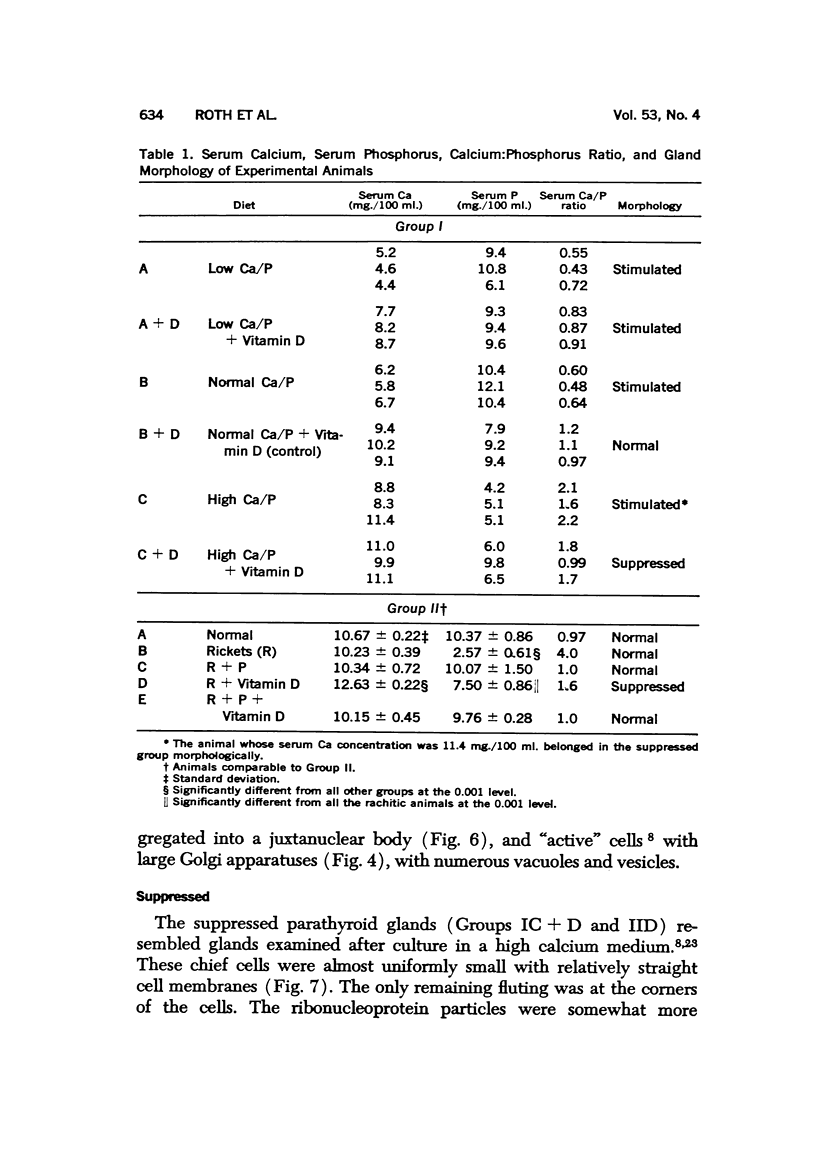
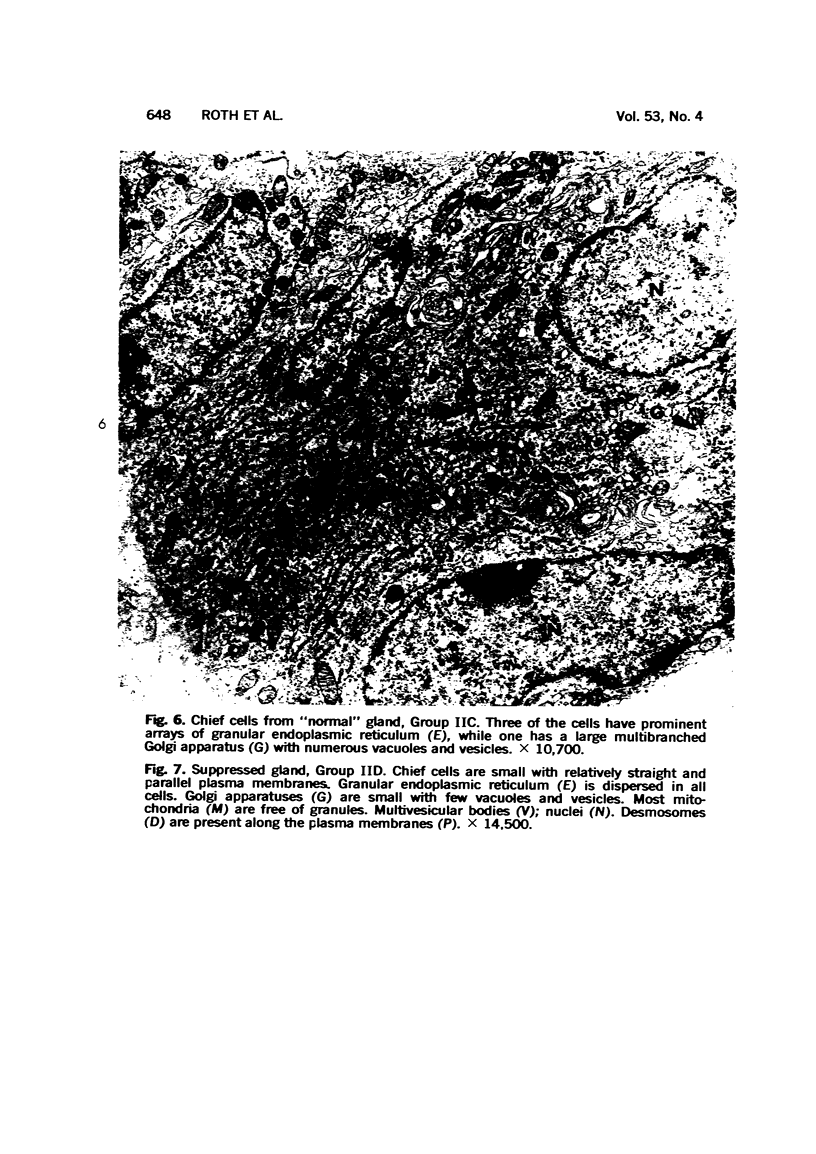
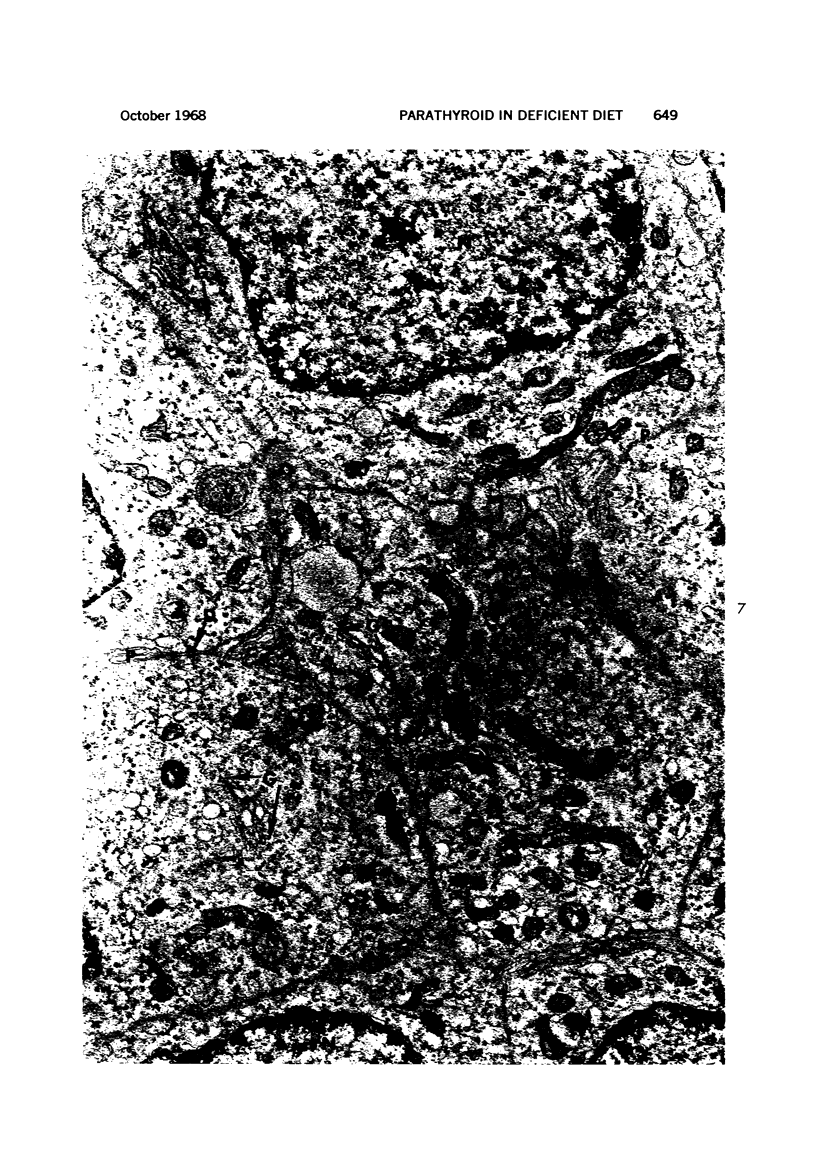
Full text
PDF
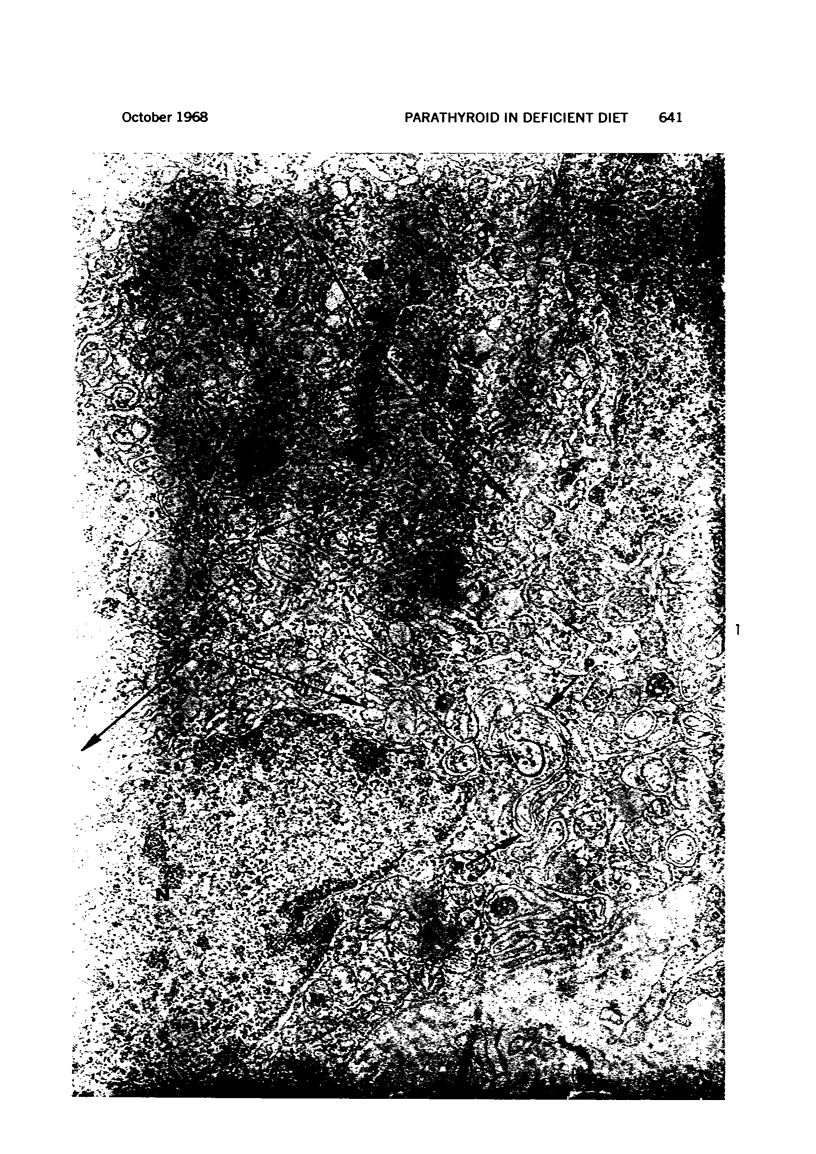
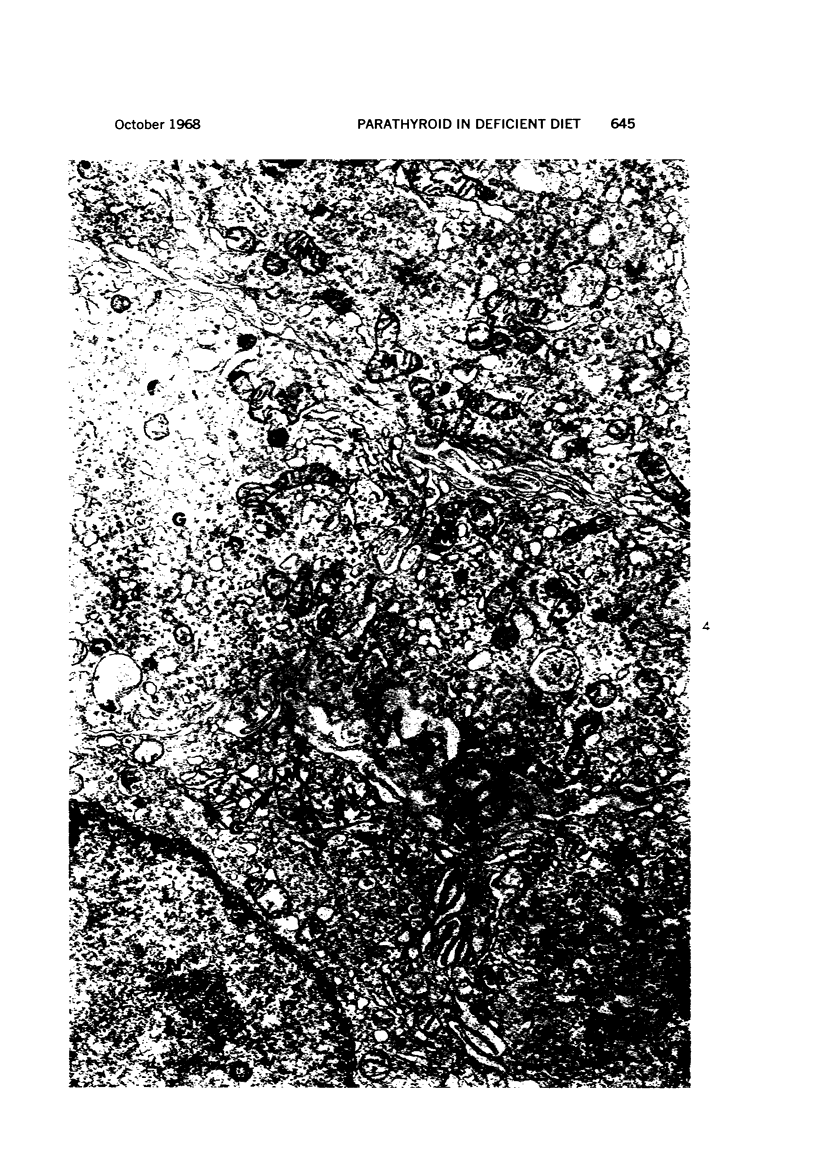
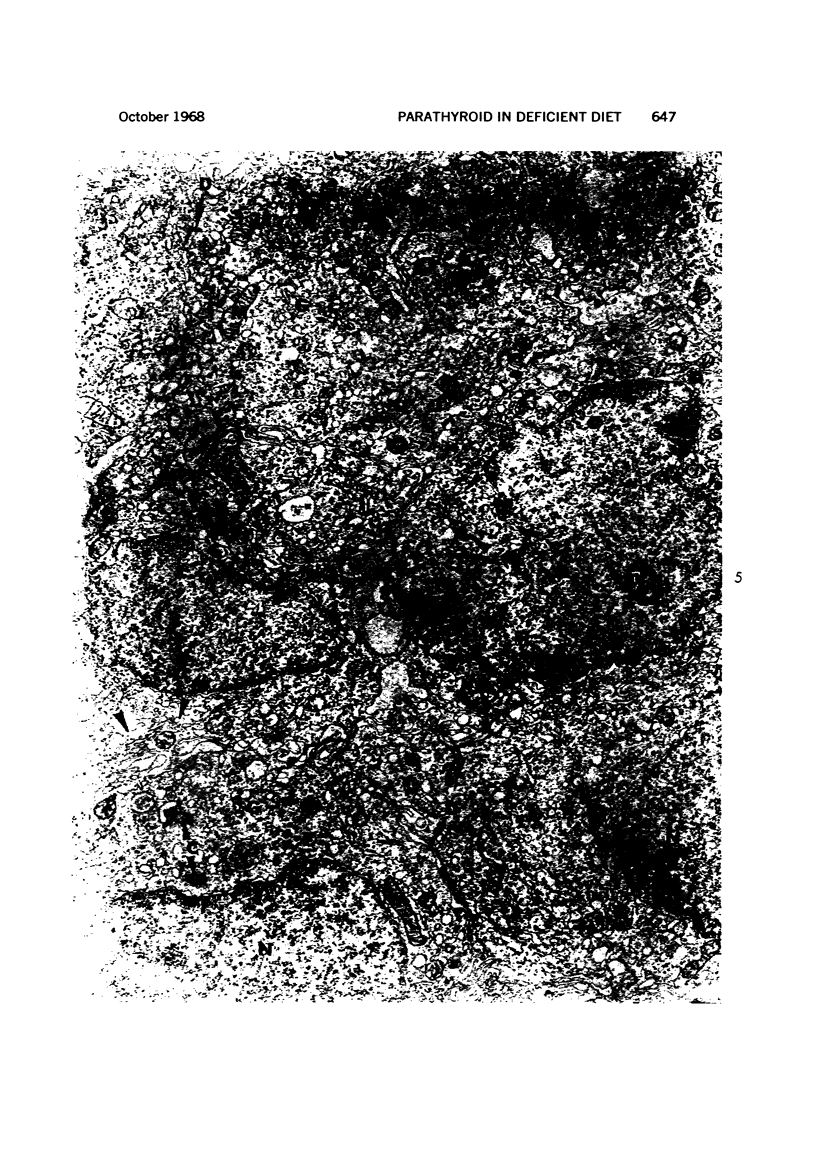
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Au W. Y., Raisz L. G. Effect of vitamin D and dietary calcium on parathyroid activity. Am J Physiol. 1965 Sep;209(3):637–642. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.3.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEALE R. N., BOSTROM J. O. Sensitive methods for the titrimetric microdetermination of biological calcium and magnesium. J Clin Pathol. 1963 May;16:252–255. doi: 10.1136/jcp.16.3.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD J. D., GRIBETZ D., DINER W. C., HURST P., CASTLEMAN B. The influence of vitamin D on parathyroid activity and the metabolism of calcium and citrate during calcium deprivation. Endocrinology. 