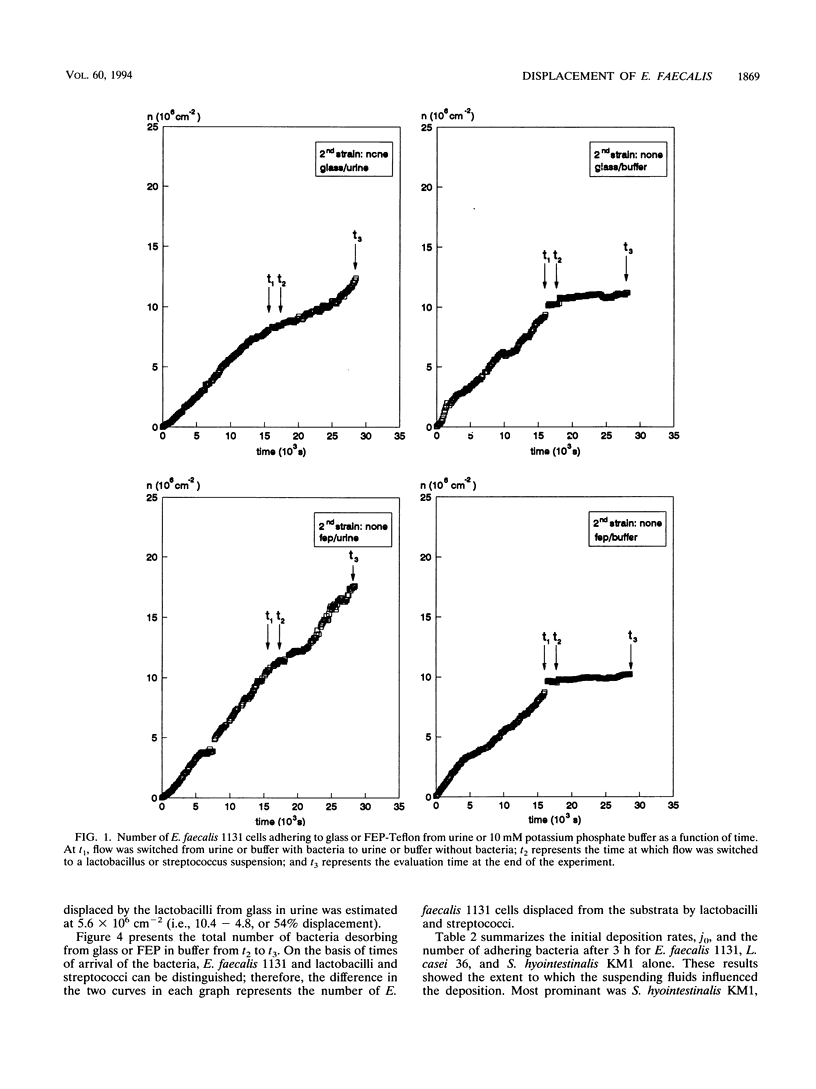
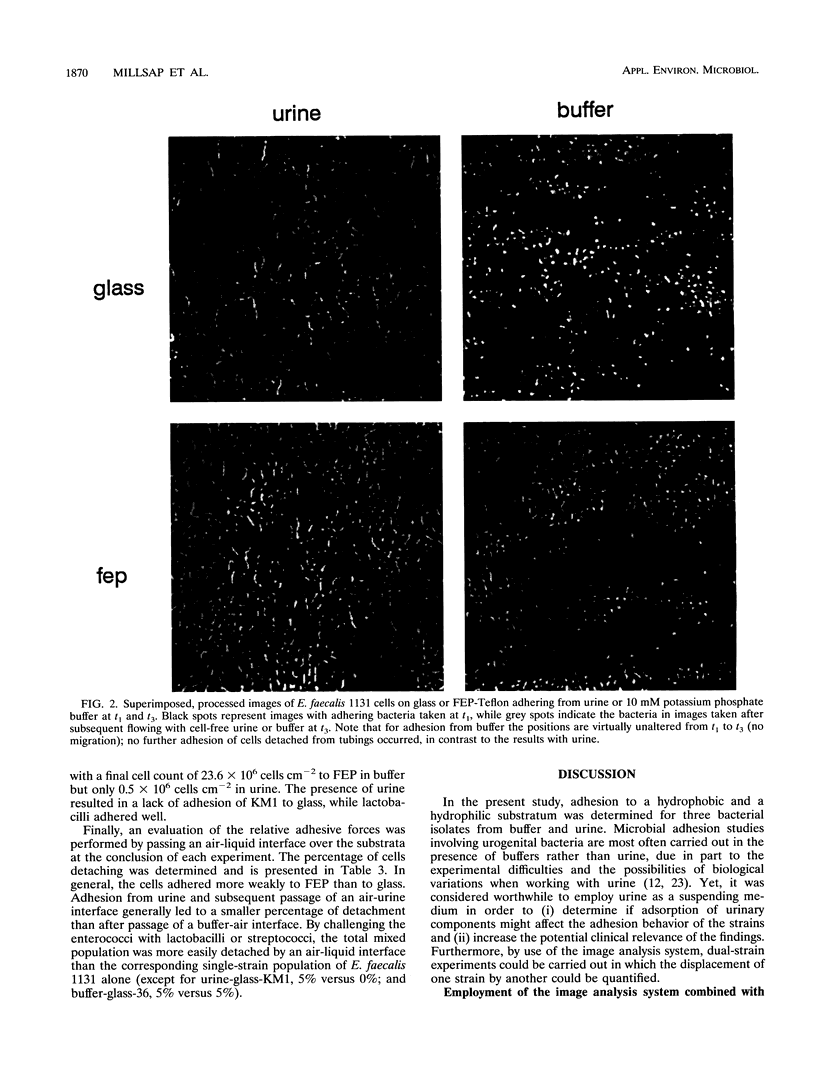
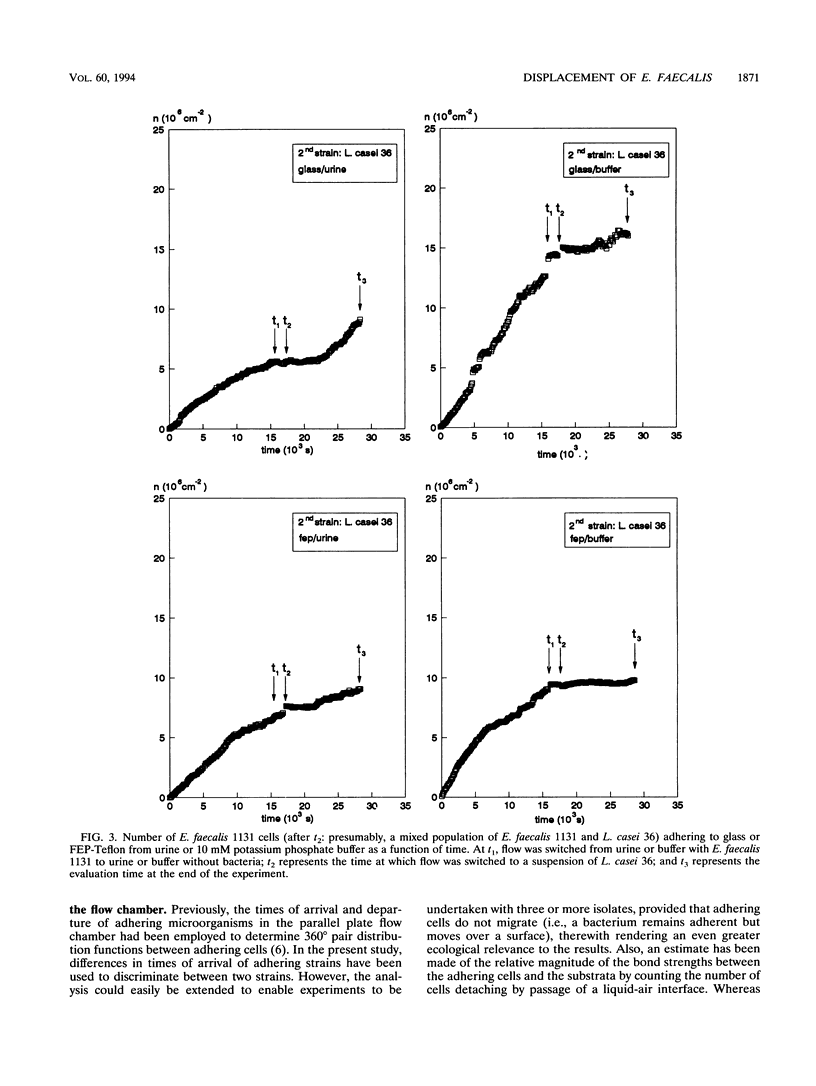
Abstract
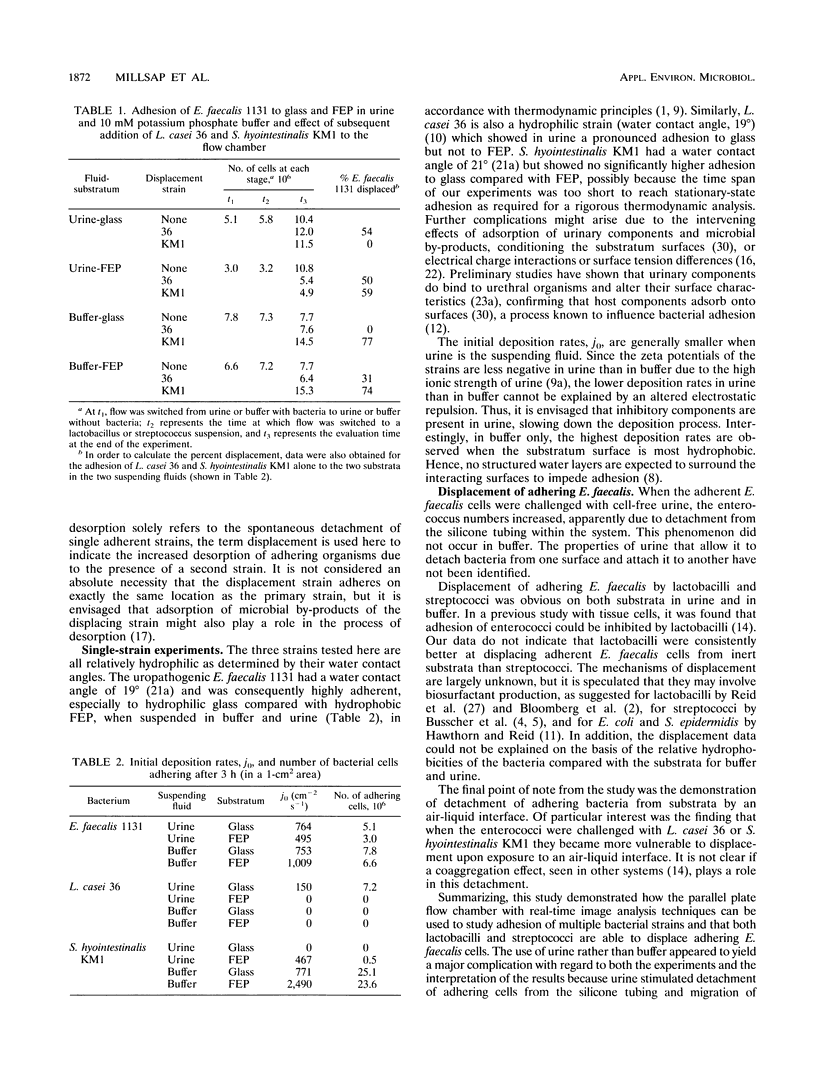
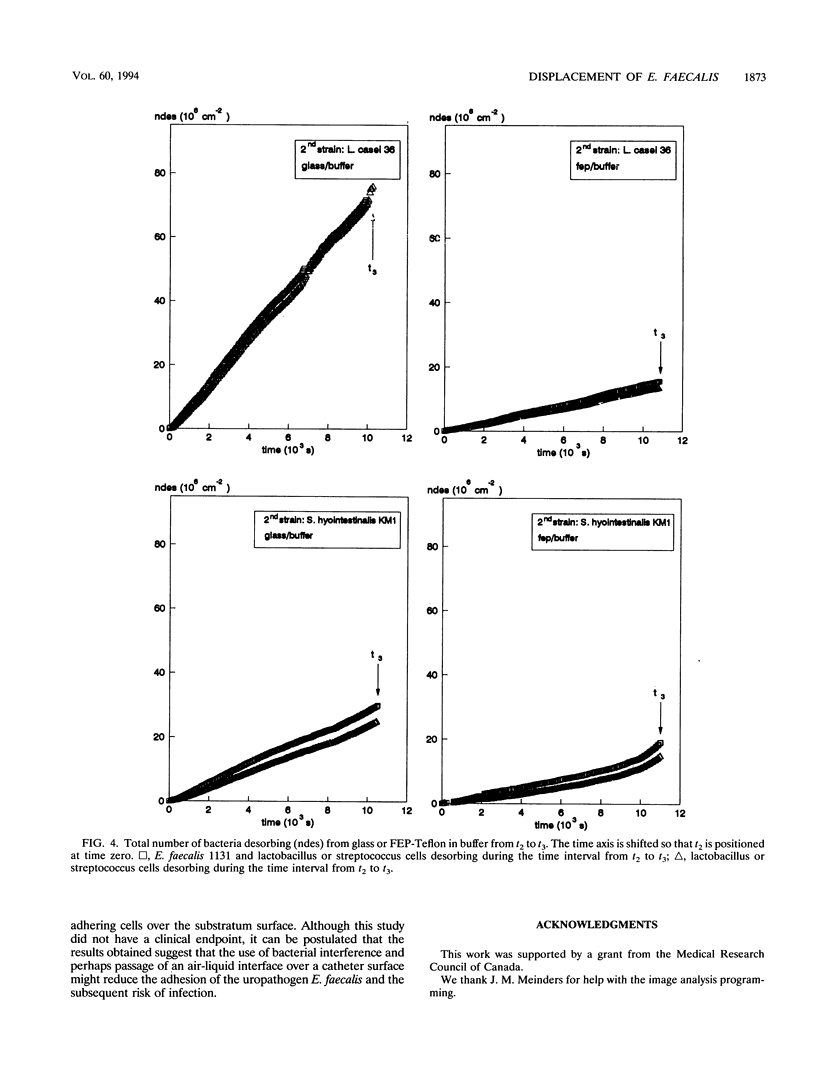
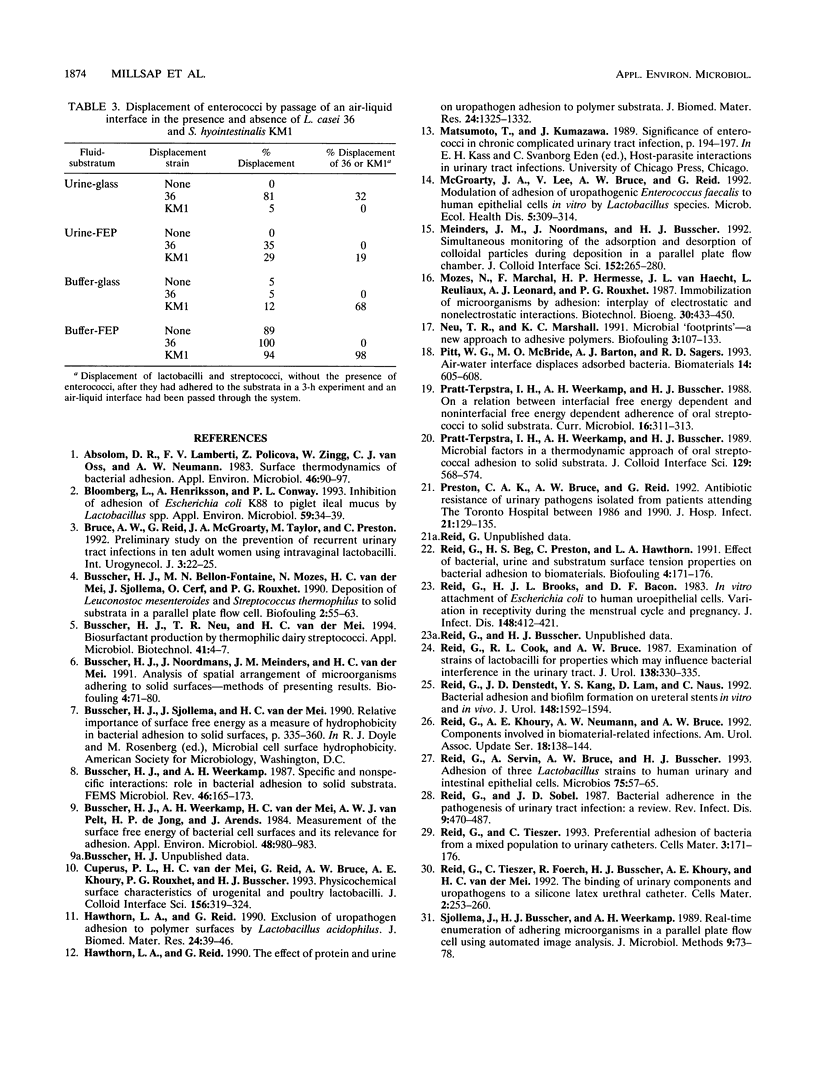
The displacement of Enterococcus faecalis 1131 from hydrophobic and hydrophilic substrata by isolates of Lactobacillus casei 36 and Streptococcus hyointestinalis KM1 was studied in a parallel plate flow chamber. The experiments were conducted with either 10 mM potassium phosphate buffer or human urine as the suspending fluid, and adhesion and displacement were measured by real-time in situ image analysis. The results showed that E. faecalis 1131 was displaced by lactobacilli (31%) and streptococci (74%) from fluorinated ethylene propylene in buffer and that displacement by lactobacilli was even more effective on a glass substratum in urine (54%). The passage of an air-liquid interface