Abstract
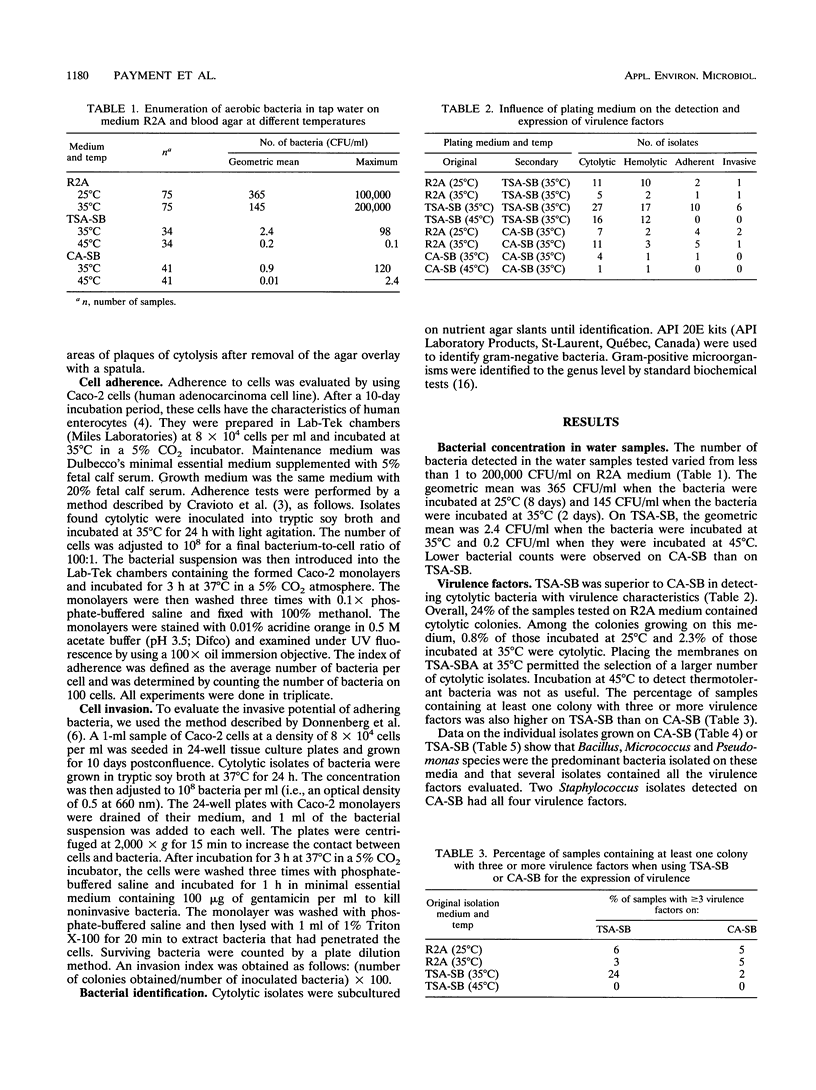
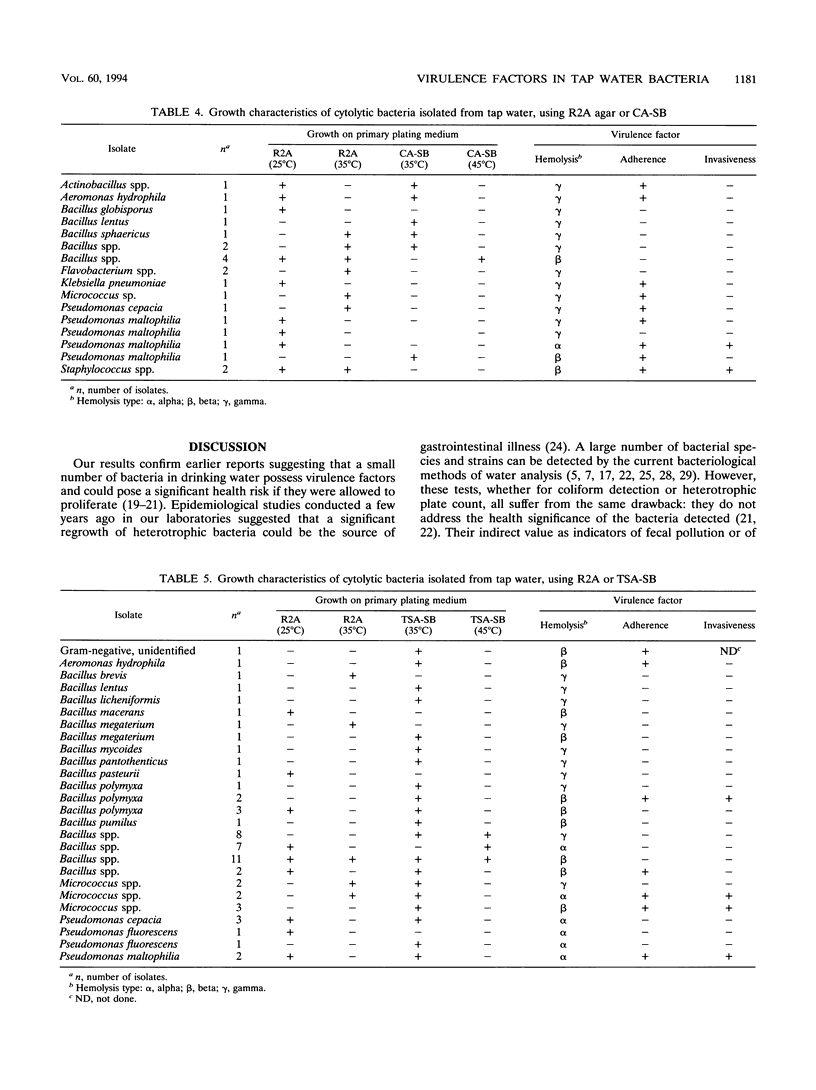
Cytolytic colonies were found in 57% of tap water samples, and up to 6% of samples were found to contain bacteria having three or more virulence factors. The factors evaluated were cytotoxicity, hemolysis, cell adherence, and cell invasiveness. Overall, 17% of the samples contained cytolytic colonies that were adherent and hemolytic. Among the media tested, tryptic soy agar with sheep blood (incubated at 35 degrees C for 48 h) was the best medium for the detection of cytolytic colonies. Of the colonies growing on this medium, 13% were cytolytic, whereas on medium R2A, less than 3% were cytolytic. Furthermore, when tryptic soy agar with blood was used, 24% of the samples contained colonies with at least three virulence factors whereas only 5% were positive with R2A. Routine monitoring by using tryptic soy agar with sheep blood is suggested as an appropriate procedure for the detection of bacteria with pathogenic potential in drinking water.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Darfeuille-Michaud A., Aubel D., Chauviere G., Rich C., Bourges M., Servin A., Joly B. Adhesion of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli to the human colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2 in culture. Infect Immun. 1990 Apr;58(4):893–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.4.893-902.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnenberg M. S., Donohue-Rolfe A., Keusch G. T. Epithelial cell invasion: an overlooked property of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) associated with the EPEC adherence factor. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):452–459. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edberg S. C., Piscitelli V., Cartter M. Phenotypic characteristics of coliform and noncoliform bacteria from a public water supply compared with regional and national clinical species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Sep;52(3):474–478. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.3.474-478.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthright W. E., Archer D. L., Kvenberg J. E. Estimates of incidence and costs of intestinal infectious diseases in the United States. Public Health Rep. 1988 Mar-Apr;103(2):107–115. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havelaar A. H., Schets F. M., van Silfhout A., Jansen W. H., Wieten G., van der Kooij D. Typing of Aeromonas strains from patients with diarrhoea and from drinking water. J Appl Bacteriol. 1992 May;72(5):435–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1992.tb01857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havelaar A. H., Versteegh J. F., During M. The presence of Aeromonas in drinking water supplies in The Netherlands. Zentralbl Hyg Umweltmed. 