Abstract
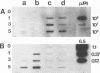
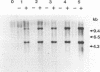
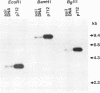
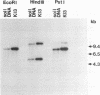
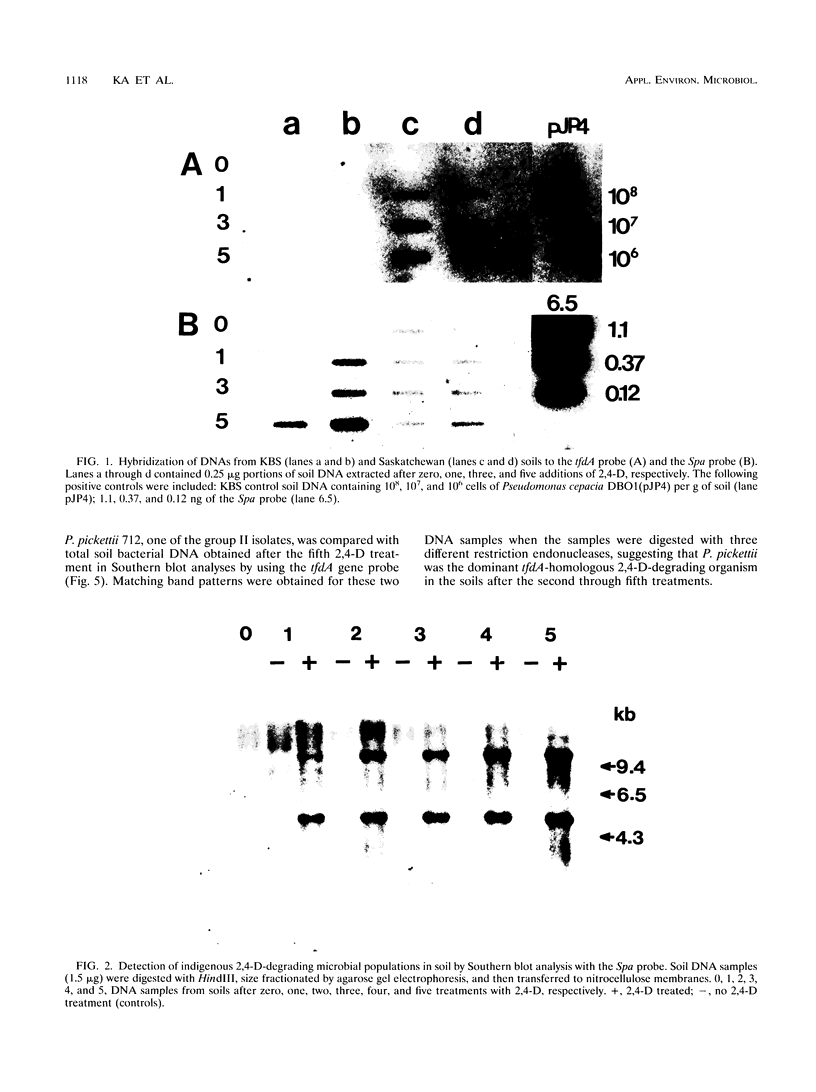
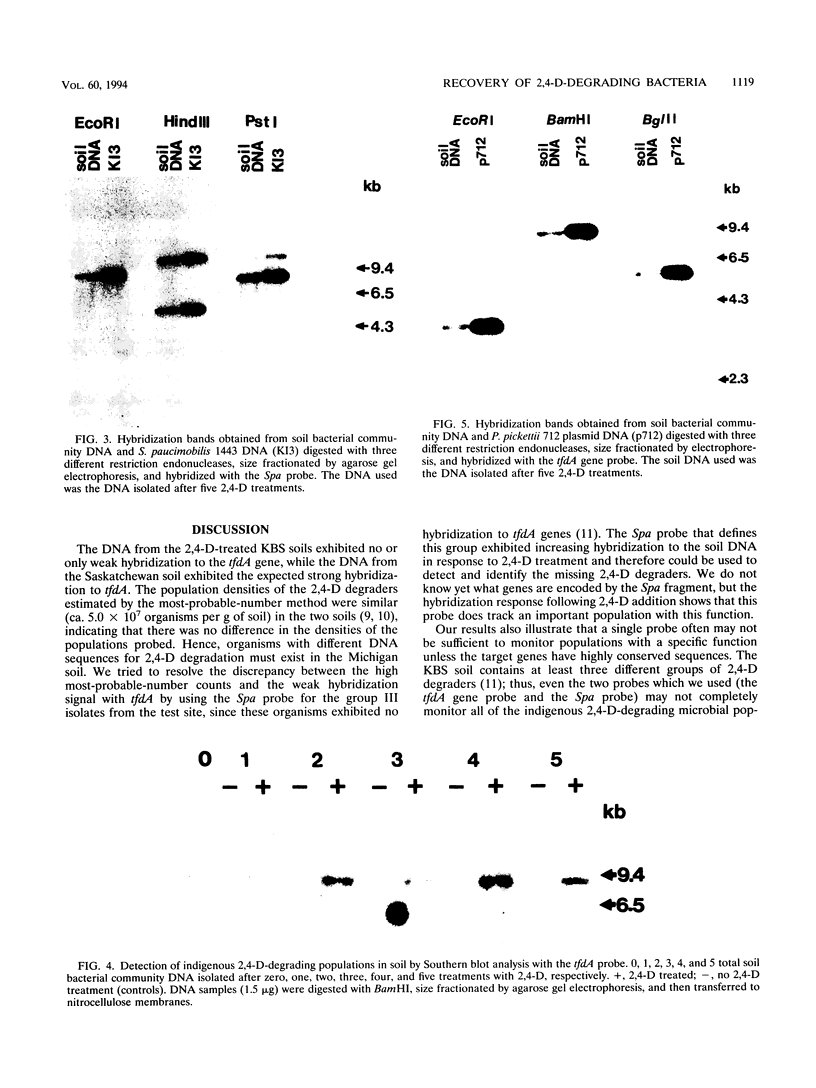
The herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) was applied to soils in microcosms, and degradation was monitored after each of five repeated additions. Total DNAs were isolated from soil bacterial communities after each 2,4-D treatment. The DNA samples were analyzed on slot blots and Southern blots by using a tfdA gene probe subcloned from plasmid pJP4 and a Spa probe derived from a different 2,4-D-degrading isolate, a Sphingomonas paucimobilis strain. 2,4-D applied to soil was quickly degraded by indigenous microbial populations. As determined by slot blot analyses of DNA from a Michigan soil, the increase in hybridization signal in response to 2,4-D treatments was greater with the Spa probe than with the tfdA probe. In contrast, the DNA from a Saskatchewan soil exhibited an increase in hybridization signal with the tfdA probe. This indicated that a population with 2,4-D-degradative gene sequences different from the tfdA gene sequence was dominant in the Michigan site, but not in the Saskatchewan site. A Southern blot analysis of DNA from Michigan soil showed that the dominant 2,4-D-degrading population was S. paucimobilis 1443. A less dominant 2,4-D-degrading population was detected with the tfdA probe; further analysis revealed that this population was a Pseudomonas pickettii 712. These gene probe analyses revealed that an important population carrying out 2,4-D degradation was not detected when the canonical tfdA gene probe was used. After a series of new strains were isolated, we identified a probe to detect and identify the dominant members of this new group.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amy P. S., Schulke J. W., Frazier L. M., Seidler R. J. Characterization of aquatic bacteria and cloning of genes specifying partial degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1237–1245. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1237-1245.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Pemberton J. M. Genetic and physical map of the 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-degradative plasmid pJP4. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):466–468. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.466-468.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harker A. R., Olsen R. H., Seidler R. J. Phenoxyacetic acid degradation by the 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (TFD) pathway of plasmid pJP4: mapping and characterization of the TFD regulatory gene, tfdR. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):314–320. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.314-320.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holben W. E., Schroeter B. M., Calabrese V. G., Olsen R. H., Kukor J. K., Biederbeck V. O., Smith A. E., Tiedje J. M. Gene probe analysis of soil microbial populations selected by amendment with 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Dec;58(12):3941–3948. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.12.3941-3948.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holben William E., Jansson Janet K., Chelm Barry K., Tiedje James M. DNA Probe Method for the Detection of Specific Microorganisms in the Soil Bacterial Community. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):703–711. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.703-711.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ka J. O., Holben W. E., Tiedje J. M. Genetic and phenotypic diversity of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D)-degrading bacteria isolated from 2,4-D-treated field soils. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Apr;60(4):1106–1115. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.4.1106-1115.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai Y. L., Olson B. H. Effects of Hg, CH(3)-Hg, and Temperature on the Expression of Mercury Resistance Genes in Environmental Bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3266–3272. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3266-3272.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]