Abstract
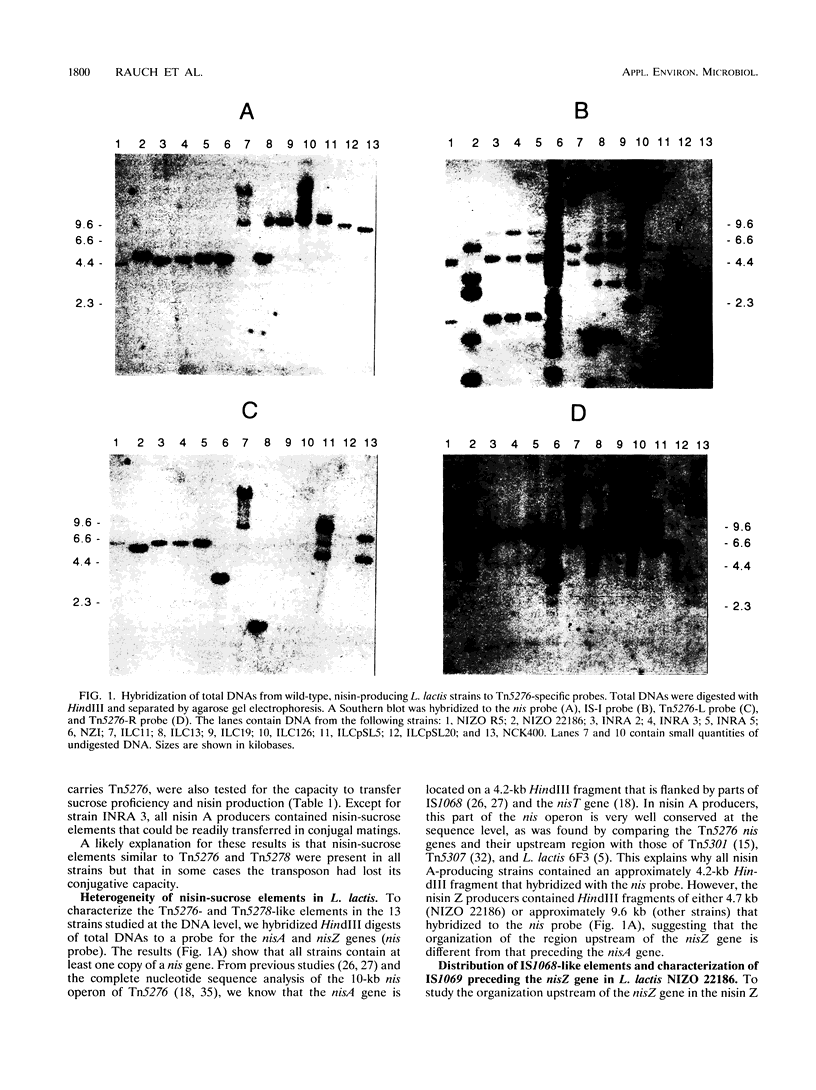
The distribution, architecture, and conjugal capacity of nisin-sucrose elements in wild-type Lactococcus lactis strains were studied. Element architecture was analyzed with the aid of hybridizations to different probes derived from the nisin-sucrose transposon Tn5276 of L. lactis NIZO R5, including its left and right ends, the nisA gene, and IS1068 (previously designated iso-IS904), located between the left end and the nisA gene. Three classes of nisin-sucrose elements could be distinguished in the 13 strains investigated. Classes I and II consist of conjugative transposons containing a nisA gene and a nisZ gene, respectively. Representative conjugative transposons of these classes include Tn5276 (class I) from L. lactis NIZO R5 and Tn5278 (class II) from L. lactis ILC11. The class II transposon found in L. lactis NCK400 and probably all class II elements are devoid of IS1068-like elements, which eliminates the involvement of an iso-IS1068 element in conjugative transposition. Members of class III contain a nisZ gene, are nonconjugative, and do not contain sequences similar to the left end of Tn5276 at the appropriate position. The class III element from L. lactis NIZO 22186 was found to contain an iso-IS1068 element, termed IS1069, at a position corresponding to that of IS1068 in Tn5276 but in the inverted orientation. The results suggest that an iso-IS1068-mediated rearrangement is responsible for the dislocation of the transposon's left end in this strain. A model for the evolution of nisin-sucrose elements is proposed, and the practical implications for transferring nisin A or nisin Z production and immunity are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broadbent J. R., Kondo J. K. Genetic construction of nisin-producing Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris and analysis of a rapid method for conjugation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):517–524. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.517-524.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman G. W., Banerjee S., Hansen J. N. Structure, expression, and evolution of a gene encoding the precursor of nisin, a small protein antibiotic. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16260–16266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd H. M., Horn N., Gasson M. J. Analysis of the genetic determinant for production of the peptide antibiotic nisin. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Mar;136(3):555–566. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-3-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke G., Gutowski-Eckel Z., Hammelmann M., Entian K. D. Biosynthesis of the lantibiotic nisin: genomic organization and membrane localization of the NisB protein. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Nov;58(11):3730–3743. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.11.3730-3743.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson M. J. In vivo genetic systems in lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990 Sep;7(1-2):43–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1990.tb04878.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasson M. J. Plasmid complements of Streptococcus lactis NCDO 712 and other lactic streptococci after protoplast-induced curing. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.1-9.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gireesh T., Davidson B. E., Hillier A. J. Conjugal transfer in Lactococcus lactis of a 68-kilobase-pair chromosomal fragment containing the structural gene for the peptide bacteriocin nisin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 May;58(5):1670–1676. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.5.1670-1676.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C. F., Kunka B. S. Transfer of Sucrose-Fermenting Ability and Nisin Production Phenotype among Lactic Streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):627–633. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.627-633.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross E., Morell J. L. The structure of nisin. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Sep 8;93(18):4634–4635. doi: 10.1021/ja00747a073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris L. J., Fleming H. P., Klaenhammer T. R. Characterization of two nisin-producing Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis strains isolated from a commercial sauerkraut fermentation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 May;58(5):1477–1483. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.5.1477-1483.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn N., Swindell S., Dodd H., Gasson M. Nisin biosynthesis genes are encoded by a novel conjugative transposon. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):129–135. doi: 10.1007/BF00282457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang D. C., Novel M., Novel G. A transposon-like element on the lactose plasmid of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis Z270. