Abstract
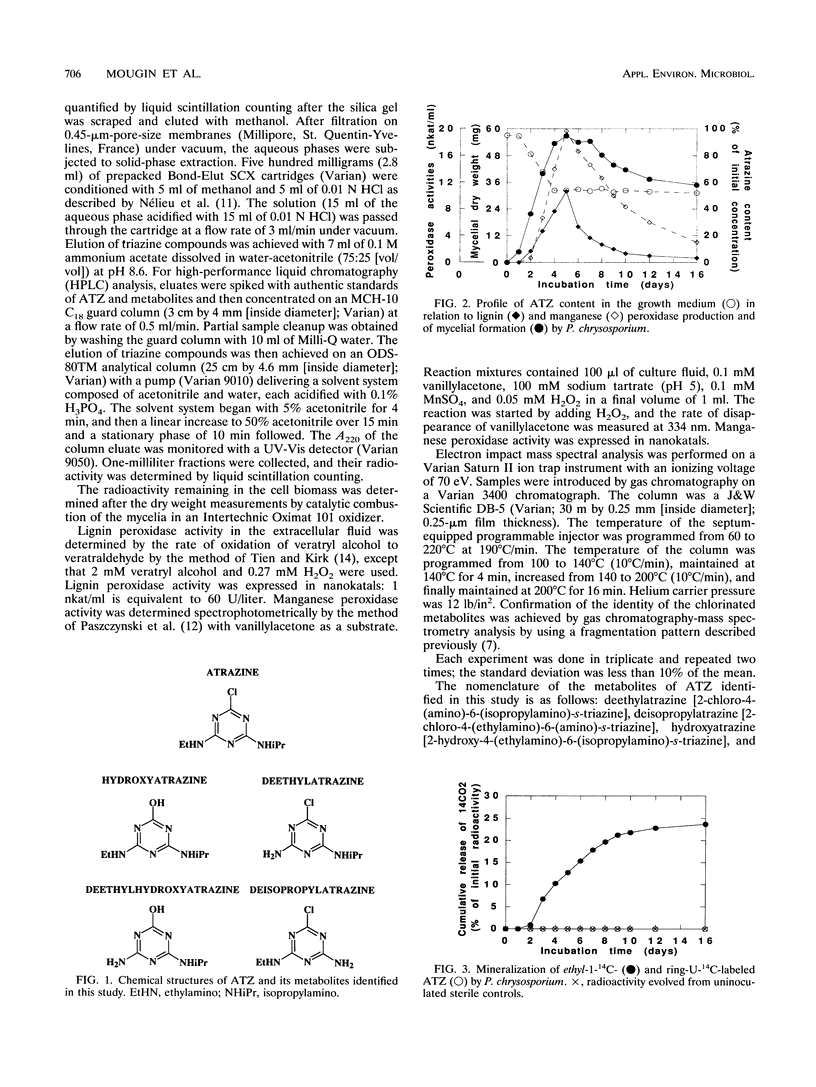
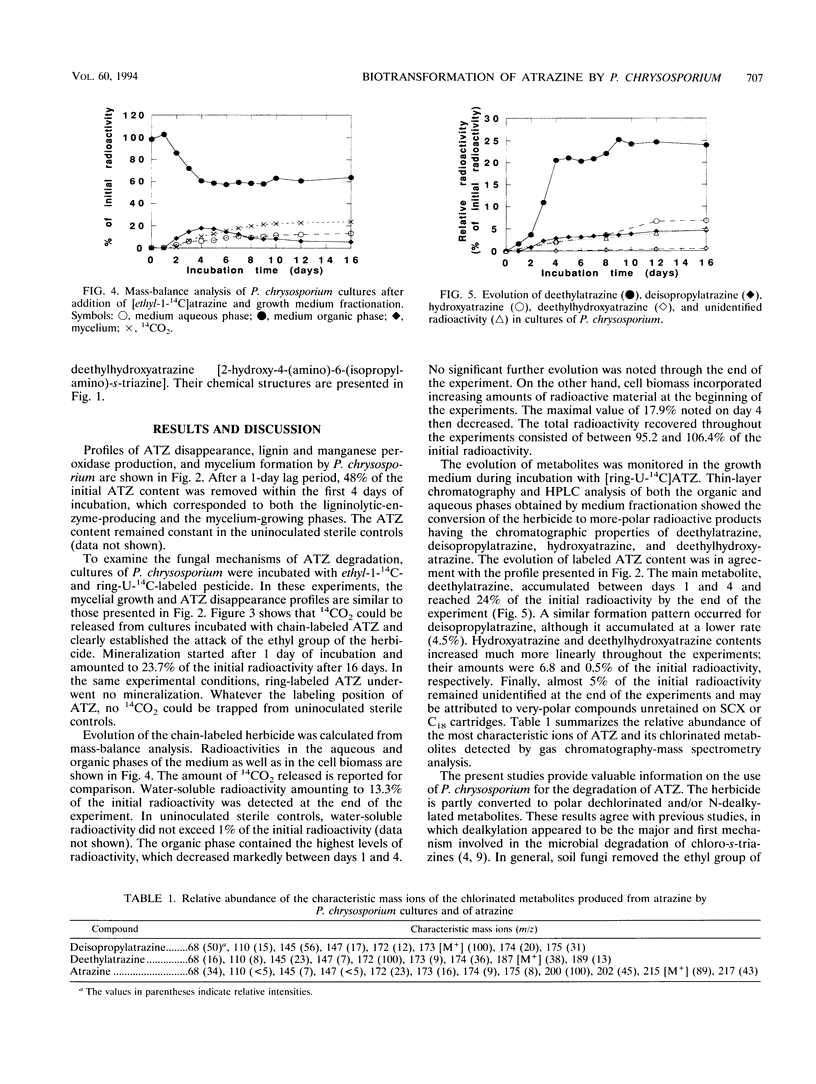
Biotransformation of atrazine by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium was demonstrated by a 48% decrease of the initial herbicide concentration in the growth medium within the first 4 days of incubation, which corresponded to the mycelium-growing phase. Results clearly established the mineralization of the ethyl group of the herbicide. Analysis of the growth medium showed the formation of hydroxylated and/or N-dealkylated metabolites of atrazine during fungal degradation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Capdevila C., Moukha S., Ghyczy M., Theilleux J., Gelie B., Delattre M., Corrieu G., Asther M. Characterization of Peroxidase Secretion and Subcellular Organization of Phanerochaete chrysosporium INA-12 in the Presence of Various Soybean Phospholipid Fractions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Dec;56(12):3811–3816. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.12.3811-3816.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. D., Kearney P. C. Microbial degradation of s-triazine herbicides. Residue Rev. 1970;32:235–265. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-8464-3_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paszczyński A., Huynh V. B., Crawford R. Comparison of ligninase-I and peroxidase-M2 from the white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Feb 1;244(2):750–765. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90644-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien M., Kirk T. K. Lignin-degrading enzyme from Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Purification, characterization, and catalytic properties of a unique H(2)O(2)-requiring oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2280–2284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



