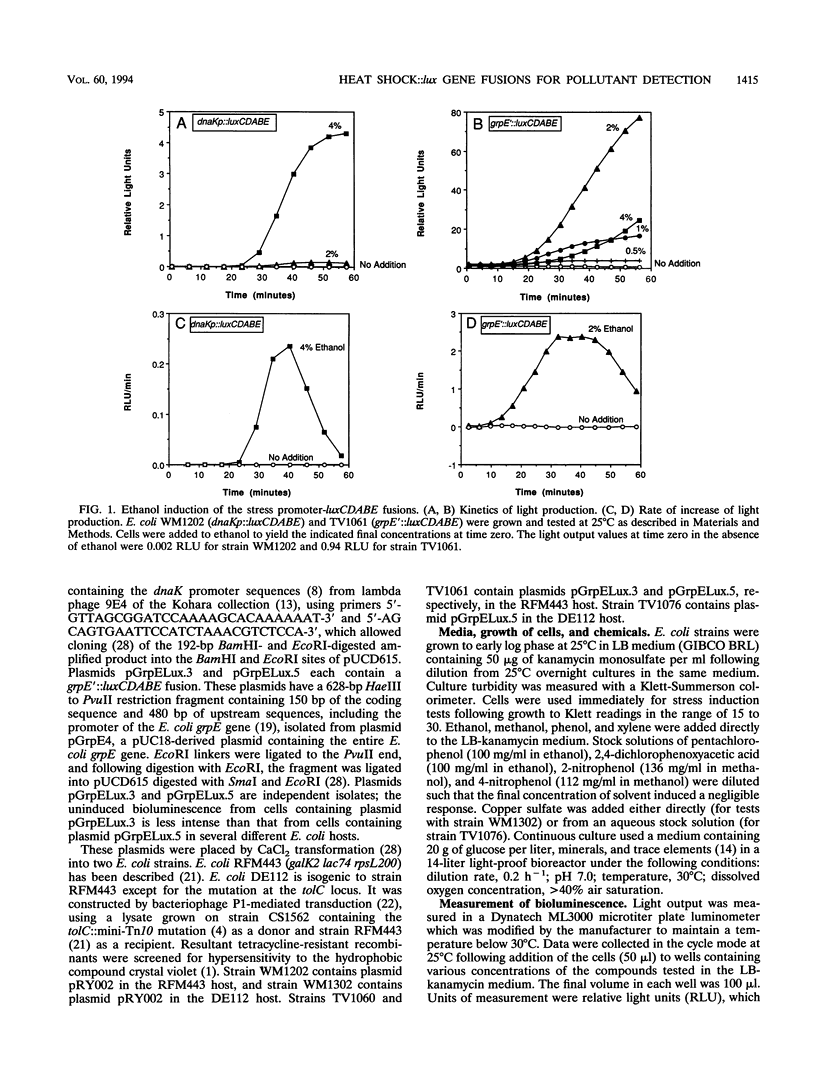
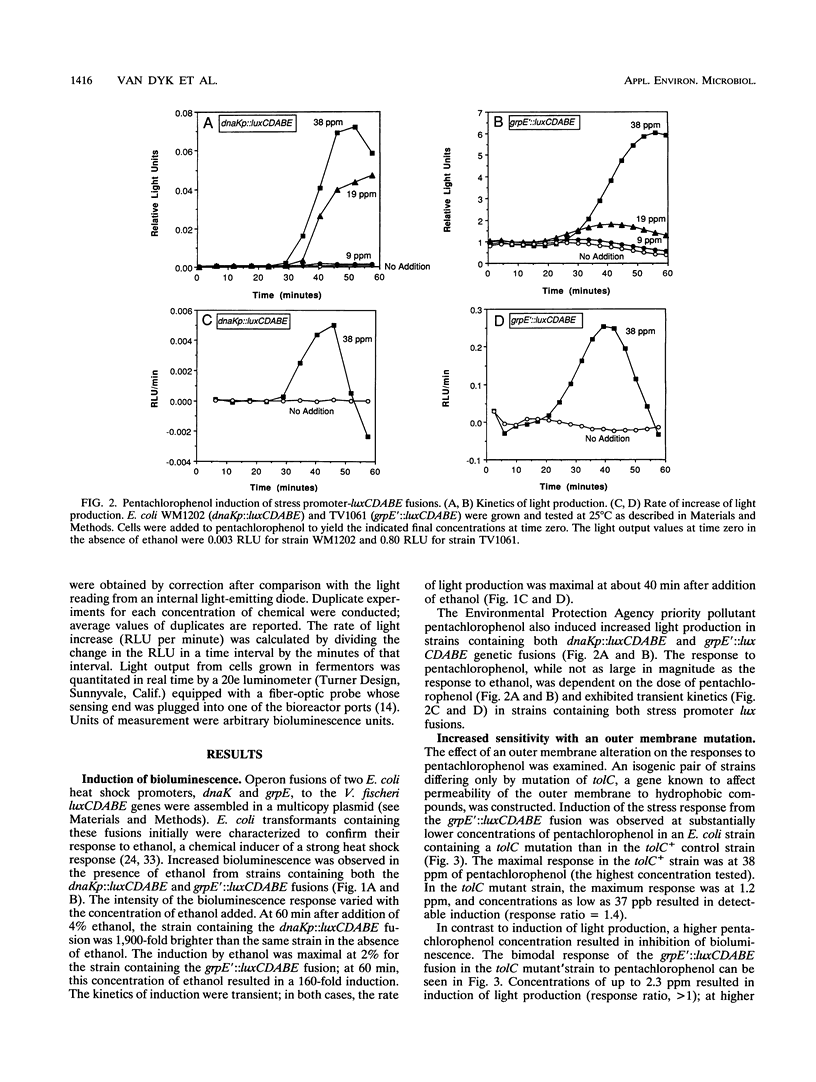
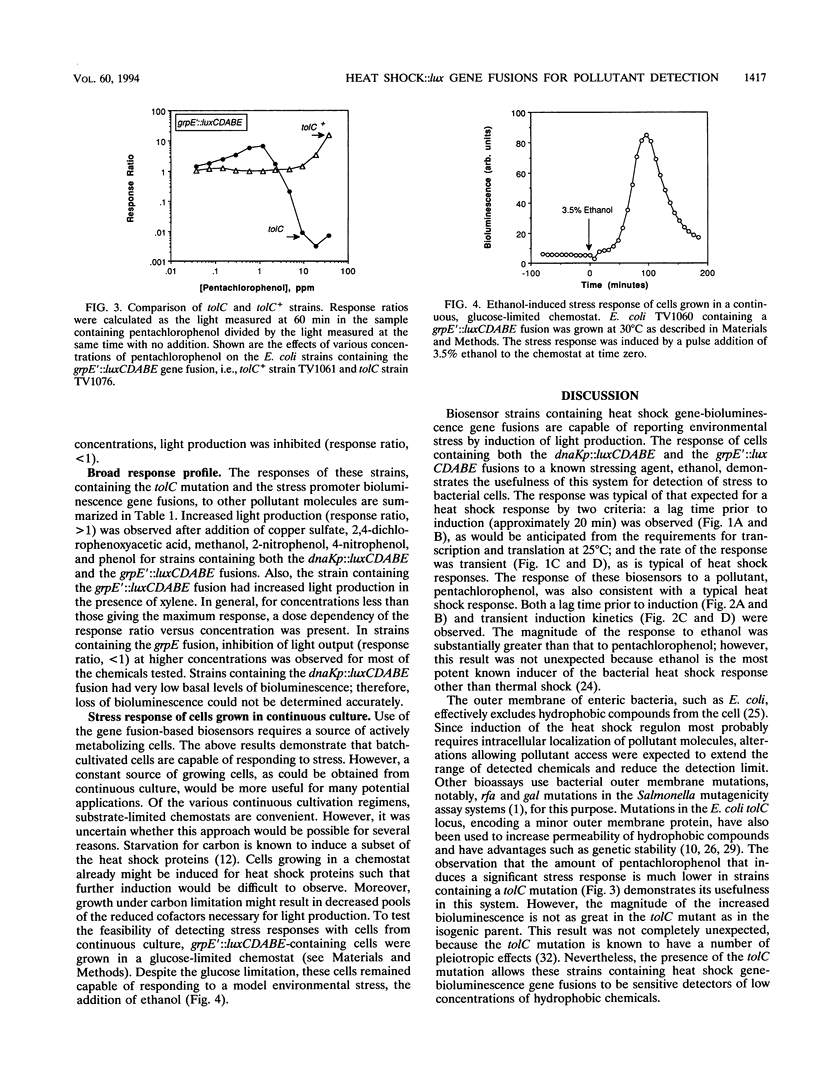
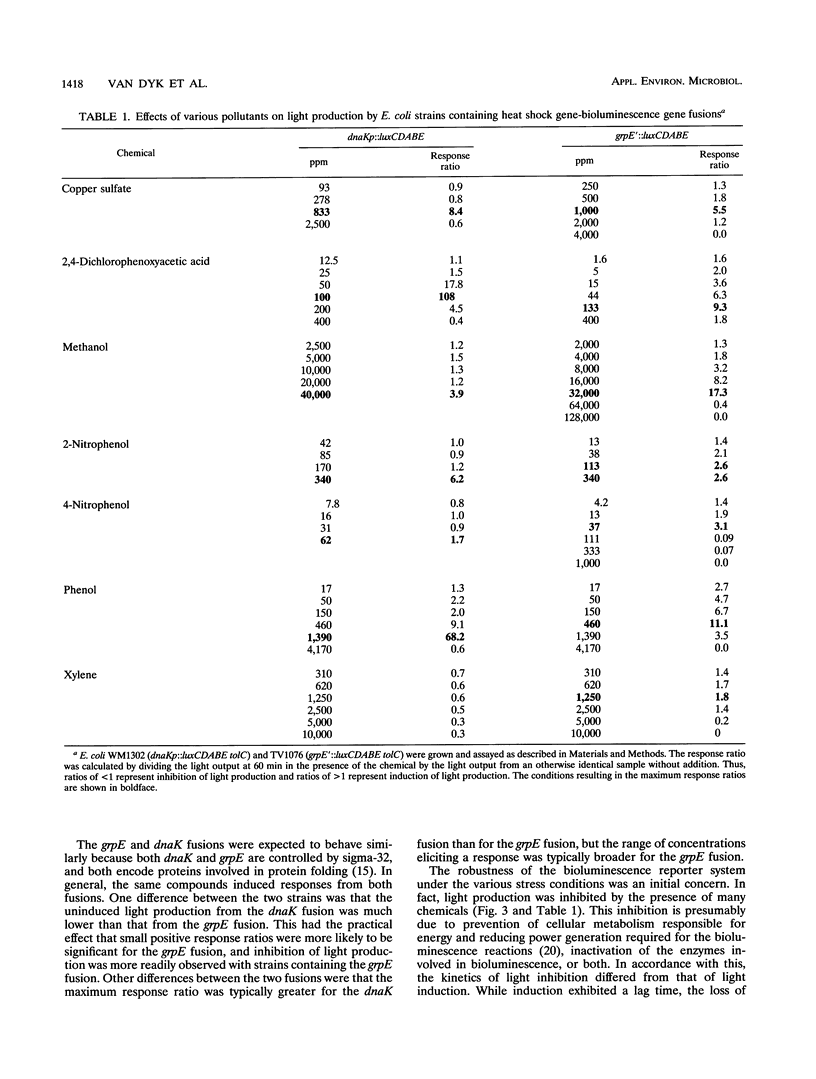
Abstract
Heat shock gene expression is induced by a variety of environmental stresses, including the presence of many chemicals. To address the utility of this response for pollutant detection, two Escherichia coli heat shock promoters, dnaK and grpE, were fused to the lux genes of Vibrio fischeri. Metals, solvents, crop protection chemicals, and other organic molecules rapidly induced light production from E. coli strains containing these plasmid-borne fusions. Introduction of an outer membrane mutation, tolC, enhanced detection of a hydrophobic molecule, pentachlorophenol. The maximal response to pentachlorophenol in the tolC+ strain was at 38 ppm, while the maximal response in an otherwise isogenic tolC mutant was at 1.2 ppm. Stress responses were observed in both batch and chemostat cultures. It is suggested that biosensors constructed in this manner may have potential for environmental monitoring.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N., Lee F. D., Durston W. E. An improved bacterial test system for the detection and classification of mutagens and carcinogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):782–786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ang D., Chandrasekhar G. N., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. Escherichia coli grpE gene codes for heat shock protein B25.3, essential for both lambda DNA replication at all temperatures and host growth at high temperature. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):25–29. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.25-29.