Abstract
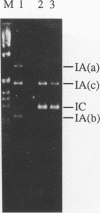
The expression of an insecticidal crystal protein gene of Bacillus thuringiensis under the control of the alpha-amylase gene promoter was investigated. The cryIC gene, which encodes a protein known to have a unique activity against Spodoptera (armyworm) species, was used in this investigation. The cryIC gene was placed, along with the alpha-amylase promoter from B. subtilis, in a B. thuringiensis-derived cloning vector, generating a pair of recombinant plasmids, pSB744 and pSB745. The cloning vector that contains the minimal replicon of B. thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki HD73 is stably maintained in a variety of B. thuringiensis strains, as previously reported by Gamel and Piot (Gene 120:17-26, 1992). The present study confirmed that the recombinant plasmids are also stably maintained in B. thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki Cry-B and HD73 growing in media without selection pressure for at least 48 h. The cryIC gene on the recombinant plasmids were notably expressed at high levels in both recombinant strains. Expression of the introduced cryIC gene on the recombinant plasmid in B. thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki HD73 did not impair expression of the resident cryIA(c) gene. The CryIA(c) protein is known to have a high level of activity against loopers such as Trichoplusia ni (the cabbage looper). As a result of coexpression of the introduced cryIC gene and the resident cryIA(c) gene, recombinant strain HD73 acquired an additional insecticidal activity against Spodoptera exigua (the beet armyworm) whereas the original activity level against T. ni was maintained.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams L. F., Brown K. L., Whiteley H. R. Molecular cloning and characterization of two genes encoding sigma factors that direct transcription from a Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein gene promoter. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3846–3854. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3846-3854.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adang M. J., Staver M. J., Rocheleau T. A., Leighton J., Barker R. F., Thompson D. V. Characterized full-length and truncated plasmid clones of the crystal protein of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki HD-73 and their toxicity to Manduca sexta. Gene. 1985;36(3):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum J. A., Coyle D. M., Gilbert M. P., Jany C. S., Gawron-Burke C. Novel cloning vectors for Bacillus thuringiensis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3420–3428. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3420-3428.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. L., Whiteley H. R. Isolation of the second Bacillus thuringiensis RNA polymerase that transcribes from a crystal protein gene promoter. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6682–6688. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6682-6688.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamel P. H., Piot J. C. Characterization and properties of a novel plasmid vector for Bacillus thuringiensis displaying compatibility with host plasmids. Gene. 1992 Oct 12;120(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honée G., van der Salm T., Visser B. Nucleotide sequence of crystal protein gene isolated from B. thuringiensis subspecies entomocidus 60.5 coding for a toxin highly active against Spodoptera species. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6240–6240. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalman S., Kiehne K. L., Libs J. L., Yamamoto T. Cloning of a novel cryIC-type gene from a strain of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. galleriae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Apr;59(4):1131–1137. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.4.1131-1137.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura F., Doi R. H. Construction of a Bacillus subtilis double mutant deficient in extracellular alkaline and neutral proteases. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):442–444. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.442-444.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecadet M. M., Chaufaux J., Ribier J., Lereclus D. Construction of Novel Bacillus thuringiensis Strains with Different Insecticidal Activities by Transduction and Transformation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Mar;58(3):840–849. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.3.840-849.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macaluso A., Mettus A. M. Efficient transformation of Bacillus thuringiensis requires nonmethylated plasmid DNA. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1353–1356. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1353-1356.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettus A. M., Macaluso A. Expression of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin genes during vegetative growth. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Apr;56(4):1128–1134. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.4.1128-1134.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Imanaka T. Expression of the insecticidal protein gene from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. aizawai in Bacillus subtilis and in the thermophile Bacillus stearothermophilus by using the alpha-amylase promoter of the thermophile. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3208–3213. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3208-3213.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson W. L., Park Y. K., Henkin T. M., Won M., Weickert M. J., Gaskell J. A., Chambliss G. H. Catabolite repression-resistant mutations of the Bacillus subtilis alpha-amylase promoter affect transcription levels and are in an operator-like sequence. J Mol Biol. 1987 Dec 20;198(4):609–618. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Coote J. G. Genetic aspects of bacterial endospore formation. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):908–962. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.908-962.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J. Mapping of asporogenous mutations of Bacillus subtilis: a minimum estimate of the number of sporeulation operons. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1241–1253. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1241-1253.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priest F. G. Extracellular enzyme synthesis in the genus Bacillus. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):711–753. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.711-753.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahly D. P., Dingman D. W., Bulla L. A., Jr, Aronson A. I. Possible origin and function of the parasporal crystal in Bacillus thuringiensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 16;84(3):581–588. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90745-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weickert M. J., Chambliss G. H. Genetic analysis of the promoter region of the Bacillus subtilis alpha-amylase gene. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3656–3666. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3656-3666.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M., Galizzi A., Henner D. Nucleotide sequence of the amylase gene from Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):237–249. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]