Abstract
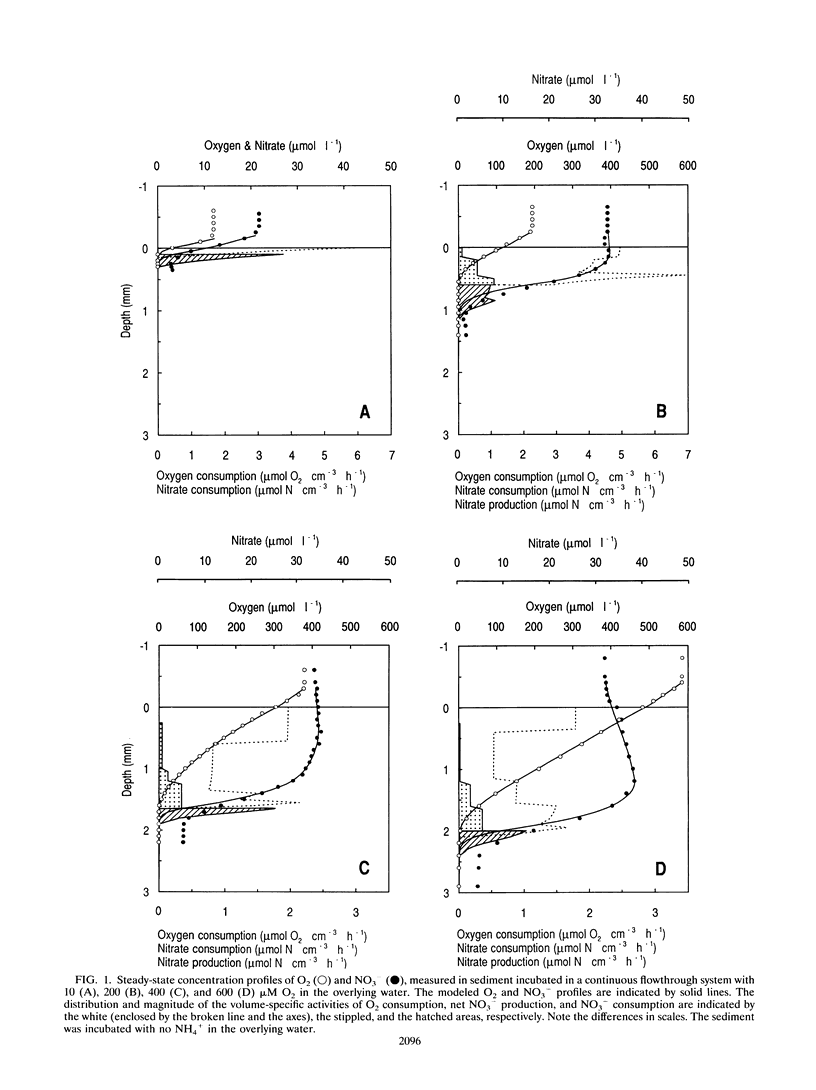
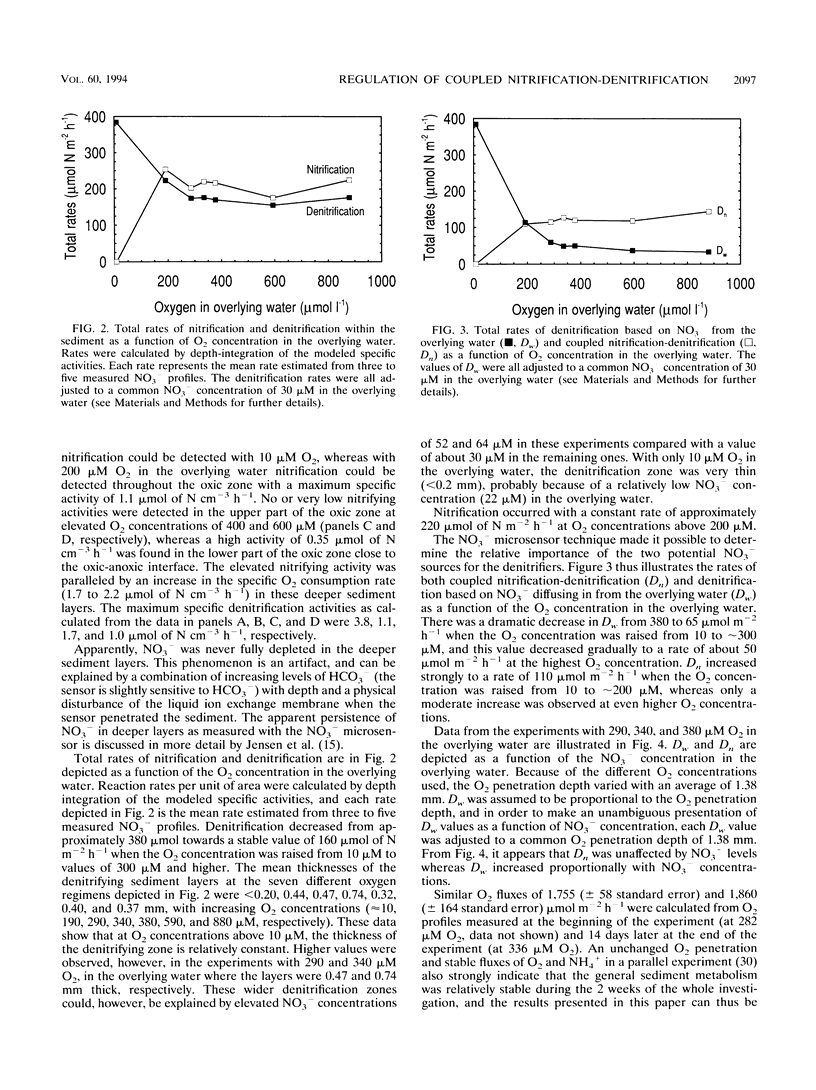
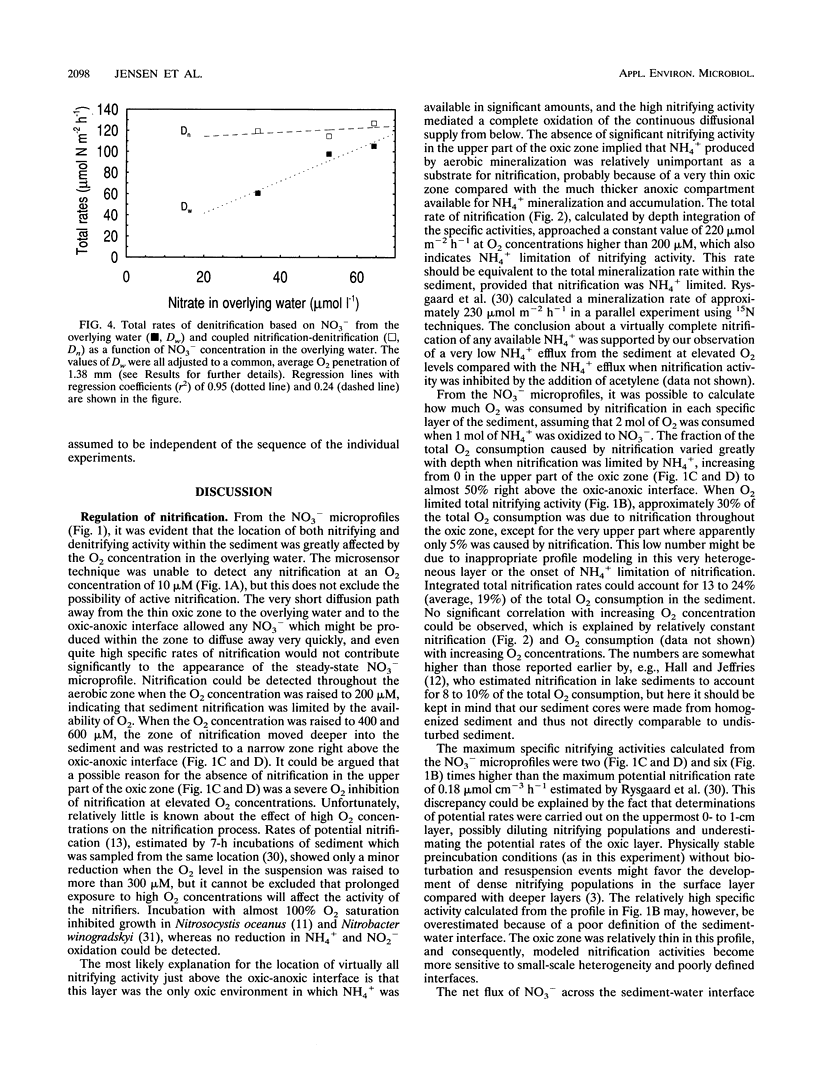
The coupling between nitrification and denitrification and the regulation of these processes by oxygen were studied in freshwater sediment microcosms with O2 and NO3- microsensors. Depth profiles of nitrification (indicated as NO3- production), denitrification (indicated as NO3- consumption), and O2 consumption activities within the sediment were calculated from the measured concentration profiles. From the concentration profiles, it was furthermore possible to distinguish between the rate of denitrification based on the diffusional supply of NO3- from the overlying water and the rate based on NO3- supplied by benthic nitrification (Dw and Dn, respectively). An increase in O2 concentration caused a deeper O2 penetration while a decrease in Dw and an increase in Dn were observed. The relative importance for total denitrification of NO3- produced by nitrification thus increased compared with NO3- supplied from the water phase. The decrease in Dw at high oxygen was due to an increase in diffusion path for NO3- from the overlying water to the denitrifying layers in the anoxic sediment. At high O2 concentrations, nitrifying activity was restricted to the lower part of the oxic zone where there was a continuous diffusional supply of NH4+ from deeper mineralization processes, and the long diffusion path from the nitrification zone to the overlying water compared with the path to the denitrifying layers led to a stimulation in Dn.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binnerup S. J., Jensen K., Revsbech N. P., Jensen M. H., Sørensen J. Denitrification, dissimilatory reduction of nitrate to ammonium, and nitrification in a bioturbated estuarine sediment as measured with N and microsensor techniques. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):303–313. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.303-313.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalsgaard T., Bak F. Effect of acetylene on nitrous oxide reduction and sulfide oxidation in batch and gradient cultures of Thiobacillus denitrificans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 May;58(5):1601–1608. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.5.1601-1608.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen K. The growth and respiration of Nitrosocystis oceanus at different partial pressures of oxygen. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Mar;42(3):387–396. doi: 10.1099/00221287-42-3-387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen K., Revsbech N. P., Nielsen L. P. Microscale distribution of nitrification activity in sediment determined with a shielded microsensor for nitrate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Oct;59(10):3287–3296. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.10.3287-3296.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühl M., Jørgensen B. B. Microsensor measurements of sulfate reduction and sulfide oxidation in compact microbial communities of aerobic biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Apr;58(4):1164–1174. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.4.1164-1174.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