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ang D., Georgopoulos C. The heat-shock-regulated grpE gene of Escherichia coli is required for bacterial growth at all temperatures but is dispensable in certain mutant backgrounds. J Bacteriol. 1989 May;171(5):2748–2755. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2748-2755.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin E. A., Graves J. F., Hite L. A., Parker C. T., Schnaitman C. A. Genetic analysis of lipopolysaccharide core biosynthesis by Escherichia coli K-12: insertion mutagenesis of the rfa locus. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5312–5325. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5312-5325.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blom A., Harder W., Matin A. Unique and overlapping pollutant stress proteins of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):331–334. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.331-334.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boylan M., Graham A. F., Meighen E. A. Functional identification of the fatty acid reductase components encoded in the luminescence operon of Vibrio fischeri. J Bacteriol. 1985 Sep;163(3):1186–1190. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.3.1186-1190.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowing D. W., Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A., Woolford C., Hendrix R. W., Gross C. A. Consensus sequence for Escherichia coli heat shock gene promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Gross C. A. Is hsp70 the cellular thermometer? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Apr;16(4):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90055-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill P. J., Rees C. E., Winson M. K., Stewart G. S. The application of lux genes. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 1993 Feb;17(Pt 1):3–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D. E., Auger E. A., Matin A. Role of RpoH, a heat shock regulator protein, in Escherichia coli carbon starvation protein synthesis and survival. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):1992–1996. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.1992-1996.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRossa R. A., Van Dyk T. K. Physiological roles of the DnaK and GroE stress proteins: catalysts of protein folding or macromolecular sponges? Mol Microbiol. 1991 Mar;5(3):529–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00724.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer T., Lu C., Echols H., Flanagan J., Hayer M. K., Hartl F. U. Successive action of DnaK, DnaJ and GroEL along the pathway of chaperone-mediated protein folding. Nature. 1992 Apr 23;356(6371):683–689. doi: 10.1038/356683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaux P. G., Herendeen S. L., Bloch P. L., Neidhardt F. C. Transient rates of synthesis of individual polypeptides in E. coli following temperature shifts. Cell. 1978 Mar;13(3):427–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90317-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberek K., Marszalek J., Ang D., Georgopoulos C., Zylicz M. Escherichia coli DnaJ and GrpE heat shock proteins jointly stimulate ATPase activity of DnaK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2874–2878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipinska B., King J., Ang D., Georgopoulos C. Sequence analysis and transcriptional regulation of the Escherichia coli grpE gene, encoding a heat shock protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7545–7562. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meighen E. A. Molecular biology of bacterial bioluminescence. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):123–142. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.123-142.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuji N., Horiuchi T., Nakata A., Kawamata J. Strains of Escherichia coli hypersensitive to representative carcinostatic and carcinogenic agents. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1978 Aug;31(8):794–796. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.31.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogowsky P. M., Close T. J., Chimera J. A., Shaw J. J., Kado C. I. Regulation of the vir genes of Agrobacterium tumefaciens plasmid pTiC58. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):5101–5112. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.5101-5112.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. S., Williams P. lux genes and the applications of bacterial bioluminescence. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Jul;138(7):1289–1300. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-7-1289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBogelen R. A., Kelley P. M., Neidhardt F. C. Differential induction of heat shock, SOS, and oxidation stress regulons and accumulation of nucleotides in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):26–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.26-32.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. E. The tol gene products and the import of macromolecules into Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1991 May;5(5):1005–1011. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano R., Imai M., Yura T. The use of operon fusions in studies of the heat-shock response: effects of altered sigma 32 on heat-shock promoter function in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):24–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00331486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



