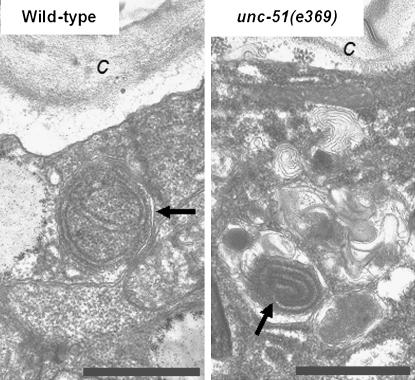
Figure 2.—
The autophagic process appears to be defective in unc-51 mutant animals. (Left) Autophagic vacuole with normal double isolation membrane (arrow) in the hypodermis from a wild-type animal. (Right) Abnormal autophagic vacuole (arrow) with strongly myelinated isolation membrane is embedded in a region of the cytoplasm abundant in membrane whorls in a hypodermal seam cell from unc51(e369) mutant. c, cuticule; bars, 1 μm. For fixation and embedding of transmission electron microscopic samples, the nematodes were treated individually. They were cut open under a dissecting microscope in a drop of fixative composed of 0.2% glutaraldehyde and 3.2% formaldehyde in 0.15 m cacodylate buffer. After an overnight fixation at 4°, the fixative was changed to washing buffer (0.1 m cacodylate buffer), and the samples were embedded in agar, post-fixed with 0.5% cacodylate-buffered OsO4, stained with 2% uranyl acetate, dehydrated in ethanol and propylene oxide, and embedded in Durcupan (Fluka Chemical, Buchs, Switzerland). Thereafter the samples were cut along the longitudinal body axis with Reichert-Jung Ultracut-E type ultramicrotome, stained with lead citrate, and examined in a JEM100CX II electron microscope.