Abstract
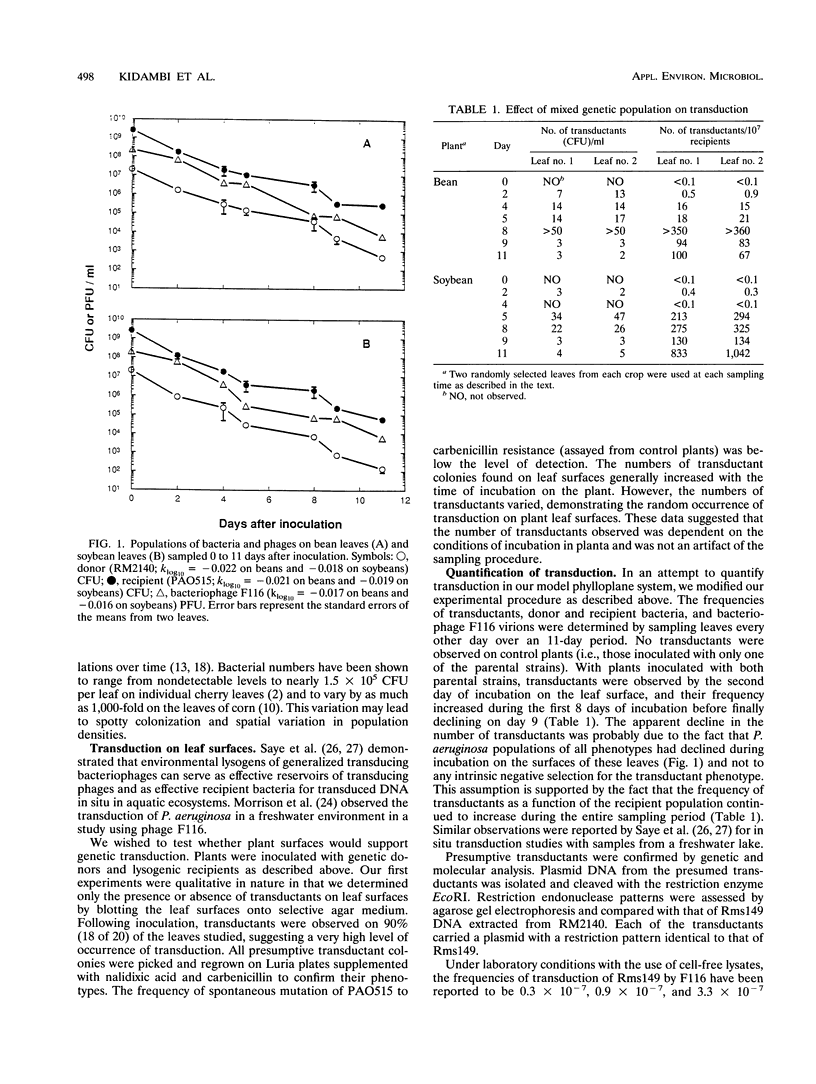
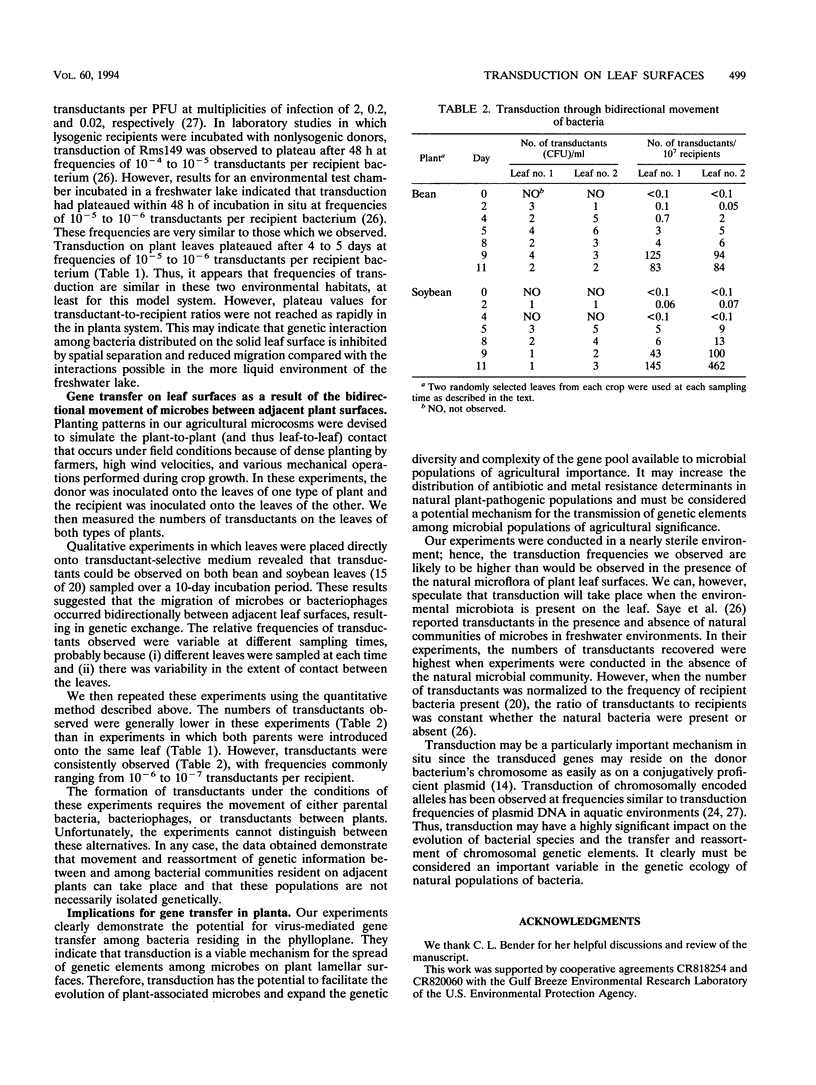
As the use of genetically engineered microorganisms for agricultural tasks becomes more frequent, the ability of bacteria to exchange genetic material in the agricultural setting must be assessed. Transduction (bacterial virus-mediated horizontal gene transfer) is a potentially important mechanism of gene transfer in natural environments. This study investigated the potential of plant leaves to act as surfaces on which transduction can take place among microorganisms. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its generalized transducing bacteriophage F116 were used as a model system. The application of P. aeruginosa lysogens of F116 to plant leaves resulted in genetic exchange among donor and recipient organisms resident on the same plant. Transduction was also observed when these bacterial strains were inoculated onto adjacent plants and contact was made possible through high-density planting.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Eisenstark A. Bacterial genes involved in response to near-ultraviolet radiation. Adv Genet. 1989;26:99–147. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60224-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germida J. J., Khachatourians G. G. Transduction of Escherichia coli in soil. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Feb;34(2):190–193. doi: 10.1139/m88-035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano S. S., Nordheim E. V., Arny D. C., Upper C. D. Lognormal distribution of epiphytic bacterial populations on leaf surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):695–700. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.695-700.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W. Genetics of Pseudomonas. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Sep;33(3):419–443. doi: 10.1128/br.33.3.419-443.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Morgan A. F. Genome organization in Pseudomonas. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:79–105. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaku S. Analysis of freezing temperature distribution in plants. Cryobiology. 1975 Apr;12(2):154–159. doi: 10.1016/s0011-2240(75)80007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnapillai V. A novel transducing phage. Its role in recognition of a possible new host-controlled modification system in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(2):134–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00332784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindow S. E., Arny D. C., Upper C. D. Distribution of ice nucleation-active bacteria on plants in nature. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):831–838. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.831-838.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Ku C. M. Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants deficient in the establishment of lysogeny. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):875–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.875-883.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Pemberton J. M., Richards K. E. F116, D3 and G101: temperate bacteriophages of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Virology. 1974 Jun;59(2):566–569. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90466-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison W. D., Miller R. V., Sayler G. S. Frequency of F116-mediated transduction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a freshwater environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Nov;36(5):724–730. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.5.724-730.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saye D. J., Ogunseitan O. A., Sayler G. S., Miller R. V. Transduction of linked chromosomal genes between Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains during incubation in situ in a freshwater habitat. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jan;56(1):140–145. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.1.140-145.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saye D. J., Ogunseitan O., Sayler G. S., Miller R. V. Potential for transduction of plasmids in a natural freshwater environment: effect of plasmid donor concentration and a natural microbial community on transduction in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):987–995. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.987-995.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



