEP), protease and elastase toxoids of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on protection against hemorrhagic pneumonia in mink due to P. aeruginosa. Jpn J Exp Med. 1978 Apr;48(2):111–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jepras R. I., Fitzgeorge R. B., Baskerville A. A comparison of virulence of two strains of Legionella pneumophila based on experimental aerosol infection of guinea-pigs. J Hyg (Lond) 1985 Aug;95(1):29–38. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400062252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ristroph J. D., Hedlund K. W., Allen R. G. Liquid medium for growth of Legionella pneumophila. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Jan;11(1):19–21. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.1.19-21.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. R., Miller R. D., Iglewski B. H. In vitro production of an extracellular protease by Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):299–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.299-302.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe T. C., Miller R. D. Extracellular enzymes of Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):632–635. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.632-635.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winn W. C., Jr, Glavin F. L., Perl D. P., Keller J. L., Andres T. L., Brown T. M., Coffin C. M., Sensecqua J. E., Roman L. N., Craighead J. E. The pathology of Legionnaires' disease. Fourteen fatal cases from the 1977 outbreak in Vermont. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1978 Jul;102(7):344–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]