Abstract
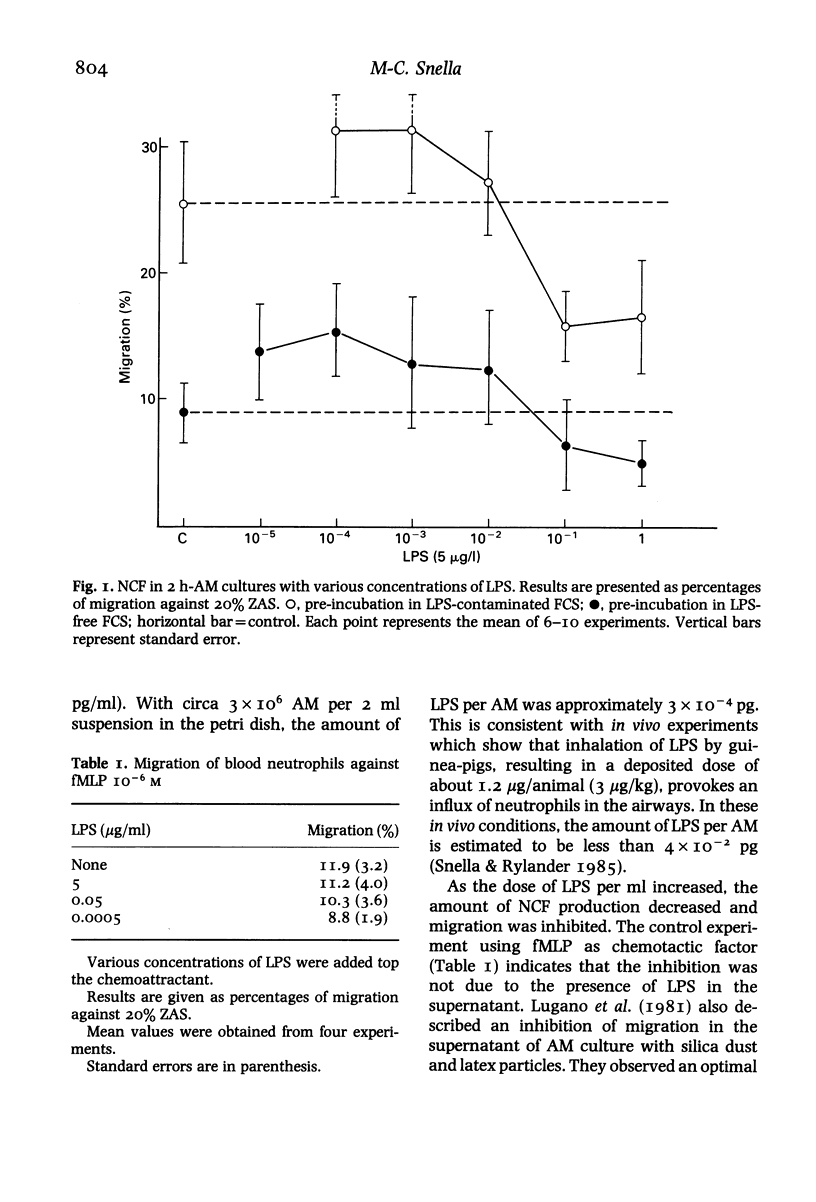
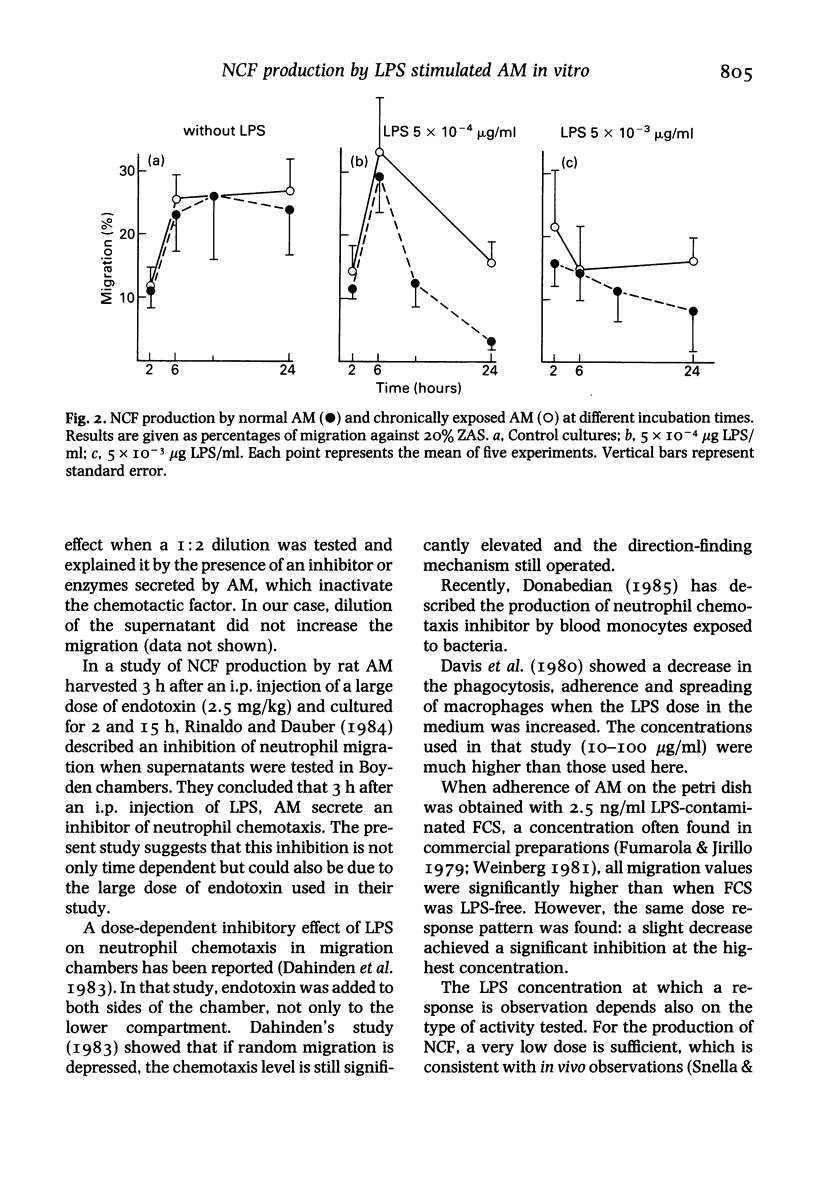
Alveolar macrophages (AM) isolated from normal guinea-pigs and from those chronically exposed to endotoxin (LPS) were cultured in the presence of various concentrations of LPS (from 0.5 ng to 5 micrograms/ml). The presence of a neutrophil chemotactic factor (NCF) in culture supernatants was tested in migrations chambers. Contamination of all reagents has been tested using LAL test (Limulus Amoebocyte Lysate). The results indicate a production of NCF with low LPS concentrations (0.5 and 5 ng/ml) within the first 6 h of incubation: when larger doses are used the response decreases and a significant inhibition is observed with 5 micrograms LPS/ml (P less than or equal to 0.05). When contaminated medium was used, all responses observed were three times higher than with LPS-free medium (P less than or equal to 0.01). However, the response pattern was the same. AM from chronically exposed animals exhibit the same response patterns: the magnitude of NCF production was higher than with normal AM but not significantly. The data suggests that initial conditions of AM in vitro or in vivo with reference to LPS contamination have to be determined as they are of importance when AM NCF production has to be tested.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davis W. B., Barsoum I. S., Ramwell P. W., Yeager H., Jr Human alveolar macrophages: effects of endotoxin in vitro. Infect Immun. 1980 Dec;30(3):753–758. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.3.753-758.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donabedian H. Human mononuclear cells exposed to staphylococci rapidly produce an inhibitor of neutrophil chemotaxis. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):24–32. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadek J. E., Hunninghake G. W., Zimmerman R. L., Crystal R. G. Regulation of the release of alveolar macrophage-derived neutrophil chemotactic factor. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Apr;121(4):723–733. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.4.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Spitalny G. L. Endotoxin-induced interferon synthesis in macrophage cultures. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1983 May;33(5):369–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugano E. M., Dauber J. H., Daniele R. P. Silica stimulation of chemotactic factor release by guinea pig alveolar macrophages. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Nov;30(5):381–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snella M. C. Manganese dioxide induces alveolar macrophage chemotaxis for neutrophils in vitro. Toxicology. 1985 Feb;34(2):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(85)90164-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snella M. C., Rylander R. Lung cell reactions after inhalation of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Respir Dis. 1982 Nov;63(6):550–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taramelli D., Holden H. T., Varesio L. Endotoxin requirement for macrophage activation by lymphokines in a rapid microcytotoxicity assay. J Immunol Methods. 1980;37(3-4):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90309-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


