Abstract
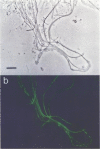
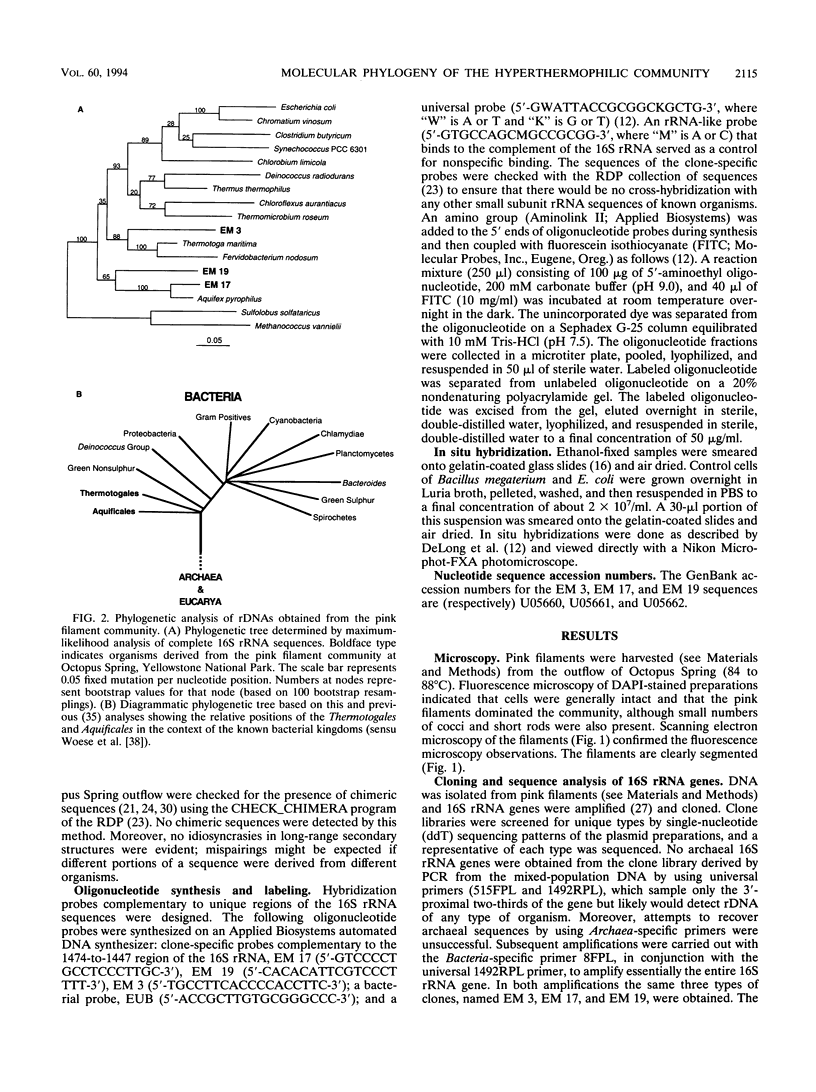
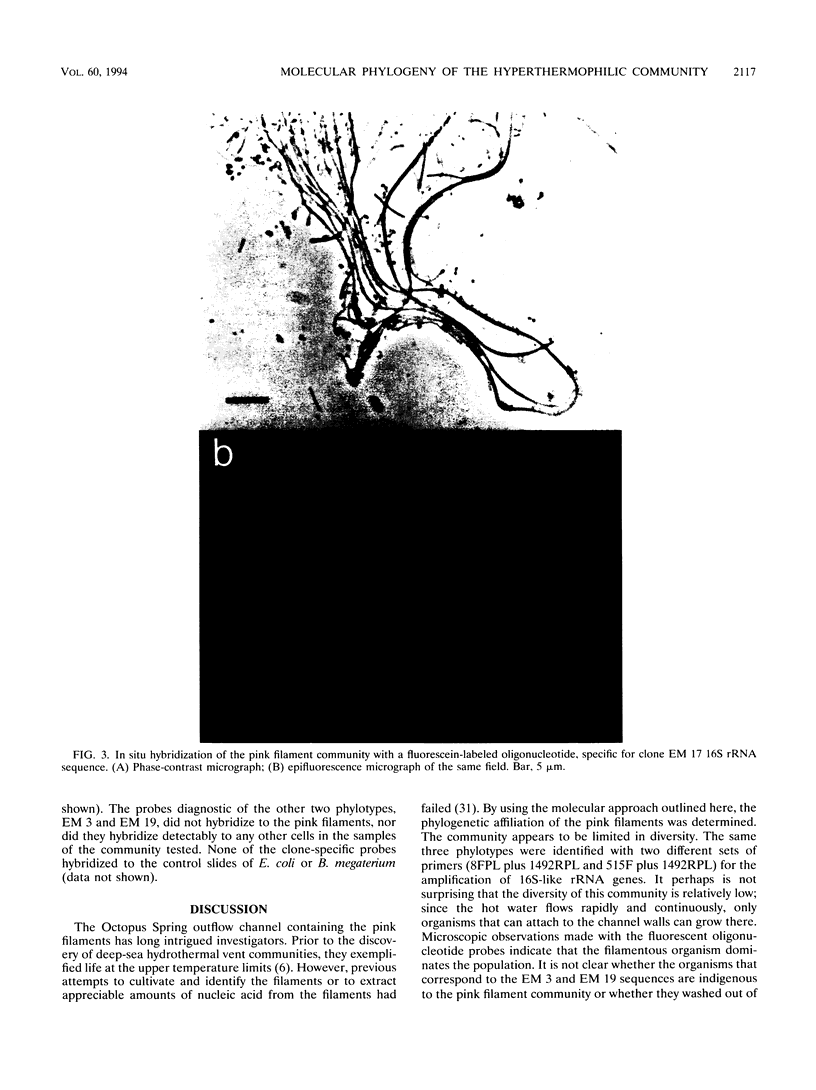
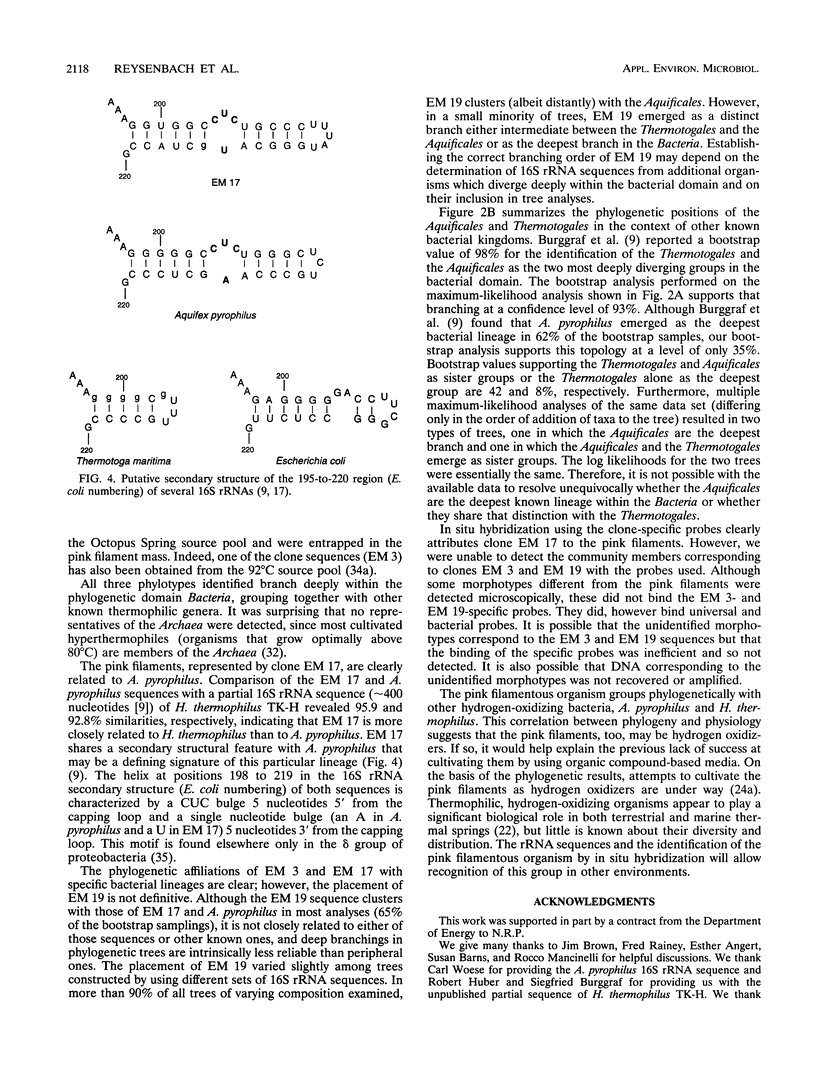
The phylogenetic diversity of a well-known pink filament community associated with the 84 to 88 degrees C outflow from Octopus Spring, Yellowstone National Park, was examined. Three phylogenetic types ("phylotypes"), designated EM 3, EM 17, and EM 19, were identified by cloning and sequencing the small subunit rRNA genes (16S rDNA) obtained by PCR amplification of mixed-population DNA. All three phylotypes diverge deeply within the phylogenetic domain Bacteria sensu Woese (C. R. Woese, O. Kandler, and M. L. Wheelis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:4576-4579, 1990). No members of the Archaea or Eucarya were detected. EM 3 comprises a unique lineage within the Thermotogales group, and EM 17 and EM 19 are affiliated with the Aquificales. A total of 35 clones were examined, of which the majority (26 clones) were of a single sequence type (EM 17) closely related to Aquifex pyrophilus. In situ hybridization with clone-specific probes attributes the majority sequence, EM 17, to the pink filaments.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angert E. R., Clements K. D., Pace N. R. The largest bacterium. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):239–241. doi: 10.1038/362239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barns S. M., Fundyga R. E., Jeffries M. W., Pace N. R. Remarkable archaeal diversity detected in a Yellowstone National Park hot spring environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1609–1613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollet C., Gevaudan M. J., de Lamballerie X., Zandotti C., de Micco P. A simple method for the isolation of chromosomal DNA from gram positive or acid-fast bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1955–1955. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott T. L., Brock T. D. Bacterial growth rates above 90 degrees C in Yellowstone hot springs. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1411–1412. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D., Brock M. L., Bott T. L., Edwards M. R. Microbial life at 90 C: the sulfur bacteria of Boulder Spring. