Abstract
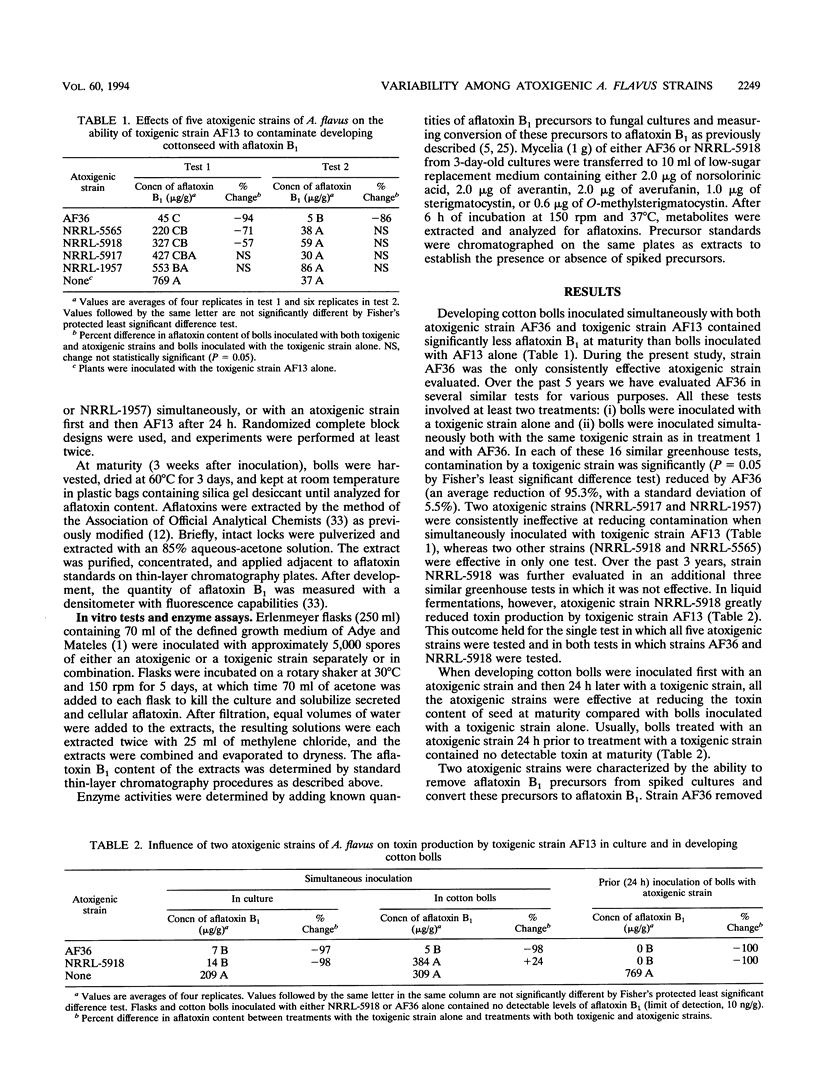
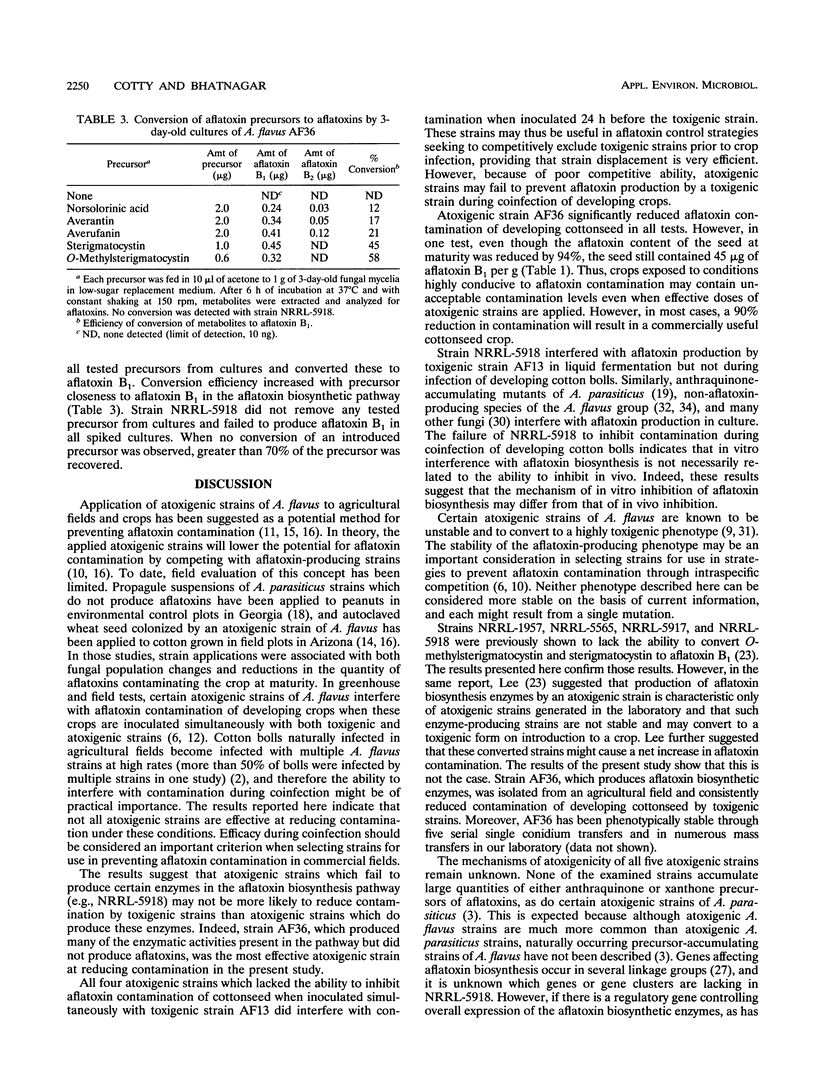
Five strains of Aspergillus flavus lacking the ability to produce aflatoxins were examined in greenhouse tests for the ability to prevent a toxigenic strain from contaminating developing cottonseed with aflatoxins. All atoxigenic strains reduced contamination when inoculated into developing bolls 24 h prior to the toxigenic strain. However, only one strain, AF36, was highly effective when inoculated simultaneously with the toxigenic strain. All five strains were able to inhibit aflatoxin production by the toxigenic strain in liquid fermentation. Thus, in vitro activity did not predict the ability of an atoxigenic strain to prevent contamination of developing bolls. Therefore, strain selection for competitive exclusion to prevent aflatoxin contamination should include evaluation of efficacy in developing crops prior to field release. Atoxigenic strains were also characterized by the ability to convert several aflatoxin precursors into aflatoxin B1. Four atoxigenic strains failed to convert any of the aflatoxin biosynthetic precursors to aflatoxins. However, the strain (AF36) most effective in preventing aflatoxin contamination in developing bolls converted all tested precursors into aflatoxin B1, indicating that this strain made enzymes in the aflatoxin biosynthetic pathway.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADYE J., MATELES R. I. INCORPORATION OF LABELLED COMPOUNDS INTO AFLATOXINS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 11;86:418–420. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar D., McCormick S. P., Lee L. S., Hill R. A. Identification of O-methylsterigmatocystin as an aflatoxin B1 and G1 precursor in Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1028–1033. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1028-1033.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P. K., Cary J. W., Bhatnagar D., Cleveland T. E., Bennett J. W., Linz J. E., Woloshuk C. P., Payne G. A. Cloning of the Aspergillus parasiticus apa-2 gene associated with the regulation of aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Oct;59(10):3273–3279. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.10.3273-3279.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevström G., Ljunggren H. Aflatoxin formation and the dual phenomenon in Aspergillus flavus Link. Mycopathologia. 