Abstract
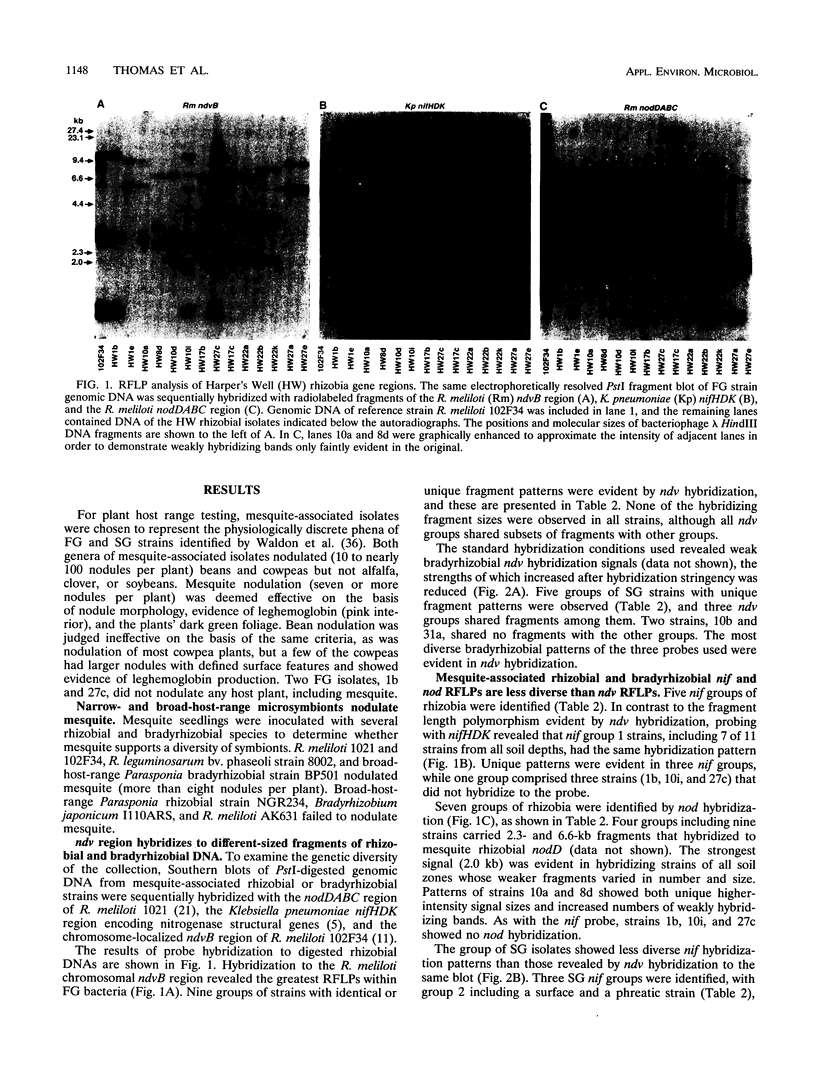
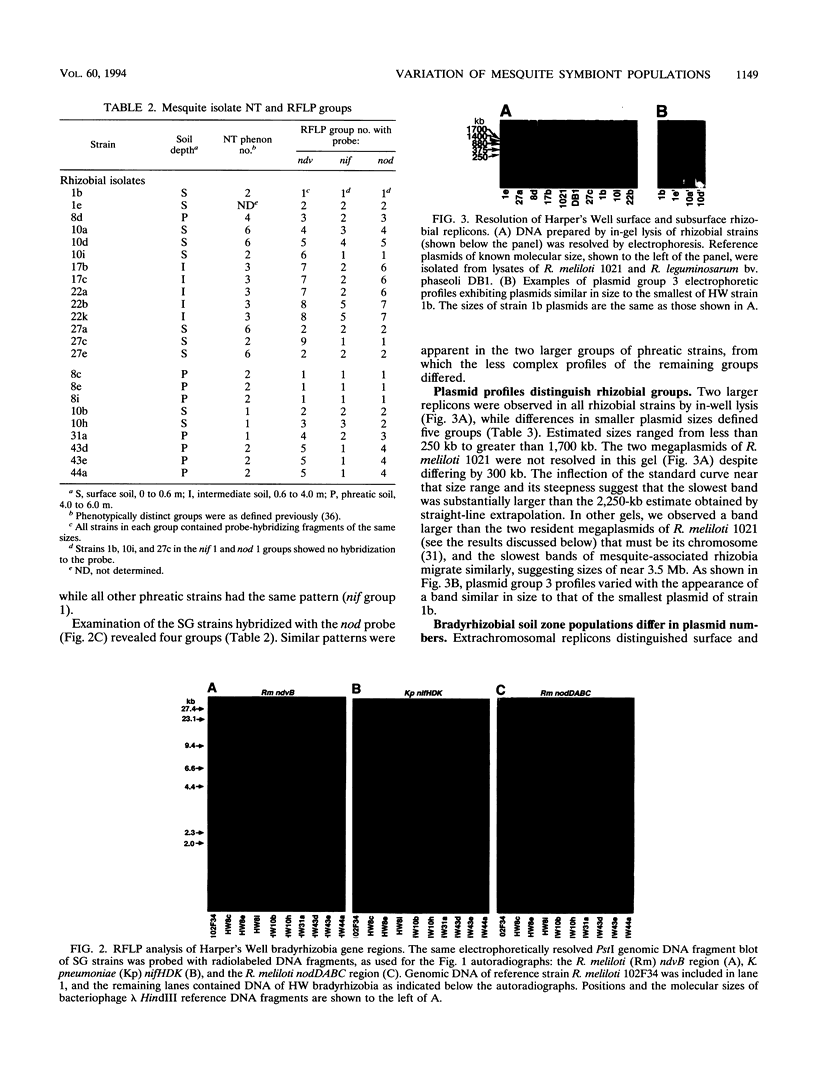
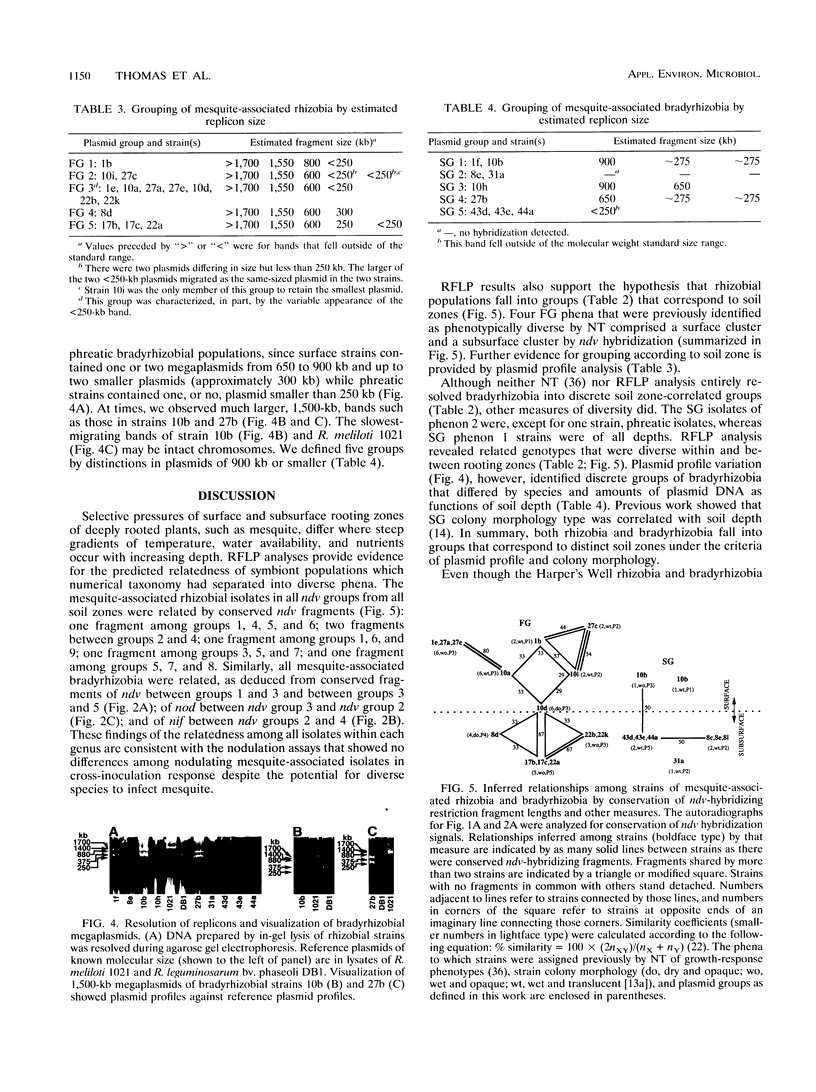
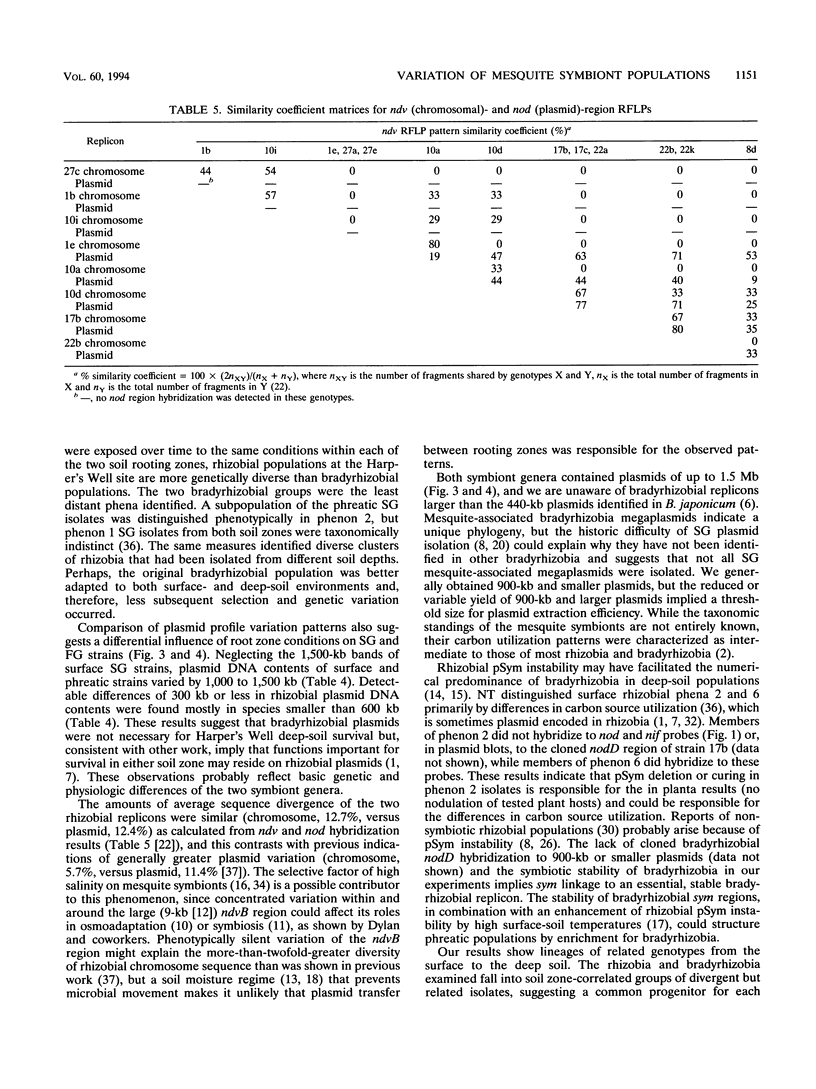
Genetic characteristics of 14 Rhizobium and 9 Bradyrhizobium mesquite (Prosopis glandulosa)-nodulating strains isolated from surface (0- to 0.5-m) and deep (4- to 6-m) rooting zones were determined in order to examine the hypothesis that surface- and deep-soil symbiont populations were related but had become genetically distinct during adaptation to contrasting soil conditions. To examine genetic diversity, Southern blots of PstI-digested genomic DNA were sequentially hybridized with the nodDABC region of Rhizobium meliloti, the Klebsiella pneumoniae nifHDK region encoding nitrogenase structural genes, and the chromosome-localized ndvB region of R. meliloti. Plasmid profile and host plant nodulation assays were also made. Isolates from mesquite nodulated beans and cowpeas but not alfalfa, clover, or soybeans. Mesquite was nodulated by diverse species of symbionts (R. meliloti, Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. phaseoli, and Parasponia bradyrhizobia). There were no differences within the groups of mesquite-associated rhizobia or bradyrhizobia in cross-inoculation response. The ndvB hybridization results showed the greatest genetic diversity among rhizobial strains. The pattern of ndvB-hybridizing fragments suggested that surface and deep strains were clonally related, but groups of related strains from each soil depth could be distinguished. Less variation was found with nifHDK and nodDABC probes. Large plasmids (>1,500 kb) were observed in all rhizobia and some bradyrhizobia. Profiles of plasmids of less than 1,000 kb were related to the soil depth and the genus of the symbiont. We suggest that interacting selection pressures for symbiotic competence and free-living survival, coupled with soil conditions that restrict genetic exchange between surface and deep-soil populations, led to the observed patterns of genetic diversity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldani J. I., Weaver R. W., Hynes M. F., Eardly B. D. Utilization of carbon substrates, electrophoretic enzyme patterns, and symbiotic performance of plasmid-cured clover rhizobia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jul;58(7):2308–2314. