Abstract
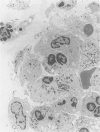
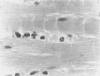
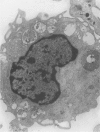
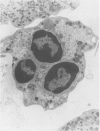
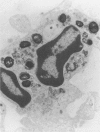
Plant pathologists have known for several years that intracellular Mollicutes (M), i.e. cell wall deficient bacteria, are plant vascular pathogens, but because those M are non-cultivatable, they can only be studied by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM). Only recently have similar M been shown to be human and animal pathogens. Those human ocular Vasculitis (V) and mouse chronic ocular and lethal systemic V producing M parasitize vitreous polymorphonuclear leucocytes, lymphocytes, and monocytes as 'viral-like' 0.005-0.010 micron elemental particles which grow within the leucocyte into 0.01-0.03 micron diameter tubules, 0.3-1.5 micron spherules, and distinctive 0.5-0.7 micron cocci with spore-like cell walls. This report describes the 48 arteriolar and capillary sized V, Aschoff nodules, valvulitis, and myocytolytic lesions in the heart and great vessels in 18 of 100 human vitreous VM containing eyelid inoculated mice versus 0 of 200 controls (P less than 0.05) plus VM within parasitized leucocytes in 15 of 15 of those lesions by TEM. The results indicate dissemination of VM from the eyelid to produce a significant incidence of distinctive multifocal VM directly induced cardiovascular micro-V lesions that probably contributed to their excessive mortality. Because several human idiopathic diseases develop similar cardiovascular lesions a TEM search for VM parasitized leucocytes in those human diseases seems justified.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Johnson L. A., Wirostko E. Chronic idiopathic vitritis. Ultrastructural properties of bacteria-like bodies within vitreous leukocyte phagolysosomes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Jul;86(1):19–24. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/86.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]