1985 Dec;92(3):129–139. doi: 10.1007/BF00437624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich K. Effect on aflatoxin production of competition between wild-type and mutant strains of Aspergillus parasiticus. Mycopathologia. 1987 Feb;97(2):93–96. doi: 10.1007/BF00436844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzman C. P., Horn B. W., Hesseltine C. W. Aspergillus nomius, a new aflatoxin-producing species related to Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus tamarii. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1987;53(3):147–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00393843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S. Metabolic precursor regulation of aflatoxin formation in toxigenic and non-toxigenic strains of Aspergillus flavus. Mycopathologia. 1989 Sep;107(2-3):127–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00707549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick S. P., Bhatnagar D., Lee L. S. Averufanin is an aflatoxin B1 precursor between averantin and averufin in the biosynthetic pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):14–16. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.14-16.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papa K. E. Genetics of Aspergillus flavus: complementation and mapping of aflatoxin mutants. Genet Res. 1979 Aug;34(1):1–9. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300019236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. A., Nystrom G. J., Bhatnagar D., Cleveland T. E., Woloshuk C. P. Cloning of the afl-2 gene involved in aflatoxin biosynthesis from Aspergillus flavus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jan;59(1):156–162. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.156-162.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shantha T., Rati E. R., Shankar T. N. Behaviour of Aspergillus flavus in presence of Aspergillus niger during biosynthesis of aflatoxin B. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1990 Aug;58(2):121–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00422728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Nakamura Y., Nakajima H., Ando Y., Hamasaki T. Enzymatic conversion of norsolorinic acid to averufin in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1340–1345. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1340-1345.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


