Abstract
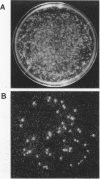
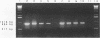
Two reporter systems, lacZY and luxAB, were stably integrated into the chromosome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa UG2, a biosurfactant-producing strain. Growth and rhamnolipid production of the UG2 wild-type and reporter gene-bearing UG2L strains were similar in liquid culture. A spontaneous rifampin-resistant detecting UG2Lr, allowed antibiotic selection. Phenotypic characteristics were compared for usefulness in detecting UG2Lr colonies: morphology, fluorescent pigment production, light emission (lux), X-Gal (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-beta-D-galactopyranoside) cleavage (lac), and rifampin resistance. Survival patterns of UG2, UG2L, and UG2Lr strains were similar in sandy loam soil microcosms over 12 12 weeks. The lac marker was not suitable for monitoring P. aeruginosa UG2Lr in soil since 20 to 42% of cultured, aerobic, heterotrophic soil microorganisms formed blue, lactose-positive colonies. The lux genes provided a stable and unequivocal reporter system, as effective as conventional antibiotic plating, for tracking microorganisms nonselectively at 10(3) CFU/g of soil. Three months after inoculation into oil-contaminated and uncontaminated soil microcosms, UG2Lr cells were recovered at 10(7) and 10(4) cells per g (dry weight) of soil, respectively. Detection by PCR amplification of part of the luxA gene confirmed a decrease in UG2Lr cell numbers in uncontaminated soil. In combination, antibiotic resistance, bioluminescence, and PCR analyses provided sensitive detection and quantitative enumeration of P. aeruginosa UG2Lr in soil.
Full text
PDF


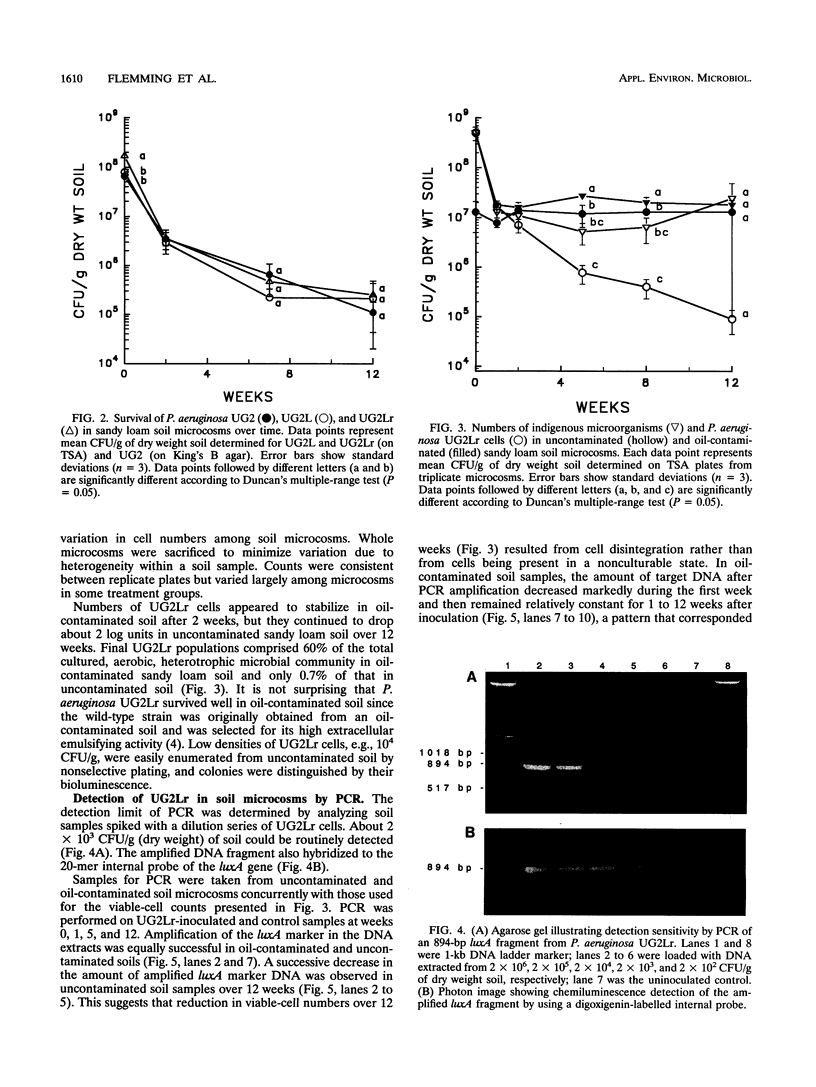



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bej A. K., DiCesare J. L., Haff L., Atlas R. M. Detection of Escherichia coli and Shigella spp. in water by using the polymerase chain reaction and gene probes for uid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):1013–1017. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1013-1017.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao W. L., Feng R. L. Survival of genetically engineered Escherichia coli in natural soil and river water. J Appl Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;68(4):319–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1990.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. H., Mileham A. J., Simon M. I., Nealson K. H., Rausch S. K., Bonam D., Baldwin T. O. Nucleotide sequence of the luxA gene of Vibrio harveyi and the complete amino acid sequence of the alpha subunit of bacterial luciferase. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6139–6146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compeau G., Al-Achi B. J., Platsouka E., Levy S. B. Survival of rifampin-resistant mutants of Pseudomonas fluorescens and Pseudomonas putida in soil systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2432–2438. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2432-2438.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkmans R., Jagers A., Kreps S., Collard J. M., Mergeay M. Rapid method for purification of soil DNA for hybridization and PCR analysis. Microb Releases. 1993 Jun;2(1):29–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower W. J., Miller J. F., Ragsdale C. W. High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6127–6145. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drahos D. J. Field testing of genetically engineered microorganisms. Biotechnol Adv. 1991;9(2):157–171. doi: 10.1016/0734-9750(91)90001-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson J. K., Bezdicek D. F., Brockman F. J., Li S. W. Enumeration of Tn5 mutant bacteria in soil by using a most- probable-number-DNA hybridization procedure and antibiotic resistance. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Feb;54(2):446–453. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.2.446-453.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill P. J., Rees C. E., Winson M. K., Stewart G. S. The application of lux genes. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 1993 Feb;17(Pt 1):3–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holben William E., Jansson Janet K., Chelm Barry K., Tiedje James M. DNA Probe Method for the Detection of Specific Microorganisms in the Soil Bacterial Community. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):703–711. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.703-711.