Abstract
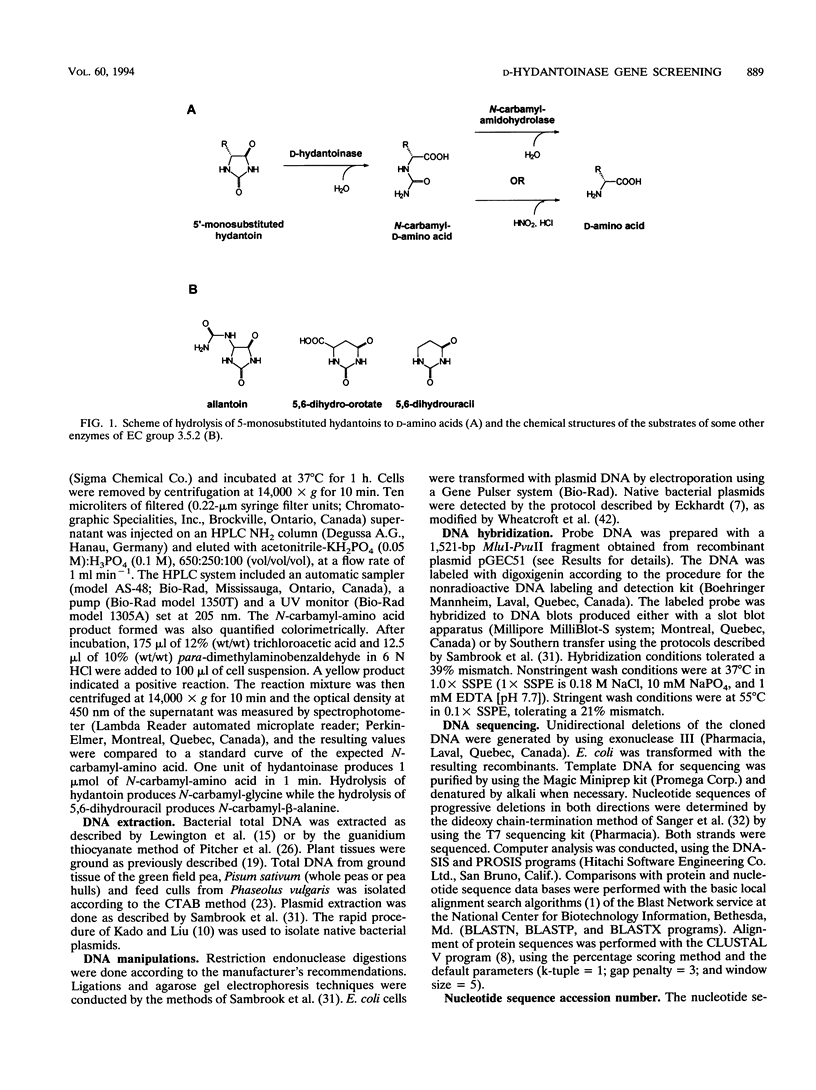
Pseudomonas putida DSM 84 produces N-carbamyl-D-amino acids from the corresponding D-5-monosubstituted hydantoins. The gene encoding this D-hydantoinase enzyme was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. The nucleotide sequence of the 1.8-kb insert of subclone pGES19 was determined. One open reading frame of 1,104 bp was found and was predicted to encode a polypeptide with a molecular size of 40.5 kDa. Local regions of identity between the predicted amino acid sequence and that of other known amidohydrolases (two other D-hydantoinases, allantionase and dihydroorotase) were found. The D-hydantoinase gene was used as a probe to screen DNA isolated from diverse organisms. Within Pseudomonas strains of rRNA group I, the probe was specific. The probe did not detect D-hydantoinase genes in pseudomonads not in rRNA group I, other bacteria, or plants known to express D-hydantoinase activity.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckholz R. G., Cooper T. G. The allantoinase (DAL1) gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1991 Dec;7(9):913–923. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. N., Chen K. C., Jamison R. S., Musmanno L. A., Kern C. B. The evolutionary history of the first three enzymes in pyrimidine biosynthesis. Bioessays. 1993 Mar;15(3):157–164. doi: 10.1002/bies.950150303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley K. H., Butler T. C., Bius D. L. The role of dihydropyrimidinase in the metabolism of some hydantoin and succinimide drugs. Drug Metab Dispos. 1974 Mar-Apr;2(2):103–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt T. A rapid method for the identification of plasmid desoxyribonucleic acid in bacteria. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):584–588. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. Fast and sensitive multiple sequence alignments on a microcomputer. Comput Appl Biosci. 1989 Apr;5(2):151–153. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/5.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., West T. P. Pyrimidine catabolism in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jan 15;61(2-3):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90547-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaPointe G., Nautiyal C. S., Chilton W. S., Farrand S. K., Dion P. Spontaneous mutation conferring the ability to catabolize mannopine in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2631–2639. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2631-2639.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazuś B., Buchowicz J. Dihydropyrimidinase of pea plants: purification and properties. Acta Biochim Pol. 1968;15(4):327–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore L., Warren G., Strobel G. Involvement of a plasmid in the hairy root disease of plants caused by Agrobacterium rhizogenes. Plasmid. 1979 Oct;2(4):617–626. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G., Thompson W. F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4321–4325. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runser S. M., Meyer P. C. Purification and biochemical characterization of the hydantoin hydrolyzing enzyme from Agrobacterium species. A hydantoinase with no 5,6-dihydropyrimidine amidohydrolase activity. Eur J Biochem. 1993 May 1;213(3):1315–1324. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvi R. J., Ahroon W., Saunders S. S., Arnold S. A. Evoked potentials: computer-automated threshold-tracking procedure using an objective detection criterion. Ear Hear. 1987 Jun;8(3):151–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogels G. D., Van der Drift C. Degradation of purines and pyrimidines by microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Jun;40(2):403–468. doi: 10.1128/br.40.2.403-468.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watabe K., Ishikawa T., Mukohara Y., Nakamura H. Cloning and sequencing of the genes involved in the conversion of 5-substituted hydantoins to the corresponding L-amino acids from the native plasmid of Pseudomonas sp. strain NS671. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):962–969. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.962-969.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watabe K., Ishikawa T., Mukohara Y., Nakamura H. Identification and sequencing of a gene encoding a hydantoin racemase from the native plasmid of Pseudomonas sp. strain NS671. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3461–3466. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3461-3466.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West T. P. Pyrimidine base and ribonucleoside catabolic enzyme activities of the Pseudomonas diminuta group. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Dec 1;78(2-3):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90045-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West T. P. Pyrimidine base and ribonucleoside utilization by the Pseudomonas alcaligenes group. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1991 May;59(4):263–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00583679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]