1957 Jul;61(1):59–71. doi: 10.1210/endo-61-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capen C. C., Cole C. R., Hibbs J. W. Influence of vitamin D on calcium metabolism and the parathyroid glands of cattle. Fed Proc. 1968 Jan-Feb;27(1):142–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capen C. C., Koestner A., Cole C. R. The ultrastructure and histochemistry of normal parathyroid glands of pregnant and nonpregnant cows. Lab Invest. 1965 Sep;14(9):1673–1690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capen C. C., Koestner A., Cole C. R. The ultrastructure, histopathology, and histochemistry of the parathyroid glands of pregnant and non-pregnant cows fed a high level of vitamin D. Lab Invest. 1965 Oct;14(10):1809–1825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capen C. C., Young D. M. The ultrastructure of the parathyroid glands and thyroid parafollicular cells of cows with parturient paresis and hypocalcemia. Lab Invest. 1967 Dec;17(6):717–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortelyou J. R., McWhinnie D. J. Parathyroid glands of amphibians. I. Parathyroid structure and function in the amphibian, with emphasis on regulation of mineral ions in body fluids. Am Zool. 1967 Nov;7(4):843–855. doi: 10.1093/icb/7.4.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON H. E., HARRISON H. C. The uptake of radiocalcium by the skeleton: the effect of vitamin D and calcium intake. J Biol Chem. 1950 Aug;185(2):857–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ham A. W., Littner N., Drake T. G., Robertson E. C., Tisdall F. F. Physiological hypertrophy of the parathyroids, its cause and its relation to rickets. Am J Pathol. 1940 May;16(3):277–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNGER B. L., ROTH S. I. The cytology of the normal parathyroid glands of man and Virginia deer; a light and electron microscopic study with morphologic evidence of secretory activity. J Cell Biol. 1963 Feb;16:379–400. doi: 10.1083/jcb.16.