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jan 1;61(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers O. P., Beerthuyzen M. M., Siezen R. J., De Vos W. M. Characterization of the nisin gene cluster nisABTCIPR of Lactococcus lactis. Requirement of expression of the nisA and nisI genes for development of immunity. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Aug 15;216(1):281–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18143.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuipers O. P., Boot H. J., de Vos W. M. Improved site-directed mutagenesis method using PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4558–4558. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg E. M. Plasmid Reference Center Registry of transposon(Tn) and insertion sequence (IS) allocations through December 1986. Gene. 1987;51(2-3):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90299-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig W., Seewaldt E., Kilpper-Bälz R., Schleifer K. H., Magrum L., Woese C. R., Fox G. E., Stackebrandt E. The phylogenetic position of Streptococcus and Enterococcus. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Mar;131(3):543–551. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-3-543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulders J. W., Boerrigter I. J., Rollema H. S., Siezen R. J., de Vos W. M. Identification and characterization of the lantibiotic nisin Z, a natural nisin variant. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Nov 1;201(3):581–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polard P., Prère M. F., Chandler M., Fayet O. Programmed translational frameshifting and initiation at an AUU codon in gene expression of bacterial insertion sequence IS911. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 5;222(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90490-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prère M. F., Chandler M., Fayet O. Transposition in Shigella dysenteriae: isolation and analysis of IS911, a new member of the IS3 group of insertion sequences. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4090–4099. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4090-4099.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch P. J., Beerthuyzen M. M., de Vos W. M. Nucleotide sequence of IS904 from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis strain NIZO R5. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4253–4254. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch P. J., De Vos W. M. Characterization of the novel nisin-sucrose conjugative transposon Tn5276 and its insertion in Lactococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1280–1287. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1280-1287.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauch P. J., de Vos W. M. Identification and characterization of genes involved in excision of the Lactococcus lactis conjugative transposon Tn5276. J Bacteriol. 1994 Apr;176(8):2165–2171. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.8.2165-2171.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steen M. T., Chung Y. J., Hansen J. N. Characterization of the nisin gene as part of a polycistronic operon in the chromosome of Lactococcus lactis ATCC 11454. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):1181–1188. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1181-1188.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Nguyen N. Y., Sackett D. L., Donkersloot J. A. Transposon-encoded sucrose metabolism in Lactococcus lactis. Purification of sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase and genetic linkage to N5-(L-1-carboxyethyl)-L-ornithine synthase in strain K1. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14573–14579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos W. M., Mulders J. W., Siezen R. J., Hugenholtz J., Kuipers O. P. Properties of nisin Z and distribution of its gene, nisZ, in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jan;59(1):213–218. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.213-218.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Guchte M., Kok J., Venema G. Gene expression in Lactococcus lactis. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1992 Feb;8(2):73–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb04958.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meer J. R., Polman J., Beerthuyzen M. M., Siezen R. J., Kuipers O. P., De Vos W. M. Characterization of the Lactococcus lactis nisin A operon genes nisP, encoding a subtilisin-like serine protease involved in precursor processing, and nisR, encoding a regulatory protein involved in nisin biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2578–2588. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2578-2588.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]