1990 Sep;190(3):236–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeChevallier M. W., Cameron S. C., McFeters G. A. New medium for improved recovery of coliform bacteria from drinking water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):484–492. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.484-492.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeChevallier M. W., Schiemann D. A., McFeters G. A. Factors contributing to the reduced invasiveness of chlorine-injured Yersinia enterocolitica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jun;53(6):1358–1364. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.6.1358-1364.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeChevallier M. W., Singh A., Schiemann D. A., McFeters G. A. Changes in virulence of waterborne enteropathogens with chlorine injury. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):412–419. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.412-419.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lye D. J., Dufour A. P. A membrane filter procedure for assaying cytotoxic activity in heterotrophic bacteria isolated from drinking water. J Appl Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;70(1):89–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1991.tb03791.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFeters G. A., LeChevallier M. W., Singh A., Kippin J. S. Health significance and occurrence of injured bacteria in drinking water. Water Sci Technol. 1986;18(10):227–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payment P. Bacterial colonization of domestic reverse-osmosis water filtration units. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Nov;35(11):1065–1067. doi: 10.1139/m89-178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payment P., Franco E., Richardson L., Siemiatycki J. Gastrointestinal health effects associated with the consumption of drinking water produced by point-of-use domestic reverse-osmosis filtration units. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):945–948. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.945-948.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payment P., Gamache F., Paquette G. Microbiological and virological analysis of water from two water filtration plants and their distribution systems. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Dec;34(12):1304–1309. doi: 10.1139/m88-228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payment P., Richardson L., Siemiatycki J., Dewar R., Edwardes M., Franco E. A randomized trial to evaluate the risk of gastrointestinal disease due to consumption of drinking water meeting current microbiological standards. Am J Public Health. 1991 Jun;81(6):703–708. doi: 10.2105/ajph.81.6.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reasoner D. J., Geldreich E. E. A new medium for the enumeration and subculture of bacteria from potable water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.1-7.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



