Abstract
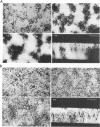
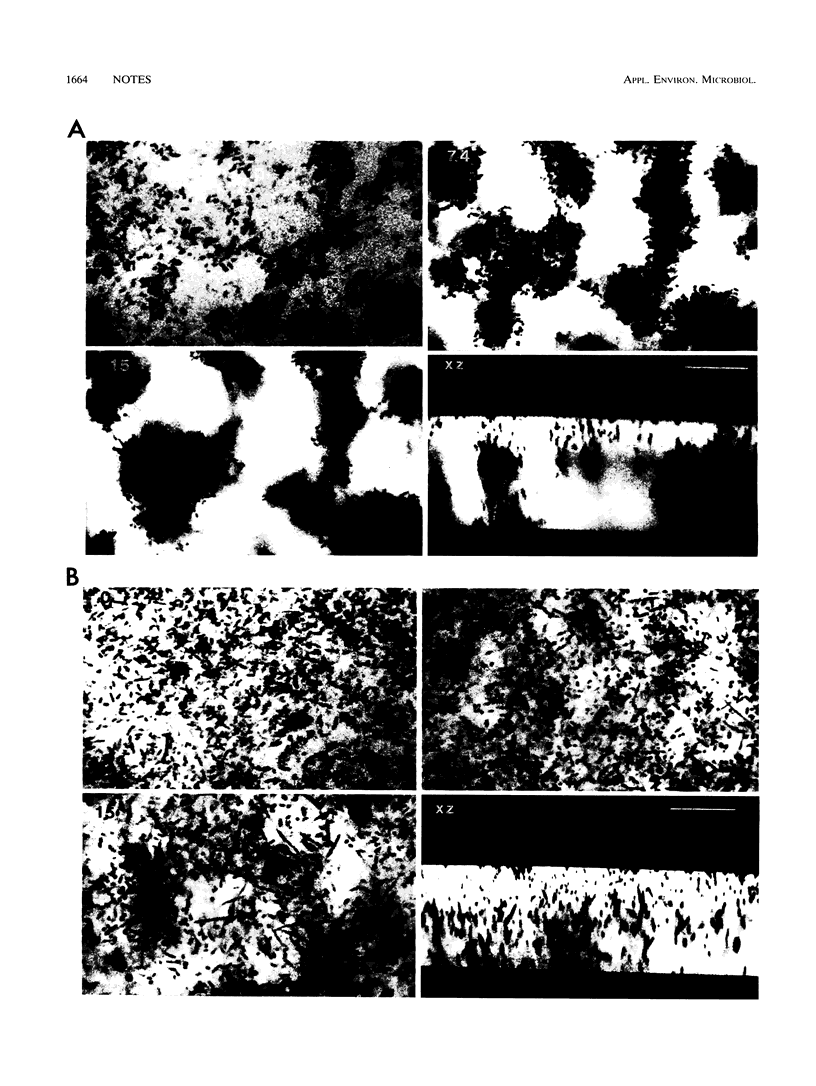
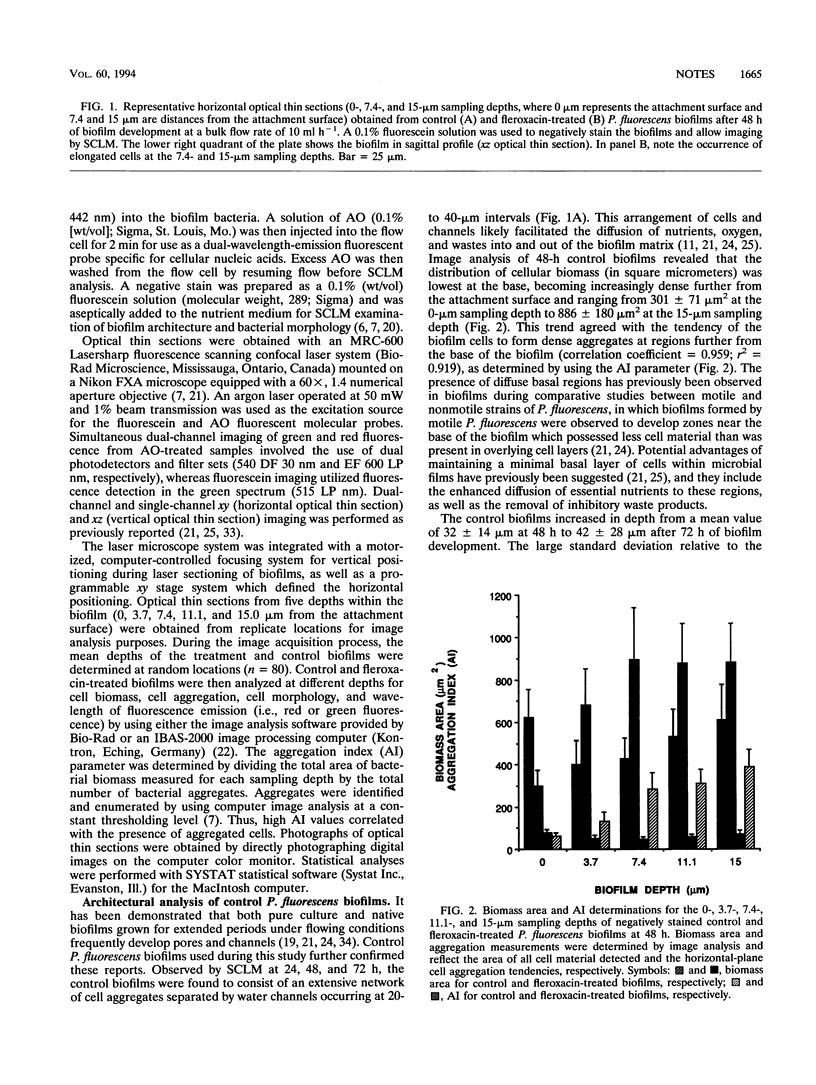
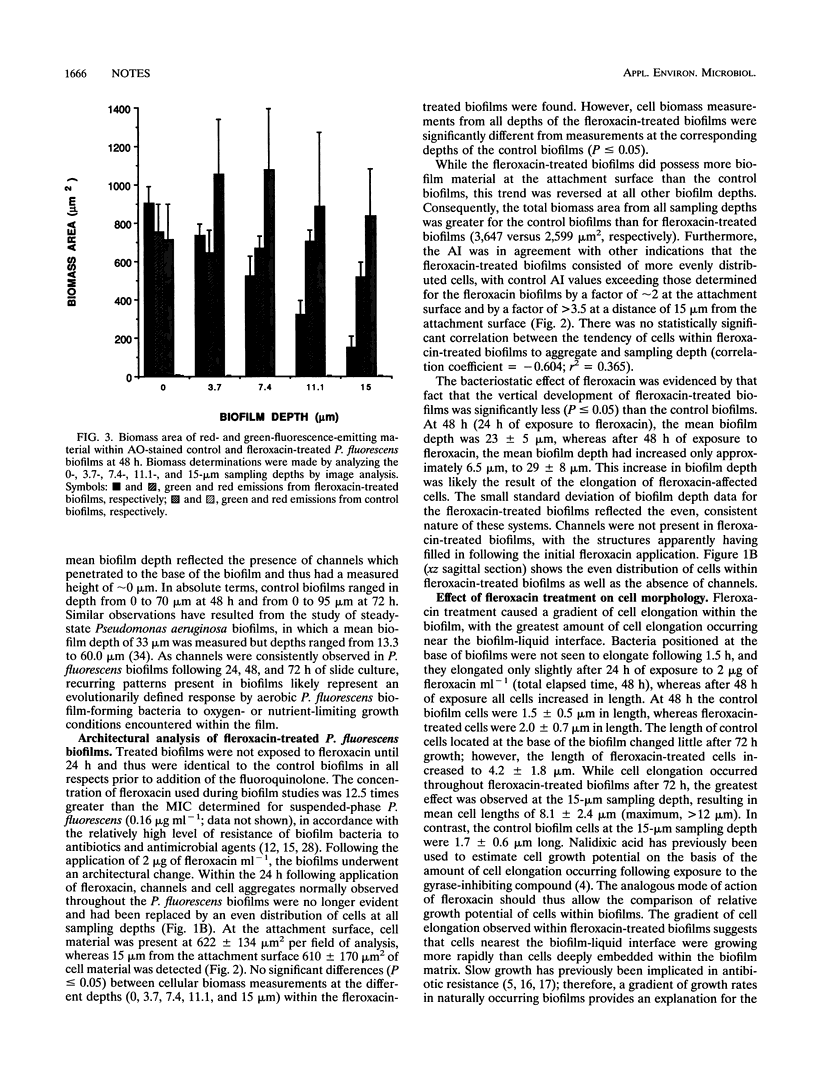
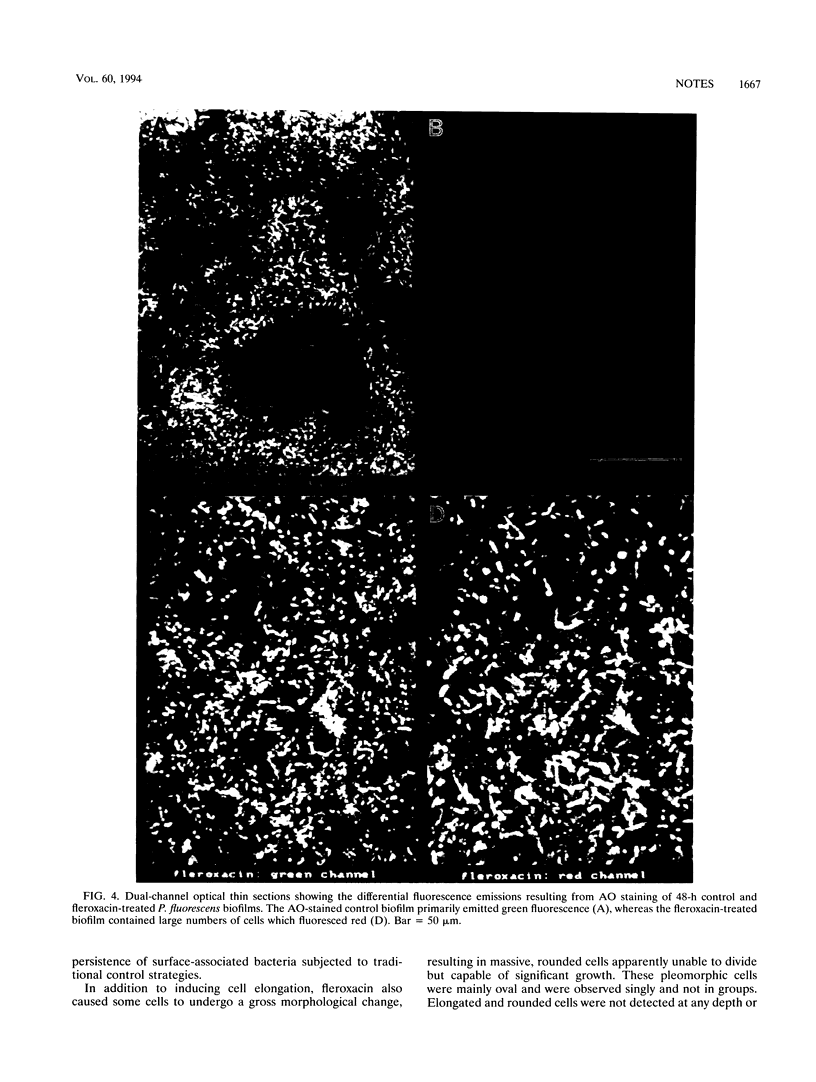
Scanning confocal laser microscopy (SCLM) and fluorescent molecular probes were used to evaluate the effect of the fluoroquinolone fleroxacin on the architecture of established Pseudomonas fluorescens biofilms. Control P. fluorescens biofilms were heterogeneous, consisting of cell aggregates extending from the attachment surface to maximum measured depths of ∼90 μm (mean biofilm depth at 72 h, 42 ± 28 μm) and penetrated by an array of channels. In contrast, fleroxacin-treated biofilms were less deep (mean biofilm depth at 72 h, 29 ± 8 μm), varied little in depth over large areas, and consisted of a homogeneous distribution of cells. Fleroxacin also caused cells to elongate, with cells located near the biofilm-liquid interface lengthening significantly more than cells located at the attachment surface. By using SCLM, acridine orange, and image analysis it was found that ∼59% of cells within fleroxacin-treated biofilms emitted red fluorescence whereas >99% of cells from control biofilms emitted green fluorescence. The fleroxacin-treated cells which emitted red fluorescence were observed to be the population of cells which elongated.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anwar H., Costerton J. W. Enhanced activity of combination of tobramycin and piperacillin for eradication of sessile biofilm cells of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1666–1671. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back J. P., Kroll R. G. The differential fluorescence of bacteria stained with acridine orange and the effects of heat. J Appl Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;71(1):51–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley P. J., Maggard S. P. Determination of viability within serotypes of a soil population of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):533–540. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.533-540.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. R., Allison D. G., Gilbert P. Resistance of bacterial biofilms to antibiotics: a growth-rate related effect? J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Dec;22(6):777–780. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.6.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. S., Georgopapadakou N. H. Routes of quinolone permeation in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):438–442. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong E. F., Wickham G. S., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic stains: ribosomal RNA-based probes for the identification of single cells. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2466341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duguid I. G., Evans E., Brown M. R., Gilbert P. Growth-rate-independent killing by ciprofloxacin of biofilm-derived Staphylococcus epidermidis; evidence for cell-cycle dependency. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Dec;30(6):791–802. doi: 10.1093/jac/30.6.791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng R. H., Padberg F. T., Smith S. M., Tan E. N., Cherubin C. E. Bactericidal effects of antibiotics on slowly growing and nongrowing bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Sep;35(9):1824–1828. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.9.1824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert P., Collier P. J., Brown M. R. Influence of growth rate on susceptibility to antimicrobial agents: biofilms, cell cycle, dormancy, and stringent response. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Oct;34(10):1865–1868. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.10.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbie J. E., Daley R. J., Jasper S. Use of nuclepore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1225–1228. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1225-1228.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. R., Korber D. R., Hoyle B. D., Costerton J. W., Caldwell D. E. Optical sectioning of microbial biofilms. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6558–6567. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6558-6567.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols W. W., Dorrington S. M., Slack M. P., Walmsley H. L. Inhibition of tobramycin diffusion by binding to alginate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):518–523. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel J. C., Ruseska I., Wright J. B., Costerton J. W. Tobramycin resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells growing as a biofilm on urinary catheter material. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):619–624. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nix P. G., Daykin M. M. Resazurin reduction tests as an estimate of coliform and heterotrophic bacterial numbers in environmental samples. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1992 Sep;49(3):354–360. doi: 10.1007/BF01239637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez G. G., Phipps D., Ishiguro K., Ridgway H. F. Use of a fluorescent redox probe for direct visualization of actively respiring bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jun;58(6):1801–1808. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.6.1801-1808.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart P. S., Peyton B. M., Drury W. J., Murga R. Quantitative observations of heterogeneities in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jan;59(1):327–329. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.327-329.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor P. S., Neihof R. A. Improved method for determination of respiring individual microorganisms in natural waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1249–1255. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1249-1255.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M. Agents that increase the permeability of the outer membrane. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Sep;56(3):395–411. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.3.395-411.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]