Abstract
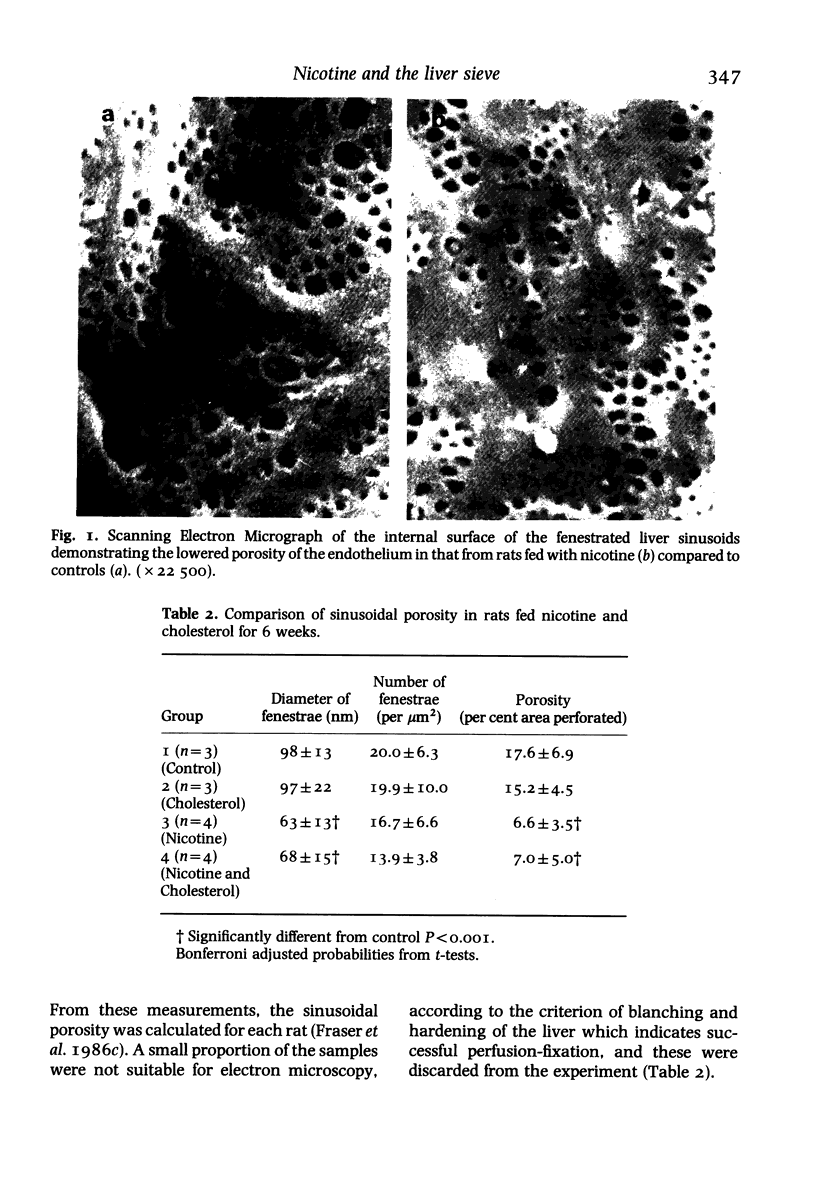
Nicotine was fed to rats for 6 weeks, as a weight adjusted dose equivalent to that of a human being smoking 50 to 100 cigarettes per day. Those rats fed nicotine developed hypercholesterolaemia. Scanning electron microscopy showed the porosity of the hepatic sinusoidal endothelium of nicotine fed animals was about 40% that of control animals. The decline in porosity was found to be due to a reduction in diameter rather than number of fenestrae. We believe that this decreased hepatic sinusoidal porosity may alter cholesterol homeostasis by increasing the circulation time of chylomicron remnants too large to pass through the fenestrae. This phenomenon may be an aetiological factor in the known correlation between cigarette smoking, atherosclerosis, and coronary heart disease in humans.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booyse F. M., Osikowicz G., Quarfoot A. J. Effects of chronic oral consumption of nicotine on the rabbit aortic endothelium. Am J Pathol. 1981 Feb;102(2):229–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dousset J. C., Gutierrès J. B., Dousset N. Hypercholesterolaemia after administration of nicotine chewing gum. Lancet. 1986 Dec 13;2(8520):1393–1394. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florén C. H. Binding of apolipoprotein E-rich remnant lipoproteins to human liver membranes. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1984 Jun;19(4):473–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser R., Bosanquet A. G., Day W. A. Filtration of chylomicrons by the liver may influence cholesterol metabolism and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 1978 Feb;29(2):113–123. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(78)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser R., Bowler L. M., Day W. A. Damage of rat liver sinusoidal endothelium by ethanol. Pathology. 1980 Jul;12(3):371–376. doi: 10.3109/00313028009077098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser R., Heslop V. R., Murray F. E., Day W. A. Ultrastructural studies of the portal transport of fat in chickens. Br J Exp Pathol. 1986 Dec;67(6):783–791. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn T., Christoffersen P., Henriksen J. H. Alcoholic liver injury: defenestration in noncirrhotic livers--a scanning electron microscopic study. Hepatology. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1):77–82. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak K. M., Lieber C. S. Alterations in endothelial fenestrations in liver sinusoids of baboons fed alcohol: a scanning electron microscopic study. Hepatology. 1984 May-Jun;4(3):386–391. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito M., Wisse E. Filtration effect of endothelial fenestrations on chylomicron transport in neonatal rat liver sinusoids. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Jul 10;190(3):371–382. doi: 10.1007/BF00219553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanovich V., Gore I., Kajiyama G., Iwanaga Y. The effect of nicotine on dietary atherogenesis in rabbits. Exp Mol Pathol. 1969 Aug;11(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(69)90071-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisse E., De Zanger R. B., Charels K., Van Der Smissen P., McCuskey R. S. The liver sieve: considerations concerning the structure and function of endothelial fenestrae, the sinusoidal wall and the space of Disse. Hepatology. 1985 Jul-Aug;5(4):683–692. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman M., McGeachie J. The effect of nicotine on aortic endothelial cell turnover. An autoradiographic study. Atherosclerosis. 1985 Dec;58(1-3):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(85)90054-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]