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.7.2308-2314.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockman F. J., Bezdicek D. F. Diversity within Serogroups of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viceae in the Palouse Region of Eastern Washington as Indicated by Plasmid Profiles, Intrinsic Antibiotic Resistance, and Topography. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jan;55(1):109–115. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.1.109-115.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon F. C., Riedel G. E., Ausubel F. M. Overlapping sequences of Klebsiella pneumoniae nifDNA cloned and characterized. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jul 2;174(1):59–66. doi: 10.1007/BF00433306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles T. C., Finan T. M. Analysis of a 1600-kilobase Rhizobium meliloti megaplasmid using defined deletions generated in vivo. Genetics. 1991 Jan;127(1):5–20. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupuy N. C., Dreyfus B. L. Bradyrhizobium Populations Occur in Deep Soil under the Leguminous Tree Acacia albida. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Aug;58(8):2415–2419. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.8.2415-2419.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dylan T., Helinski D. R., Ditta G. S. Hypoosmotic adaptation in Rhizobium meliloti requires beta-(1----2)-glucan. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1400–1408. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1400-1408.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dylan T., Ielpi L., Stanfield S., Kashyap L., Douglas C., Yanofsky M., Nester E., Helinski D. R., Ditta G. Rhizobium meliloti genes required for nodule development are related to chromosomal virulence genes in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4403–4407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ielpi L., Dylan T., Ditta G. S., Helinski D. R., Stanfield S. W. The ndvB locus of Rhizobium meliloti encodes a 319-kDa protein involved in the production of beta-(1----2)-glucan. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2843–2851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins M. B., Virginia R. A., Jarrell W. M. Rhizobial Ecology of the Woody Legume Mesquite (Prosopis glandulosa) in the Sonoran Desert. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):36–40. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.36-40.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterson R. V., Russell P. R., Atherly A. G. Nitrogen fixation (nif) genes and large plasmids of Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):928–931. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.928-931.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H. M., Long S. R., Ruvkun G. B., Brown S. E., Ausubel F. M. Physical and genetic characterization of symbiotic and auxotrophic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti induced by transposon Tn5 mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.114-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Li W. H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5269–5273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plazinski J., Cen Y. H., Rolfe B. G. General method for the identification of plasmid species in fast-growing soil microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Apr;49(4):1001–1003. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.4.1001-1003.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero D., Brom S., Martínez-Salazar J., Girard M. L., Palacios R., Dávila G. Amplification and deletion of a nod-nif region in the symbiotic plasmid of Rhizobium phaseoli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2435–2441. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2435-2441.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWINGHAMER E. A. Studies on induced variation in the rhizobia. I. Defined media and nodulation test techniques. Appl Microbiol. 1960 Nov;8:349–352. doi: 10.1128/am.8.6.349-352.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Gibson A. H., Dudman W. F., Watson J. M. Evidence for genetic exchange and recombination of Rhizobium symbiotic plasmids in a soil population. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Dec;53(12):2942–2947. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.12.2942-2947.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segovia L., Piñero D., Palacios R., Martínez-Romero E. Genetic structure of a soil population of nonsymbiotic Rhizobium leguminosarum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):426–433. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.426-433.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobral B. W., Honeycutt R. J., Atherly A. G., McClelland M. Electrophoretic separation of the three Rhizobium meliloti replicons. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5173–5180. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5173-5180.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tepfer D., Goldmann A., Pamboukdjian N., Maille M., Lepingle A., Chevalier D., Dénarié J., Rosenberg C. A plasmid of Rhizobium meliloti 41 encodes catabolism of two compounds from root exudate of Calystegium sepium. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1153–1161. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1153-1161.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldon H. B., Jenkins M. B., Virginia R. A., Harding E. E. Characteristics of woodland rhizobial populations from surface- and deep-soil environments of the sonoran desert. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3058–3064. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3058-3064.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]