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagami K. Comparative electron microscopic studies of the parathyroid glands. II. Fine structure of the parathyroid gland of the normal and the calcium chloride treated mouse. Arch Histol Jpn. 1967 Apr;28(2):185–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALADE G. E. A study of fixation for electron microscopy. J Exp Med. 1952 Mar;95(3):285–298. doi: 10.1084/jem.95.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH S. I., MUNGER B. L. The cytology of the adenomatous, atrophic, and hyperplastic parathyroid glands of man. A light- and electron-microscopic study. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med. 1962;335:389–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00957031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH S. I., RAISZ L. G. EFFECT OF CALCIUM CONCENTRATION ON THE ULTRASTRUCTURE OF RAT PARATHYROID IN ORGAN CULTURE. Lab Invest. 1964 Apr;13:331–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. C. An electron microscope study of the parathyroid gland of the frog (Rana clamitans). J Ultrastruct Res. 1965 Dec;13(5):478–499. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(65)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth S. I., Raisz L. G. The course and reversibility of the calcium effect on the ultrastructure of the rat parathyroid gland in organ culture. Lab Invest. 1966 Jul;15(7):1187–1211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckel M. E., Porte A. Observations ultrastructurales sur la parathyroide de souris. II. Etude expérimentale. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1966 Aug 22;73(4):503–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoeckel M. E., Porte A. Observations ultrastructurales sur la parathyroïde de souris. I. Etude chez la souris normale. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1966 Aug 22;73(4):488–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON M. L. Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):475–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]