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam M. S., Hasan M. K., Miah M. A., Sur G. C., Felsenstein A., Venkatesan M., Sack R. B., Albert M. J. Use of the polymerase chain reaction and fluorescent-antibody methods for detecting viable but nonculturable Shigella dysenteriae type 1 in laboratory microcosms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Feb;59(2):536–540. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.2.536-540.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson L., Comeau Y., Brousseau R., Samson R., Greer C. Construction and application of chromosomally integrated lac-lux gene markers to monitor the fate of a 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-degrading bacterium in contaminated soils. Microb Releases. 1993 Mar;1(4):209–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuko M., Hosoi S., Hayakawa T. A novel method for detection and counting of single bacteria in a wide field using an ultra-high-sensitivity TV camera without a microscope. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jul 1;65(3):287–290. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90229-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meighen E. A. Molecular biology of bacterial bioluminescence. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):123–142. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.123-142.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto C. M., Boylan M., Graham A. F., Meighen E. A. Organization of the lux structural genes of Vibrio harveyi. Expression under the T7 bacteriophage promoter, mRNA analysis, and nucleotide sequence of the luxD gene. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13393–13399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. A., Rhodes G., Pickup R. W. Survival of nonculturable Aeromonas salmonicida in lake water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Mar;59(3):874–880. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.3.874-880.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. A., Winstanley C., Pickup R. W., Jones J. G., Saunders J. R. Direct phenotypic and genotypic detection of a recombinant pseudomonad population released into lake water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2537–2544. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2537-2544.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan P., Watkinson R. J. Hydrocarbon degradation in soils and methods for soil biotreatment. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 1989;8(4):305–333. doi: 10.3109/07388558909148196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser J. I. Molecular marker systems for detection of genetically engineered micro-organisms in the environment. Microbiology. 1994 Jan;140(Pt 1):5–17. doi: 10.1099/13500872-140-1-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. J., Dane F., Geiger D., Kloepper J. W. Use of bioluminescence for detection of genetically engineered microorganisms released into the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):267–273. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.267-273.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffan R. J., Atlas R. M. DNA amplification to enhance detection of genetically engineered bacteria in environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Sep;54(9):2185–2191. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.9.2185-2191.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai Y. L., Olson B. H. Rapid method for separation of bacterial DNA from humic substances in sediments for polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jul;58(7):2292–2295. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.7.2292-2295.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M., Lindow S. E. Release of recombinant microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1993;47:913–944. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.47.100193.004405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winstanley C., Morgan J. A., Pickup R. W., Saunders J. R. Use of a xylE marker gene to monitor survival of recombinant Pseudomonas putida populations in lake water by culture on nonselective media. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jul;57(7):1905–1913. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.7.1905-1913.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weger L. A., Dunbar P., Mahafee W. F., Lugtenberg B. J., Sayler G. S. Use of Bioluminescence Markers To Detect Pseudomonas spp. in the Rhizosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Dec;57(12):3641–3644. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.12.3641-3644.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]