Abstract
Enzymes Ia and Ib of Corynebacterium sp. strain N-1074 exhibit halohydrin hydrogen-halide-lyase (H-lyase) activity, catalyzing the interconversion of halohydrins to epoxides and hydrogen halide. H-lyase B produced in a recombinant Escherichia coli strain carrying one of the enzyme genes of Corynebacterium sp. strain N-1074 was purified and characterized. The purified enzyme catalyzed the transformation of prochiral 1,3-dichloro-2-propanol (DCP) into R-rich epichlorohydrin (ECH). The apparent Km values for DCP, ECH, and chloride were calculated to be 1.03, 5.00, and 4.00 mM, respectively. Maximum activity for the conversion of DCP to ECH was found at pH 8.0 to 9.0, and that for the reverse reaction was found at about pH 5.0. H-lyase B seemed to be identical to enzyme Ib of Corynebacterium sp. strain N-1074 from the comparison of the properties of each. The properties of H-lyase B and H-lyase A, which had been previously purified from another recombinant carrying its gene from Corynebacterium sp. strain N-1074, were also compared.
Full text
PDF
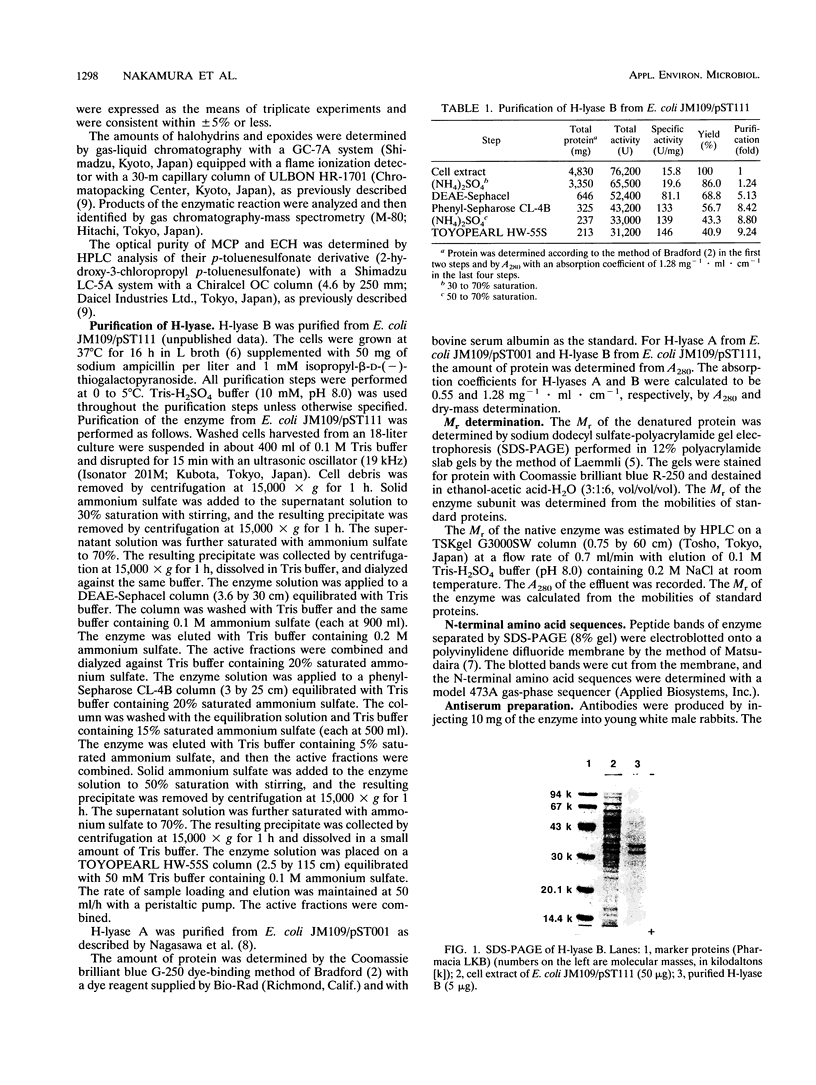
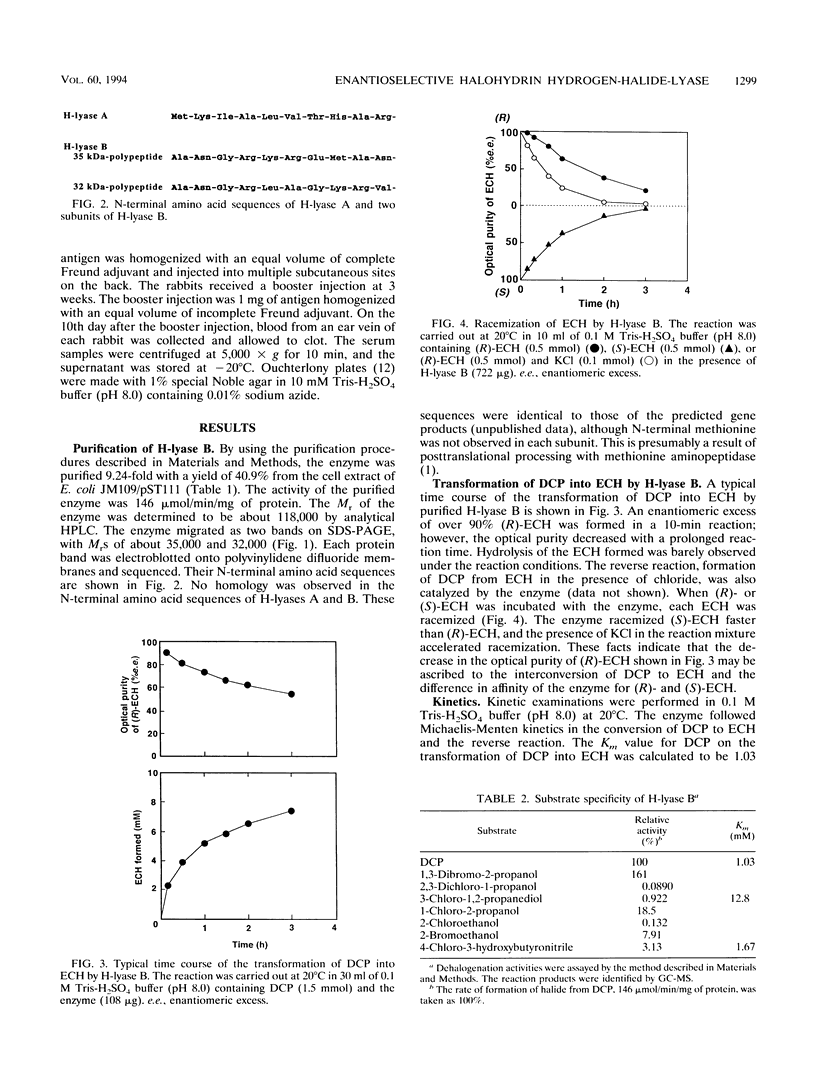


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Bassat A., Bauer K., Chang S. Y., Myambo K., Boosman A., Chang S. Processing of the initiation methionine from proteins: properties of the Escherichia coli methionine aminopeptidase and its gene structure. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):751–757. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.751-757.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro C. E., Bartnicki E. W. Biodehalogenation. Epoxiation of halohydrins, epoxide opening, and transhalogenation by a Flavobacterium sp. Biochemistry. 1968 Sep;7(9):3213–3218. doi: 10.1021/bi00849a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Yu F., Mizunashi W., Watanabe I. Production of (R)-3-Chloro-1,2-Propanediol from Prochiral 1,3-Dichloro-2-Propanol by Corynebacterium sp. Strain N-1074. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jan;59(1):227–230. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.227-230.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Wijngaard A. J., Reuvekamp P. T., Janssen D. B. Purification and characterization of haloalcohol dehalogenase from Arthrobacter sp. strain AD2. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):124–129. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.124-129.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]