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):303–314. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.303-314.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D., Darland G. K. Limits of microbial existence: temperature and pH. Science. 1970 Sep 25;169(3952):1316–1318. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3952.1316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D. Life at high temperatures. Evolutionary, ecological, and biochemical significance of organisms living in hot springs is discussed. Science. 1967 Nov;158(3804):1012–1019. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3804.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burggraf S., Olsen G. J., Stetter K. O., Woese C. R. A phylogenetic analysis of Aquifex pyrophilus. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1992 Aug;15(3):352–356. doi: 10.1016/S0723-2020(11)80207-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong E. F. Archaea in coastal marine environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5685–5689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong E. F., Wickham G. S., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic stains: ribosomal RNA-based probes for the identification of single cells. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1360–1363. doi: 10.1126/science.2466341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol. 1981;17(6):368–376. doi: 10.1007/BF01734359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., DeLong E. F., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic group-specific oligodeoxynucleotide probes for identification of single microbial cells. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):720–726. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.720-726.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R. Collection of small subunit (16S- and 16S-like) ribosomal RNA structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3051–3054. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Woese C. R. Higher order structural elements in ribosomal RNAs: pseudo-knots and the use of noncanonical pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):663–667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopczynski E. D., Bateson M. M., Ward D. M. Recognition of chimeric small-subunit ribosomal DNAs composed of genes from uncultivated microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Feb;60(2):746–748. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.2.746-748.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen N., Olsen G. J., Maidak B. L., McCaughey M. J., Overbeek R., Macke T. J., Marsh T. L., Woese C. R. The ribosomal database project. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3021–3023. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reysenbach A. L., Giver L. J., Wickham G. S., Pace N. R. Differential amplification of rRNA genes by polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Oct;58(10):3417–3418. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.10.3417-3418.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D. A., Lane D. J., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Characterization of a Yellowstone hot spring microbial community by 5S rRNA sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1379–1384. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1379-1384.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Giovannoni S. J., Woese C. R. The Deinococcus-Thermus phylum and the effect of rRNA composition on phylogenetic tree construction. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1989;11:128–134. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(89)80051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Achenbach L., Rouviere P., Mandelco L. Archaeal phylogeny: reexamination of the phylogenetic position of Archaeoglobus fulgidus in light of certain composition-induced artifacts. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1991;14(4):364–371. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(11)80311-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Gutell R., Gupta R., Noller H. F. Detailed analysis of the higher-order structure of 16S-like ribosomal ribonucleic acids. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Dec;47(4):621–669. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.4.621-669.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Kandler O., Wheelis M. L. Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4576–4579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]