Abstract
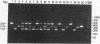
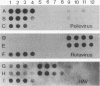
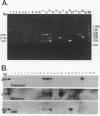
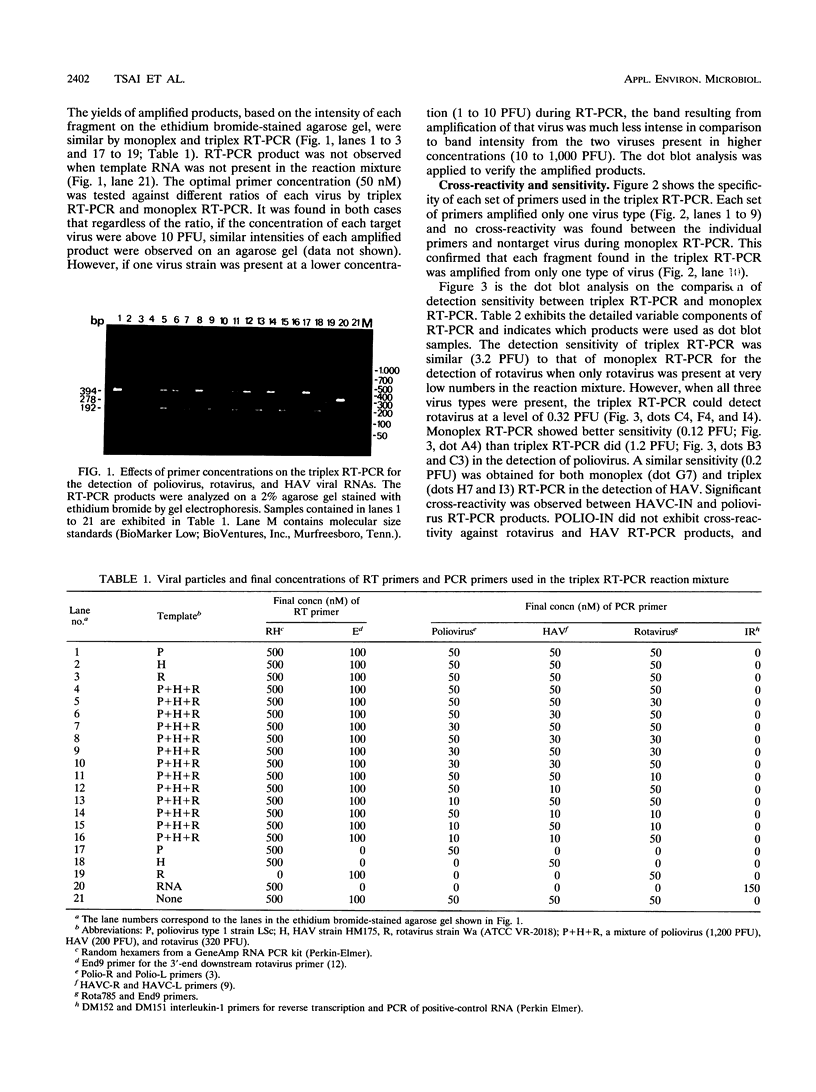
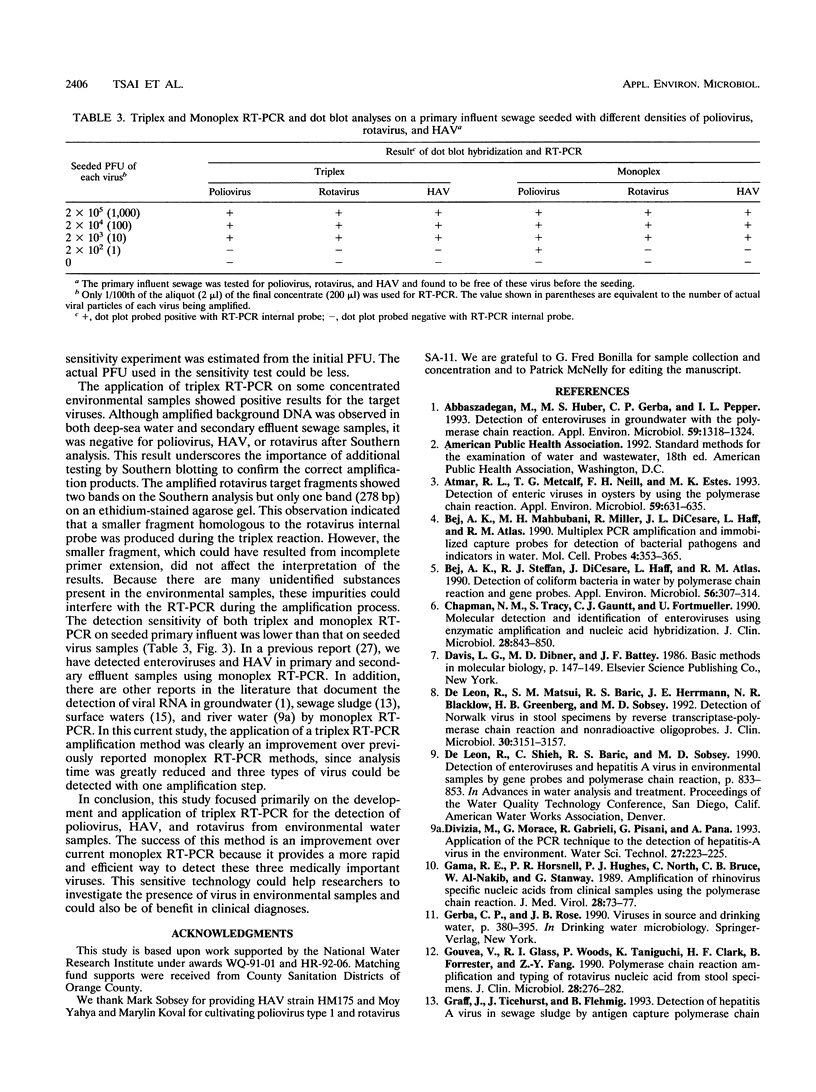
A triplex reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) was developed to simultaneously detect poliovirus, hepatitis A virus (HAV), and rotavirus in sewage and ocean water. Sewage and ocean water samples seeded with the three different viruses were concentrated by ultrafiltration. The unseeded ocean water and sewage samples were concentrated by vortex flow filtration and/or ultrafiltration. Random hexamers and a rotavirus downstream primer were used to initiate reverse transcription. Three different sets of primers specific for poliovirus, HAV, and rotavirus cDNAs were mixed in the PCR mixture to amplify the target DNA. Three distinct amplified DNA products representing poliovirus, HAV, and rotavirus were identified by gel electrophoresis as 394-, 192-, and 278-bp sequences, respectively. Dot blot and Southern analyses were used to confirm the amplified products for each virus present in the environmental samples. Except for poliovirus, the sensitivity of triplex RT-PCR for the detection of rotavirus and HAV was found to be similar to that of monoplex RT-PCR, which uses only one set of primers to amplify a single type of virus. The triplex RT-PCR has greater advantages over monoplex RT-PCR for virus detection, namely, the rapid turnaround time and cost effectiveness.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbaszadegan M., Huber M. S., Gerba C. P., Pepper I. L. Detection of enteroviruses in groundwater with the polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 May;59(5):1318–1324. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.5.1318-1324.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atmar R. L., Metcalf T. G., Neill F. H., Estes M. K. Detection of enteric viruses in oysters by using the polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Feb;59(2):631–635. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.2.631-635.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bej A. K., Mahbubani M. H., Miller R., DiCesare J. L., Haff L., Atlas R. M. Multiplex PCR amplification and immobilized capture probes for detection of bacterial pathogens and indicators in water. Mol Cell Probes. 1990 Oct;4(5):353–365. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(90)90026-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bej A. K., Steffan R. J., DiCesare J., Haff L., Atlas R. M. Detection of coliform bacteria in water by polymerase chain reaction and gene probes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):307–314. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.307-314.