Abstract
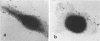
Aeromonas hydrophila strains isolated from the same geographical region (southern Italy) but from different sources (sea sediments and human diarrhea cases) were characterized for the production of potential virulence determinants, such as production of cytotoxins, cytotonic toxins, hemolysin, and dermonecrotic factors and their capacity to adhere to human intestinal 407 cells in vitro. The results showed that isolates from both the sources produced all or some of the virulence factors which may be involved in the pathogenesis of Aeromonas-associated infections. Our study indicates that further epidemiological studies are necessary to elucidate the public health significance of infections caused by Aeromonas spp.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaise C. R., Armstrong J. B. Lipolytic bacteria in the Ottawa river. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Nov;26(5):733–740. doi: 10.1128/am.26.5.733-740.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke V., Robinson J., Gracey M., Peterson D., Partridge K. Isolation of Aeromonas hydrophila from a metropolitan water supply: seasonal correlation with clinical isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):361–366. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.361-366.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrello A., Silburn K. A., Budden J. R., Chang B. J. Adhesion of clinical and environmental Aeromonas isolates to HEp-2 cells. J Med Microbiol. 1988 May;26(1):19–27. doi: 10.1099/00222615-26-1-19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. P. A permeability factor (toxin) found in cholera stools and culture filtrates and its neutralization by convalescent cholera sera. Nature. 1965 Aug 7;207(997):614–616. doi: 10.1038/207614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran D. M., Montville T. J. Bicarbonate inhibition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Hansenula wingei growth in apple juice. Int J Food Microbiol. 1989 Feb;8(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(89)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray S. J., Stickler D. J., Bryant T. N. The incidence of virulence factors in mesophilic Aeromonas species isolated from farm animals and their environment. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Oct;105(2):277–294. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800047889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J. M., Duffey P. S. Mesophilic aeromonads in human disease: current taxonomy, laboratory identification, and infectious disease spectrum. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Sep-Oct;10(5):980–997. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.5.980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirov S. M., Rees B., Wellock R. C., Goldsmid J. M., Van Galen A. D. Virulence characteristics of Aeromonas spp. in relation to source and biotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Nov;24(5):827–834. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.5.827-834.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krovacek K., Conte M., Galderisi P., Morelli G., Postiglione A., Dumontet S. Fatal septicaemia caused by Aeromonas hydrophila in a patient with cirrhosis. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1993 Oct;16(4):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(93)90155-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krovacek K., Faris A., Eriksson L., Jansson E., Ljungberg O., Månsson I. Virulence, cytotoxic and inflammatory activities of Vibrio anguillarum and Aeromonas salmonicida isolated from cultivated salmonid fish in Sweden. Acta Vet Scand. 1987;28(1):47–54. doi: 10.1186/BF03548255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krovacek K., Faris A., Månsson I. In vitro invasion of Aeromonas spp. to HEp-2 tissue culture cells. Acta Vet Scand. 1991;32(1):139–143. doi: 10.1186/BF03547007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mateos D., Anguita J., Naharro G., Paniagua C. Influence of growth temperature on the production of extracellular virulence factors and pathogenicity of environmental and human strains of Aeromonas hydrophila. J Appl Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;74(2):111–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1993.tb03003.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. R., Johnson P. C., DuPont H. L., Satterwhite T. K., Wood L. V. Lack of correlation between known virulence properties of Aeromonas hydrophila and enteropathogenicity for humans. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):62–65. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.62-65.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okitsu T., Asai Y., Yasuda T., Takizawa K. [Studies of Aeromonas spp. isolated from patients with sporadic diarrhea]. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 1985 Oct;59(10):977–983. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.59.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal S. C., Singh S. J., Sen P. C. Enteropathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and Plesiomonas shigelloides. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):195–198. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotts E. B., Jr, Gaines J. L., Jr, Martin L., Prestwood A. K. Aeromonas-induced deaths among fish and reptiles in an eutrophic inland lake. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1972 Sep 15;161(6):603–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR J., MALTBY M. P., PAYNE J. M. Factors influencing the response of ligated rabbit-gut segments to injected Escherichia coli. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1958 Oct;76(2):491–499. doi: 10.1002/path.1700760218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wretlind B., Möllby R., Wadström T. Separation of two hemolysins from Aeromonas hydrophila by isoelectric focusing. Infect Immun. 1971 Oct;4(4):503–505. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.4.503-505.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]