Abstract
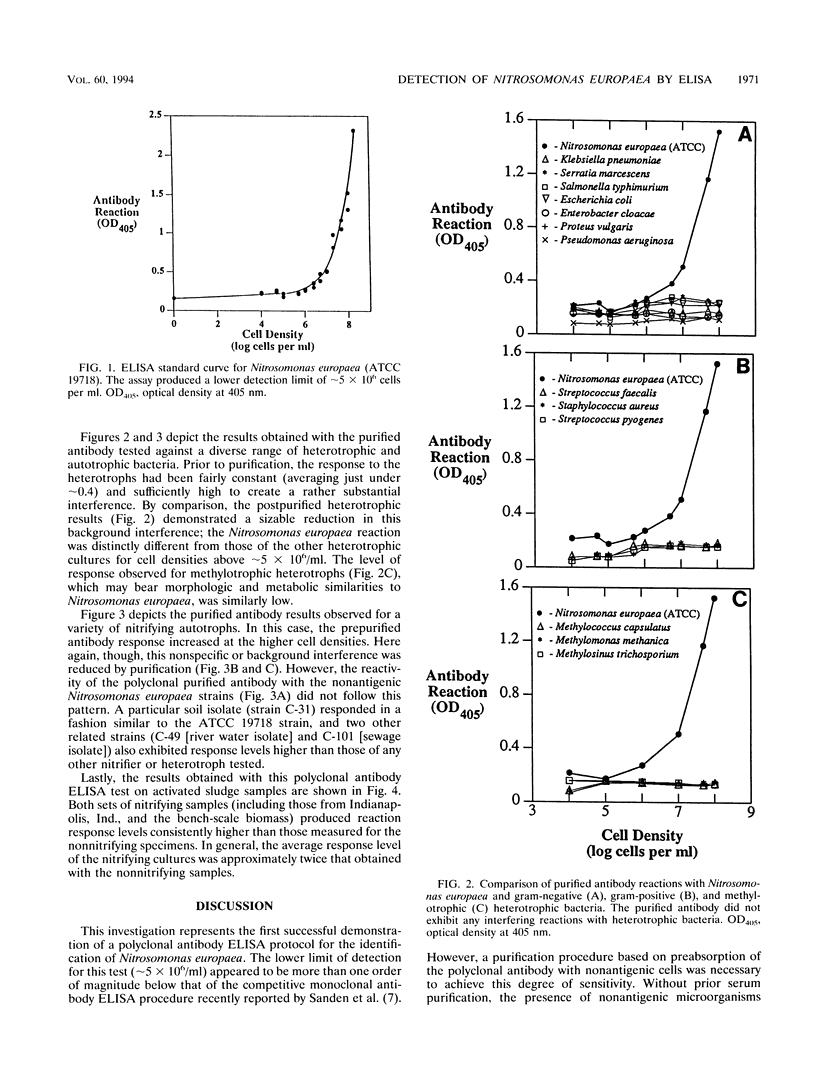
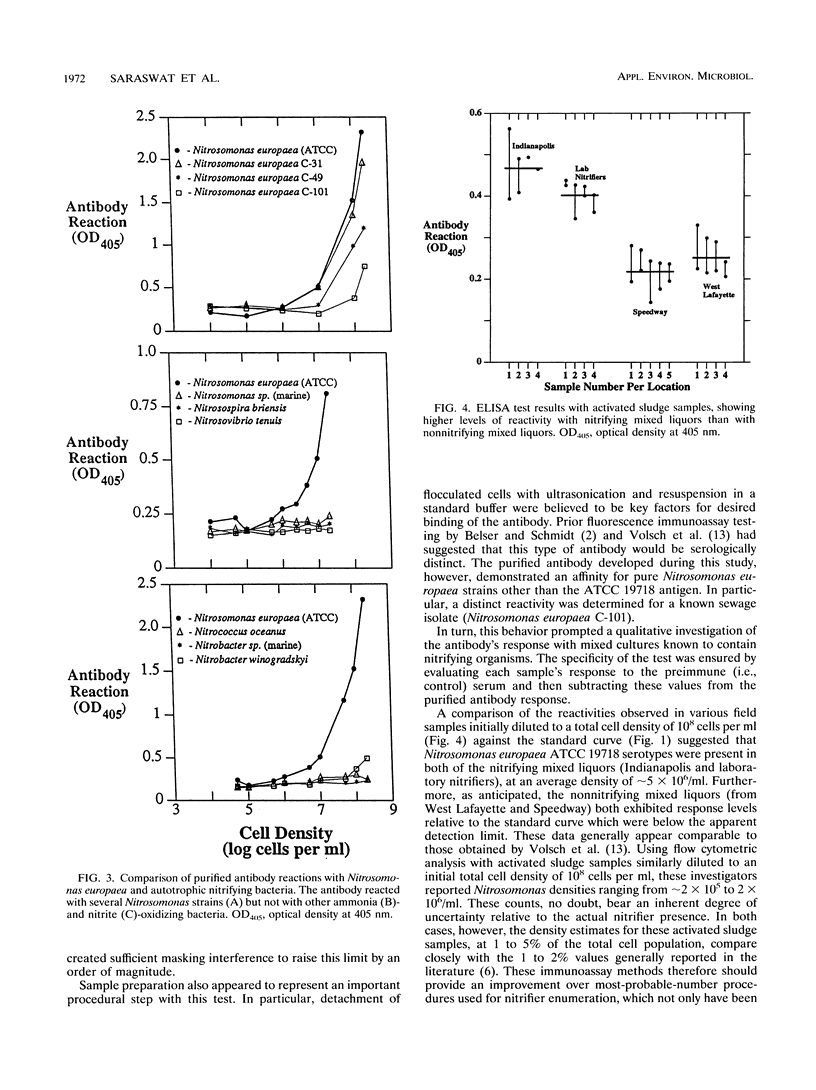
An exploratory effort to selectively detect the presence of a nitrifying bacterium, Nitrosomonas europaea, successfully demonstrated the fundamental utility of an enzyme-based immunoassay protocol. The applied polyclonal antibody test seemingly offered a marked improvement over the available analytical options, including plating, activity, and fluorescence immunoassay techniques. Following an initial purification step to enhance overall specificity, this procedure had an apparent lower limit of detection of ∼5 × 106 cells per ml. Tests conducted with activated sludge samples exhibited a distinct difference between nitrifying and nonnitrifying mixed liquors, although the highest Nitrosomonas levels observed (i.e., at 1 to 2% of the overall viable cell density) were relatively close to the latter detection boundary.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belser L. W., Mays E. L. Use of nitrifier activity measurements to estimate the efficiency of viable nitrifier counts in soils and sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Apr;43(4):945–948. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.4.945-948.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belser L. W., Schmidt E. L. Serological diversity within a terrestrial ammonia-oxidizing population. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Oct;36(4):589–593. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.4.589-593.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. B. Population ecology of nitrifiers in a stream receiving geothermal inputs of ammonium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1170–1177. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1170-1177.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Bohlool B. B., Schmidt E. L. Autecological study of the chemoautotroph Nitrobacter by immunofluorescence. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):124–129. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.124-129.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matulewich V. A., Strom P. F., Finstein M. S. Length of incubation for enumerating nitrifying bacteria present in various environments. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Feb;29(2):265–268. doi: 10.1128/am.29.2.265-268.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E. L., Bakole R. O., Bohlool B. B. Fluorescent-antibody approach to study of rhizobia in soil. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):1987–1992. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.1987-1992.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Völsch A., Nader W. F., Geiss H. K., Nebe G., Birr C. Detection and analysis of two serotypes of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in sewage plants by flow cytometry. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Aug;56(8):2430–2435. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.8.2430-2435.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward B. B., Carlucci A. F. Marine ammonia- and nitrite-oxidizing bacteria: serological diversity determined by immunofluorescence in culture and in the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Aug;50(2):194–201. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.2.194-201.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward B. B., Perry M. J. Immunofluorescent Assay for the Marine Ammonium-Oxidizing Bacterium Nitrosococcus oceanus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):913–918. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.913-918.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