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman N. M., Tracy S., Gauntt C. J., Fortmueller U. Molecular detection and identification of enteroviruses using enzymatic amplification and nucleic acid hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):843–850. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.843-850.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Leon R., Matsui S. M., Baric R. S., Herrmann J. E., Blacklow N. R., Greenberg H. B., Sobsey M. D. Detection of Norwalk virus in stool specimens by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and nonradioactive oligoprobes. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Dec;30(12):3151–3157. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.12.3151-3157.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gama R. E., Horsnell P. R., Hughes P. J., North C., Bruce C. B., al-Nakib W., Stanway G. Amplification of rhinovirus specific nucleic acids from clinical samples using the polymerase chain reaction. J Med Virol. 1989 Jun;28(2):73–77. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890280204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouvea V., Glass R. I., Woods P., Taniguchi K., Clark H. F., Forrester B., Fang Z. Y. Polymerase chain reaction amplification and typing of rotavirus nucleic acid from stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):276–282. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.276-282.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graff J., Ticehurst J., Flehmig B. Detection of hepatitis A virus in sewage sludge by antigen capture polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Oct;59(10):3165–3170. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.10.3165-3170.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang X., Wang J., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. Detection of Norwalk virus in stool by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Oct;30(10):2529–2534. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.10.2529-2534.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecka H., Dubrou S., Prevot J., Marechal J., López-Pila J. M. Detection of naturally occurring enteroviruses in waters by reverse transcription, polymerase chain reaction, and hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Apr;59(4):1213–1219. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.4.1213-1219.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse D. L., Guzewich J. J., Hanrahan J. P., Stricof R., Shayegani M., Deibel R., Grabau J. C., Nowak N. A., Herrmann J. E., Cukor G. Widespread outbreaks of clam- and oyster-associated gastroenteritis. Role of Norwalk virus. N Engl J Med. 1986 Mar 13;314(11):678–681. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198603133141103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir P., Nicholson F., Jhetam M., Neogi S., Banatvala J. E. Rapid diagnosis of enterovirus infection by magnetic bead extraction and polymerase chain reaction detection of enterovirus RNA in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jan;31(1):31–38. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.1.31-38.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy A. M., Grohmann G. S., Christopher P. J., Lopez W. A., Davey G. R., Millsom R. H. An Australia-wide outbreak of gastroenteritis from oysters caused by Norwalk virus. Med J Aust. 1979 Oct 6;2(7):329–333. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1979.tb104133.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul M. O., Erinle E. A. Influence of humidity on rotavirus prevalence among Nigerian infants and young children with gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;15(2):212–215. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.2.212-215.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Kohara M., Kataoka Y., Suganuma T., Omata T., Imura N., Nomoto A. Complete nucleotide sequences of all three poliovirus serotype genomes. Implication for genetic relationship, gene function and antigenic determinants. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):561–585. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai Y. L., Palmer C. J., Sangermano L. R. Detection of Escherichia coli in sewage and sludge by polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Feb;59(2):353–357. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.2.353-357.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai Y. L., Sobsey M. D., Sangermano L. R., Palmer C. J. Simple method of concentrating enteroviruses and hepatitis A virus from sewage and ocean water for rapid detection by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Oct;59(10):3488–3491. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.10.3488-3491.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanke C. A., Guerrant R. L. Viral hepatitis and gastroenteritis transmitted by shellfish and water. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1987 Sep;1(3):649–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. S., Josephson K. L., Pillai S. D., Abbaszadegan M., Gerba C. P., Pepper I. L. Specific detection of Salmonella spp. by multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 May;59(5):1473–1479. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.5.1473-1479.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde J., Van R., Pickering L., Eiden J., Yolken R. Detection of rotaviruses in the day care environment by reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1992 Sep;166(3):507–511. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.3.507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]