significantly impacted on adhesion, especially when the surface had been challenged with lactobacilli (up to 100% displacement) or streptococci (up to 94% displacement). These results showed that the parallel plate flow system with real-time in situ image analysis was effective for studying bacterial adhesion and that uropathogenic enterococci can be displaced by indigenous bacteria.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Absolom D. R., Lamberti F. V., Policova Z., Zingg W., van Oss C. J., Neumann A. W. Surface thermodynamics of bacterial adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):90–97. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.90-97.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomberg L., Henriksson A., Conway P. L. Inhibition of adhesion of Escherichia coli K88 to piglet ileal mucus by Lactobacillus spp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jan;59(1):34–39. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.34-39.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busscher H. J., Weerkamp A. H., van der Mei H. C., van Pelt A. W., de Jong H. P., Arends J. Measurement of the surface free energy of bacterial cell surfaces and its relevance for adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Nov;48(5):980–983. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.5.980-983.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorn L. A., Reid G. Exclusion of uropathogen adhesion to polymer surfaces by Lactobacillus acidophilus. J Biomed Mater Res. 1990 Jan;24(1):39–46. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820240105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorn L., Reid G. The effect of protein and urine on uropathogen adhesion to polymer substrata. J Biomed Mater Res. 1990 Oct;24(10):1325–1332. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820241005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt W. G., McBride M. O., Barton A. J., Sagers R. D. Air-water interface displaces adsorbed bacteria. Biomaterials. 1993 Jul;14(8):605–608. doi: 10.1016/0142-9612(93)90179-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. A., Bruce A. W., Reid G. Antibiotic resistance of urinary pathogens isolated from patients attending the Toronto Hospital between 1986 and 1990. J Hosp Infect. 1992 Oct;22(2):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(92)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G., Brooks H. J., Bacon D. F. In vitro attachment of Escherichia coli to human uroepithelial cells: variation in receptivity during the menstrual cycle and pregnancy. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):412–421. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G., Cook R. L., Bruce A. W. Examination of strains of lactobacilli for properties that may influence bacterial interference in the urinary tract. J Urol. 1987 Aug;138(2):330–335. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)43137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G., Denstedt J. D., Kang Y. S., Lam D., Nause C. Microbial adhesion and biofilm formation on ureteral stents in vitro and in vivo. J Urol. 1992 Nov;148(5):1592–1594. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)36976-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G., Servin A. L., Bruce A. W., Busscher H. J. Adhesion of three Lactobacillus strains to human urinary and intestinal epithelial cells. Microbios. 1993;75(302):57–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G., Sobel J. D. Bacterial adherence in the pathogenesis of urinary tract infection: a review. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 May-Jun;9(3):470–487. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.3.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]