Abstract
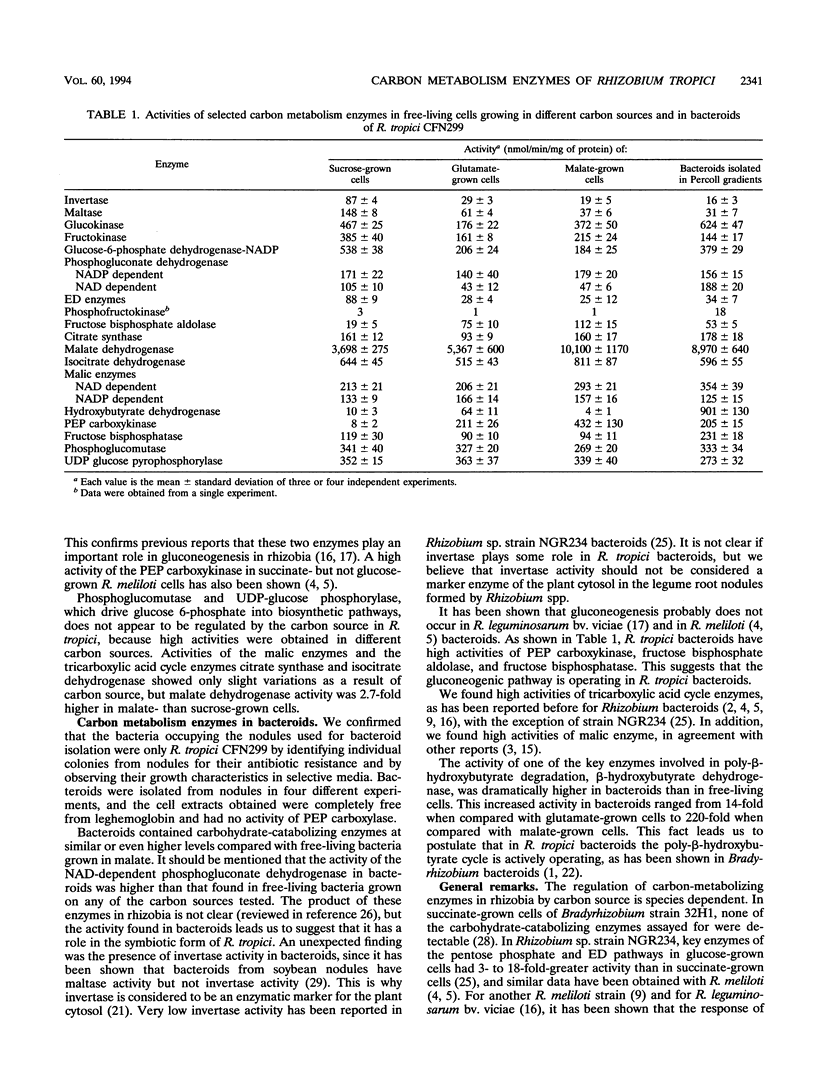
We determined the activities of selected enzymes involved in carbon metabolism in free-living cells of Rhizobium tropici CFN299 grown in minimal medium with different carbon sources and in bacteroids of the same strain. The set of enzymatic activities in sucrose-grown cells suggests that the pentose phosphate pathway, with the participation of the Entner-Doudoroff pathway, is probably the primary route for sugar catabolism. In glutamate- and malate-grown cells, high activities of the gluconeogenic enzymes (phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, fructose-6-phosphate aldolase, and fructose bisphosphatase) were detected. In bacteroids, isolated in Percoll gradients, the levels of activity for many of the enzymes measured were similar to those of malate-grown cells, except that higher activities of glucokinase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, and NAD-dependent phosphogluconate dehydrogenase were detected. Phosphoglucomutase and UDP glucose pyrophosphorylase showed high and constant levels under all growth conditions and in bacteroids.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Driscoll B. T., Finan T. M. NAD(+)-dependent malic enzyme of Rhizobium meliloti is required for symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(6):865–873. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Oresnik I., Bottacin A. Mutants of Rhizobium meliloti defective in succinate metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3396–3403. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3396-3403.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irigoyen Juan Jose, Sanchez-Diaz Manuel, Emerich David W. Carbon Metabolism Enzymes of Rhizobium meliloti Cultures and Bacteroids and Their Distribution within Alfalfa Nodules. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Aug;56(8):2587–2589. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.8.2587-2589.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRue T. A., Child J. J. Sensitive fluorometric assay for leghemoglobin. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 1;92(1):11–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90618-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessie T. G., Wyk J. C. Multiple forms of Pseudomonas multivorans glucose-6-phosphate and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenases: differences in size, pyridine nucleotide specificity, and susceptibility to inhibition by adenosine 5'-triphosphate. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1107–1117. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1107-1117.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maino V. C., Young F. E. Regulation of glucosylation of teichoic acid. I. Isolation of phosphoglucomutase in Bacillus subtilis 168. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5169–5175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Romero Esperanza, Rosenblueth Monica. Increased Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) Nodulation Competitiveness of Genetically Modified Rhizobium Strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Aug;56(8):2384–2388. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.8.2384-2388.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Romero E., Segovia L., Mercante F. M., Franco A. A., Graham P., Pardo M. A. Rhizobium tropici, a novel species nodulating Phaseolus vulgaris L. beans and Leucaena sp. trees. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;41(3):417–426. doi: 10.1099/00207713-41-3-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel K. D., Sanchez A., Fernandez L., Leemans J., Cevallos M. A. Rhizobium phaseoli symbiotic mutants with transposon Tn5 insertions. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):148–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.148-155.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reibach P. H., Mask P. L., Streeter J. G. A rapid one-step method for the isolation of bacteroids from root nodules of soybean plants, utilizing self-generating Percoll gradients. Can J Microbiol. 1981 May;27(5):491–495. doi: 10.1139/m81-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudick V. L., Weisman R. A. Uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase of Acanthamoeba castellanii. Purification, kinetic, and developmental studies. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):7832–7840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stowers M. D. Carbon metabolism in Rhizobium species. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:89–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H. U., Zander R., Lang W. An automated continuous determination of oxygen with high sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1976 Aug;74(2):585–591. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90241-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



