Abstract
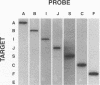
Oligodeoxynucleotide hybridization probes were developed to complement specific regions of the small subunit (SSU) rRNA sequences of cultivated and uncultivated cyanobacteria and Chloroflexus-like bacteria, which inhabit hot spring microbial mats. The probes were used to investigate the natural distribution of SSU rRNAs from these species in mats of Yellowstone hot springs of different temperatures and pHs as well as changes in SSU rRNA distribution resulting from 1-week in situ shifts in temperature, pH, and light intensity. Synechococcus lividus Y-7c-s SSU rRNA was detected only in the mat of a slightly acid spring, from which it may have been initially isolated, or when samples from a more alkaline spring were incubated in the more acid spring. Chloroflexus aurantiacus Y-400-fl SSU rRNA was detected only in a high-temperature mat sample from the alkaline Octopus Spring or when lower-temperature samples from this mat were incubated at the high-temperature site. SSU rRNAs of uncultivated species were more widely distributed. Temperature distributions and responses to in situ temperature shifts suggested that some of the uncultivated cyanobacteria might be adapted to high-, moderate-, and low-temperature ranges whereas an uncultivated Chloroflexus-like bacterium appears to have broad temperature tolerance. SSU rRNAs of all uncultivated species inhabiting a 48 to 51 degrees C Octopus Spring mat site were most abundant in the upper 1 mm and were not detected below a 2.5-to 3.5-mm depth, a finding consistent with their possible phototrophic nature. However, the effects of light intensity reduction on these SSU rRNAs were variable, indicating the difficulty of demonstrating a phototrophic phenotype in light reduction experiments.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bateson M. M., Ward D. M. Photoexcretion and fate of glycolate in a hot spring cyanobacterial mat. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1738–1743. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1738-1743.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D. Lower pH limit for the existence of blue-green algae: evolutionary and ecological implications. Science. 1973 Feb 2;179(4072):480–483. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4072.480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D. Micro-organisms adapted to high temperatures. Nature. 1967 May 27;214(5091):882–885. doi: 10.1038/214882a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong E. F., Wickham G. S., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic stains: ribosomal RNA-based probes for the identification of single cells. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2466341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doemel W. N., Brock T. D. Structure, growth, and decomposition of laminated algal-bacterial mats in alkaline hot springs. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Oct;34(4):433–452. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.4.433-452.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman J. A., McCallum K., Davis A. A. Phylogenetic diversity of subsurface marine microbial communities from the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 May;59(5):1294–1302. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.5.1294-1302.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., Britschgi T. B., Moyer C. L., Field K. G. Genetic diversity in Sargasso Sea bacterioplankton. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):60–63. doi: 10.1038/345060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Weiser B., Woese C. R., Noller H. F. Comparative anatomy of 16-S-like ribosomal RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:155–216. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60348-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallas T., Castenholz R. W. Internal pH and ATP-ADP pools in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. during exposure to growth-inhibiting low pH. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):229–236. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.229-236.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liesack W., Stackebrandt E. Occurrence of novel groups of the domain Bacteria as revealed by analysis of genetic material isolated from an Australian terrestrial environment. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):5072–5078. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.5072-5078.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madigan M. T., Brock T. D. Adaptation by hot spring phototrophs to reduced light intensities. Arch Microbiol. 1977 May 13;113(1-2):111–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00428590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierzwicki-Bauer S. A., Gebhardt J. S., Linkkila L., Walsh K. A comparison of UV cross-linking and vacuum baking for nucleic acid immobilization and retention. Biotechniques. 1990 Oct;9(4):472–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revsbech N. P., Ward D. M. Microelectrode studies of interstitial water chemistry and photosynthetic activity in a hot spring microbial mat. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):270–275. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.270-275.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson L. L., Castenholz R. W. Enhanced Survival of the Cyanobacterium Oscillatoria terebriformis in Darkness under Anaerobic Conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2151–2158. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2151-2158.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. M., DeLong E. F., Pace N. R. Analysis of a marine picoplankton community by 16S rRNA gene cloning and sequencing. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4371–4378. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4371-4378.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D. A., Flesher B., Mansfield H. R., Montgomery L. Use of phylogenetically based hybridization probes for studies of ruminal microbial ecology. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 May;54(5):1079–1084. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.5.1079-1084.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. M., Weller R., Bateson M. M. 16S rRNA sequences reveal numerous uncultured microorganisms in a natural community. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):63–65. doi: 10.1038/345063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. M., Weller R., Bateson M. M. 16S rRNA sequences reveal uncultured inhabitants of a well-studied thermal community. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;6(2-3):105–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller R., Bateson M. M., Heimbuch B. K., Kopczynski E. D., Ward D. M. Uncultivated cyanobacteria, Chloroflexus-like inhabitants, and spirochete-like inhabitants of a hot spring microbial mat. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Dec;58(12):3964–3969. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.12.3964-3969.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller R., Weller J. W., Ward D. M. 16S rRNA sequences of uncultivated hot spring cyanobacterial mat inhabitants retrieved as randomly primed cDNA. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1146-1151.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]