Abstract
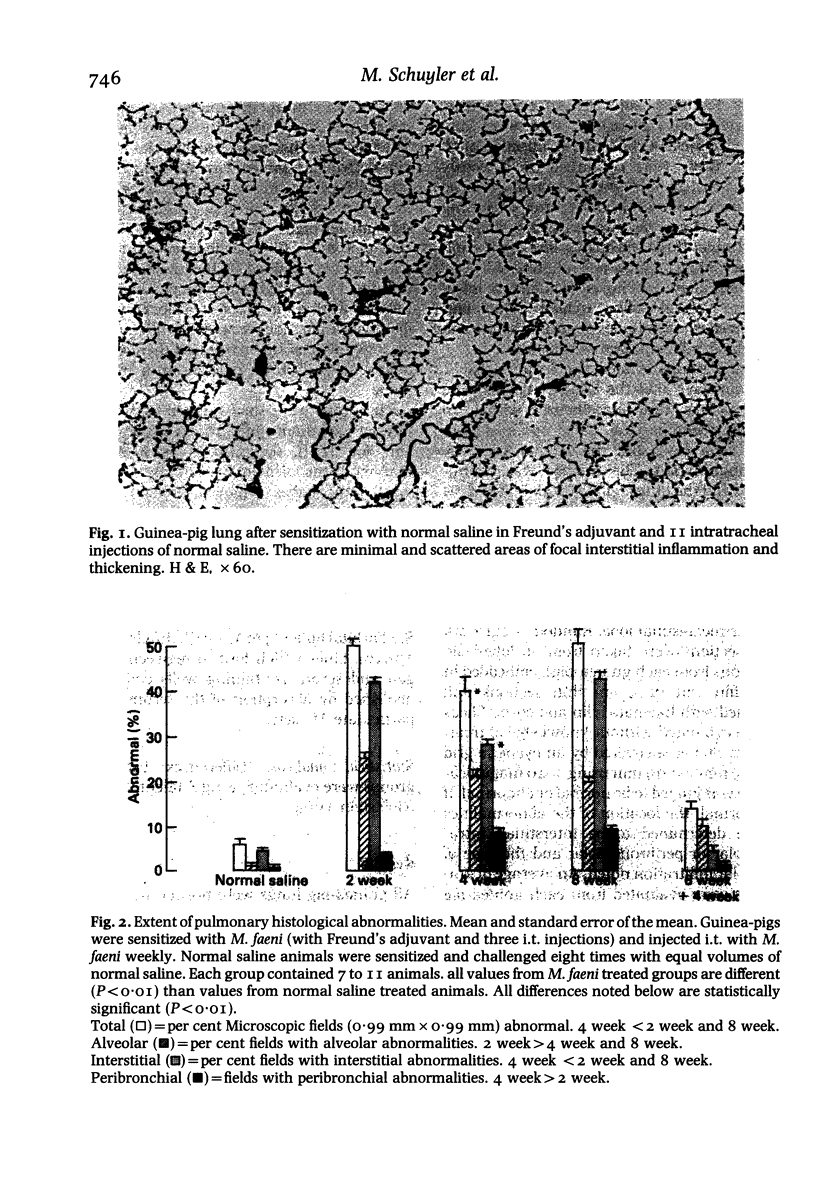
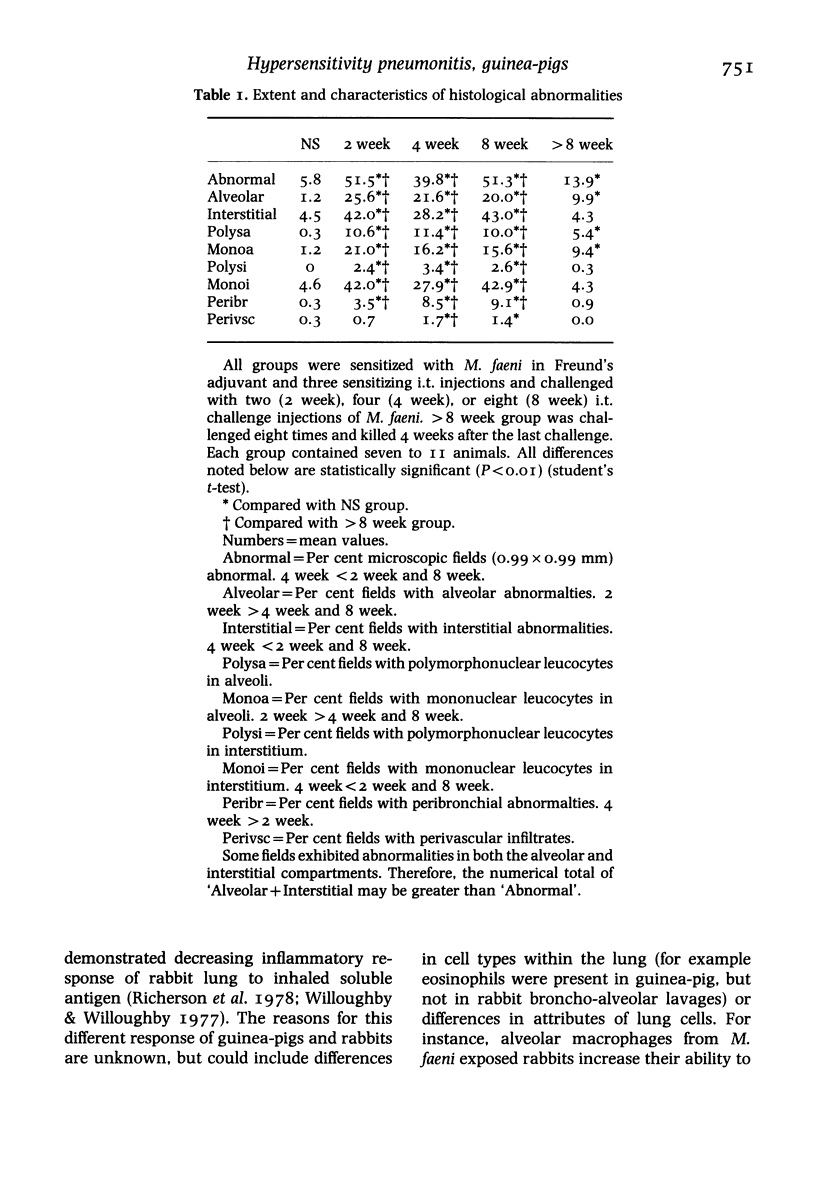
Models of hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) should exhibit progression of pulmonary histological abnormalities during continuing challenges. Strain II guinea-pigs were sensitized with Micropolyspora faeni and received 2, 4, or 8 weekly intratracheal (i.t.) particulate M. faeni challenges. Control animals received normal saline (NS). Four days after the last exposure, randomly selected microscopic fields of lung (200/animal) were judged to be normal or abnormal. If abnormal, the location and nature of the abnormalities were determined. Compared with NS treated guinea-pigs, those exposed to 2, 4 and 8 weekly M. faeni challenges exhibited more extensive (P less than 0.001) pulmonary histological abnormalities which involved both the intraalveolar and interstitial compartments. More extensive abnormalities in the 8 week group compared with the 4 week group were caused by increased extent of interstitial mononuclear cell infiltration. The extent of pulmonary interstitial histological abnormalities transiently (four challenges) decreases, but then increases, so that progressive pulmonary inflammation occurs during continuing challenges.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batra K. V., Elrod L. M., Schrek R. Species differences in the in vitro sensitivity of lymphocytes to prednisolone and x-rays. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Jun;152(3):525–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertelsen S., Malmstrom J., Heerfordt J., Pedersen H. Tumours of the thymic region. Symptomatology, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Thorax. 1975 Feb;30(1):19–25. doi: 10.1136/thx.30.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claman H. N. Corticosteroids and lymphoid cells. N Engl J Med. 1972 Aug 24;287(8):388–397. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197208242870806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMANUEL D. A., WENZEL F. J., BOWERMAN C. I., LAWTON B. R. FARMER'S LUNG: CLINICAL, PATHOLOGIC AND IMMUNOLOGIC STUDY OF TWENTY-FOUR PATIENTS. Am J Med. 1964 Sep;37:392–401. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90195-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. H., Fink J. N., Lyman S., Pedersen G. Immunoregulation in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. I. Differences in T-cell and macrophage suppressor activity in symptomatic and asymptomatic pigeon breeders. J Clin Immunol. 