Abstract
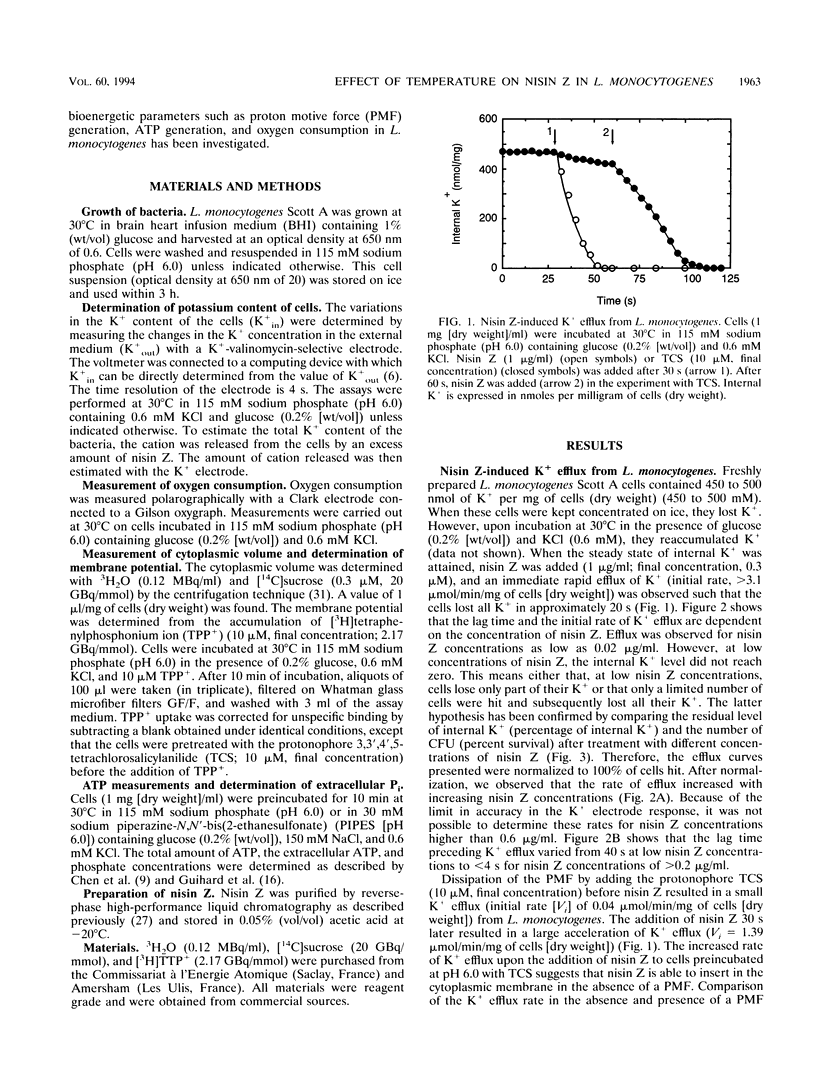
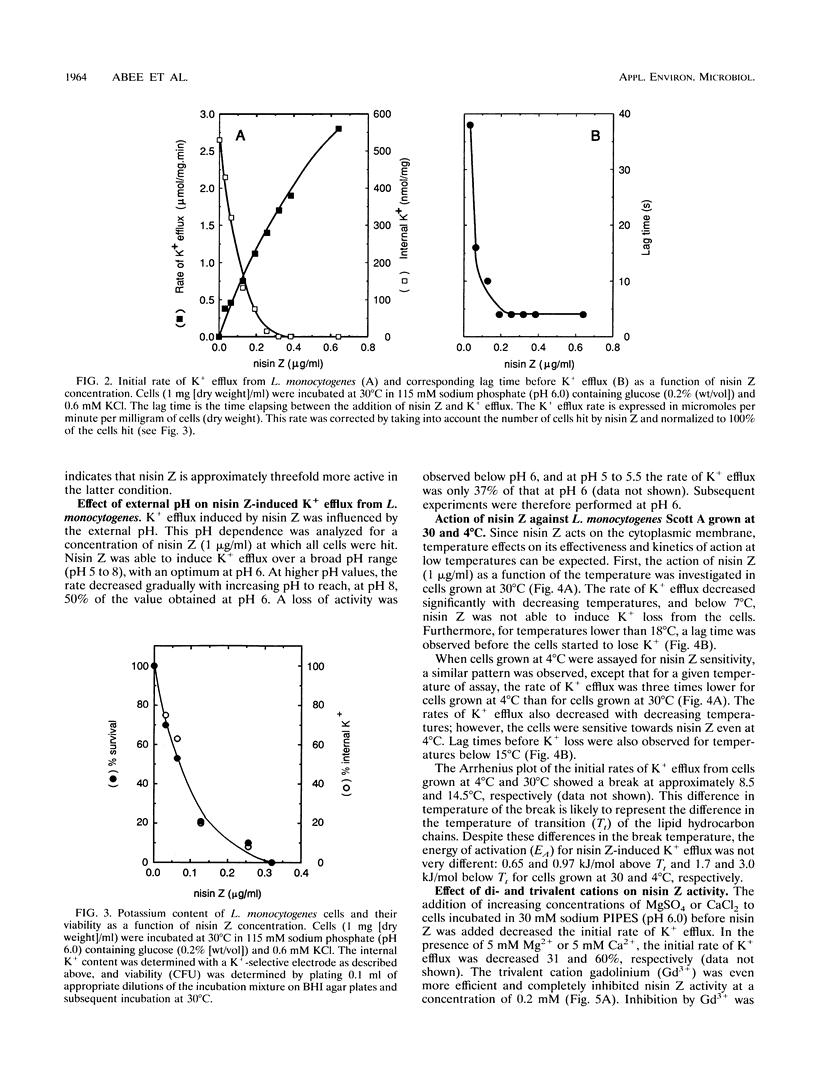
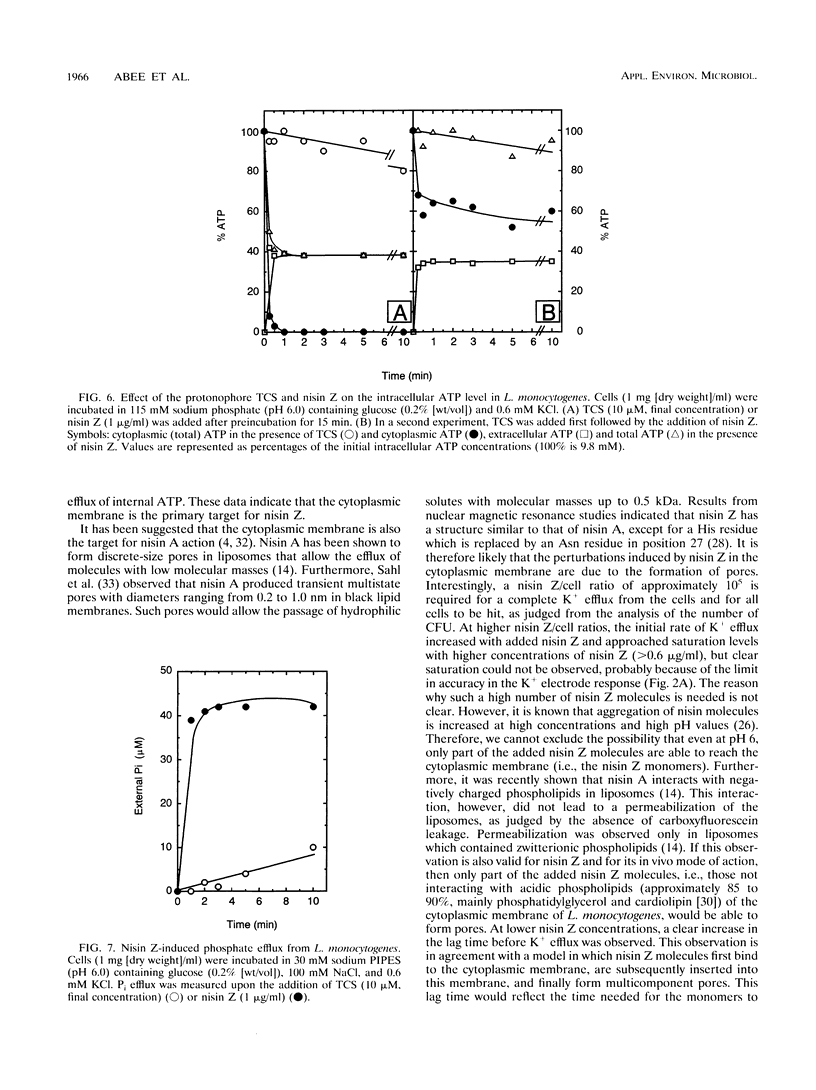
Nisin Z, a natural nisin variant, was recently isolated from Lactococcus lactis subspecies lactis NIZO 22186. The gene for this lantibiotic, designated nisZ, has been cloned, and its nucleotide sequence was found to be identical to that of the precursor nisin gene with the exception of a single mutation resulting in the substitution of Asn-27 for His-27 in the mature polypeptide (J. W. M. Mulders, I. J. Boerrigter, H. S. Rollema, R. J. Siezen, and W. M. de Vos, Eur. J. Biochem. 201:581-584, 1991). A K+ electrode was used to investigate the effect of various environmental parameters on the action of nisin Z against Listeria monocytogenes. Addition of nisin Z resulted in immediate loss of cell K+, depolarization of the cytoplasmic membrane, inhibition of respiratory activity, and hydrolysis and partial efflux of cellular ATP. The action of nisin Z was optimal at pH 6.0 and was significantly reduced by di- and trivalent cations. The lanthanide gadolinium (Gd3+) was an efficient inhibitor and prevented nisin Z activity completely at a concentration of 0.2 mM. Nisin Z-induced loss of cell K+ was reduced at low temperatures, presumably as a result of the increased ordering of the lipid hydrocarbon chains in the cytoplasmic membrane. In cells grown at 30°C, the action of nisin Z was prevented below 7°C, whereas in cells grown at 4°C nisin Z was able to induce K+ leakage at this low temperature.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abee T., Klaenhammer T. R., Letellier L. Kinetic studies of the action of lactacin F, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus johnsonii that forms poration complexes in the cytoplasmic membrane. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Mar;60(3):1006–1013. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.3.1006-1013.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benkerroum N., Sandine W. E. Inhibitory action of nisin against Listeria monocytogenes. J Dairy Sci. 1988 Dec;71(12):3237–3245. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(88)79929-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrier C., Coulombe A., Szabo I., Zoratti M., Ghazi A. Gadolinium ion inhibits loss of metabolites induced by osmotic shock and large stretch-activated channels in bacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 1;206(2):559–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger P., Letellier L. Characterization of ion channels involved in the penetration of phage T4 DNA into Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9767–9775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruno M. E., Kaiser A., Montville T. J. Depletion of proton motive force by nisin in Listeria monocytogenes cells. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jul;58(7):2255–2259. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.7.2255-2259.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cociancich S., Ghazi A., Hetru C., Hoffmann J. A., Letellier L. Insect defensin, an inducible antibacterial peptide, forms voltage-dependent channels in Micrococcus luteus. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19239–19245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. M., Peterkin P. I. Listeria monocytogenes, a food-borne pathogen. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):476–511. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.476-511.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao F. H., Abee T., Konings W. N. Mechanism of action of the peptide antibiotic nisin in liposomes and cytochrome c oxidase-containing proteoliposomes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Aug;57(8):2164–2170. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.8.2164-2170.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcerá M. J., Elferink M. G., Driessen A. J., Konings W. N. In vitro pore-forming activity of the lantibiotic nisin. Role of protonmotive force and lipid composition. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Mar 1;212(2):417–422. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17677.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gounot A. M. Bacterial life at low temperature: physiological aspects and biotechnological implications. J Appl Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;71(5):386–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1991.tb03806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guihard G., Bénédetti H., Besnard M., Letellier L. Phosphate efflux through the channels formed by colicins and phage T5 in Escherichia coli cells is responsible for the fall in cytoplasmic ATP. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):17775–17780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaenhammer T. R. Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria. Biochimie. 1988 Mar;70(3):337–349. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaenhammer T. R. Genetics of bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1993 Sep;12(1-3):39–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1993.tb00012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu W., Hansen J. N. Some chemical and physical properties of nisin, a small-protein antibiotic produced by Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Aug;56(8):2551–2558. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.8.2551-2558.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulders J. W., Boerrigter I. J., Rollema H. S., Siezen R. J., de Vos W. M. Identification and characterization of the lantibiotic nisin Z, a natural nisin variant. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Nov 1;201(3):581–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojcius D. M., Young J. D. Cytolytic pore-forming proteins and peptides: is there a common structural motif? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Jun;16(6):225–229. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90090-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H. The measurement of membrane potential and deltapH in cells, organelles, and vesicles. Methods Enzymol. 1979;55:547–569. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)55066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahl H. G., Kordel M., Benz R. Voltage-dependent depolarization of bacterial membranes and artificial lipid bilayers by the peptide antibiotic nisin. Arch Microbiol. 1987;149(2):120–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00425076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens K. A., Klapes N. A., Sheldon B. W., Klaenhammer T. R. Antimicrobial action of nisin against Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharide mutants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 May;58(5):1786–1788. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.5.1786-1788.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens K. A., Sheldon B. W., Klapes N. A., Klaenhammer T. R. Nisin treatment for inactivation of Salmonella species and other gram-negative bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Dec;57(12):3613–3615. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.12.3613-3615.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