1982 Jan;2(1):46–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00915978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore V. L., Pedersen G. M., Hauser W. C., Fink J. N. A study of lung lavage materials in patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis: in vitro response to mitogen and antigen in pigeon breeders' disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1980 May;65(5):365–370. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(80)90214-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mönkäre S., Ikonen M., Haahtela T. Radiologic findings in farmer's lung. Prognosis and correlation to lung function. Chest. 1985 Apr;87(4):460–466. doi: 10.1378/chest.87.4.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richerson H. B., Seidenfeld J. J., Ratajczak H. V., Richards D. W. Chronic experimental interstitial pneumonitis in the rabbit. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jan;117(1):5–13. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMMONS S. C. Recurrent jaundice in pregnancy. Lancet. 1963 Jul 13;2(7298):60–61. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuyler M. R., Kleinerman J., Pensky J. R., Brandt C., Schmitt D. Pulmonary response to repeated exposure to Micropolyspora faeni. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Dec;128(6):1071–1076. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.6.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuyler M. R., Schmitt D. Experimental hypersensitivity pneumonitis: lack of tolerance. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Nov;130(5):772–777. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.5.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuyler M. R., Steinberg D. Activated alveolar macrophages: IgG and complement receptors. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Dec;100(6):932–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seal R. M., Hapke E. J., Thomas G. O., Meek J. C., Hayes M. The pathology of the acute and chronic stages of farmer's lung. Thorax. 1968 Sep;23(5):469–489. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.5.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willoughby J. B., Willoughby W. F. In vivo responses to inhaled proteins. I. Quantitative analysis of antigen uptake, fate, and immunogenicity in a rabbit model system. J Immunol. 1977 Dec;119(6):2137–2146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]










