Abstract
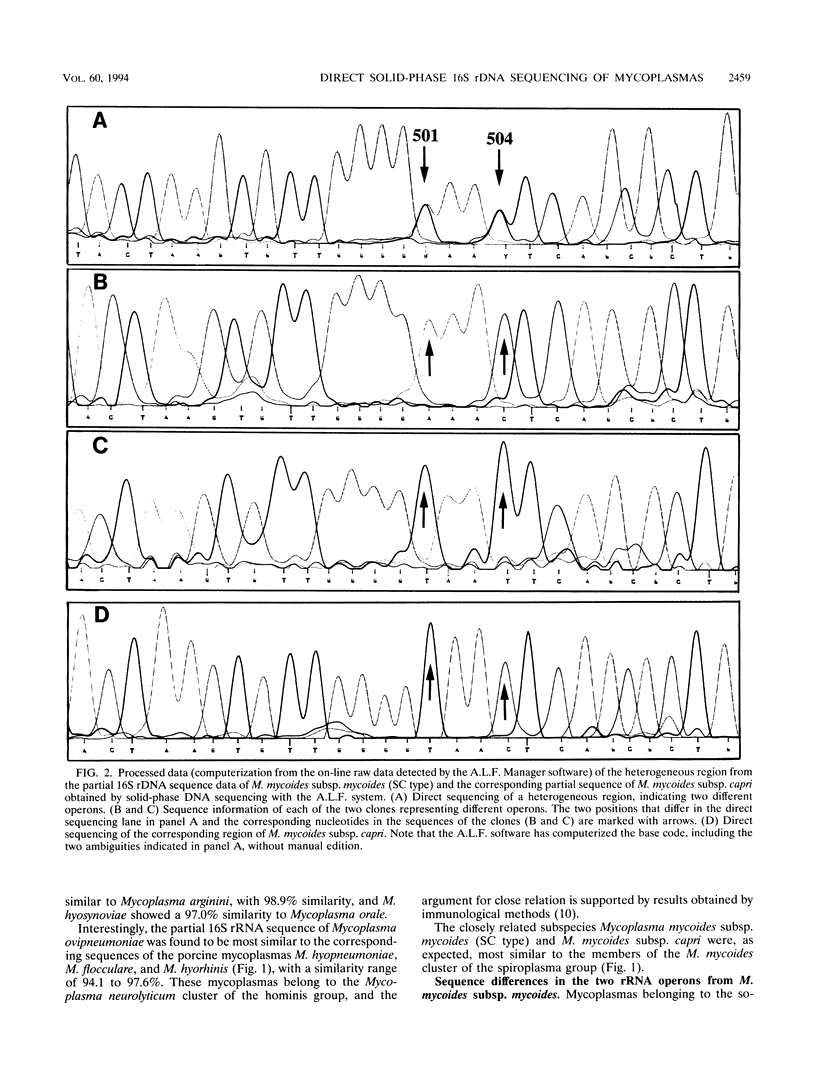
Automated solid-phase DNA sequencing was used for determination of partial 16S ribosomal DNA sequences of mycoplasmas. The sequence information was used to establish phylogenetic relationships of 11 different mycoplasmas whose 16S rRNA sequences had not been determined earlier. A biotinylated fragment corresponding to positions 344 to 939 in the Escherichia coli sequence was generated by PCR. The PCR product was immobilized onto streptavidin-coated paramagnetic beads, and direct sequencing was performed in both directions. One previously unclassified avian mycoplasma was found to belong to the Mycoplasma lipophilum cluster of the hominis group. Microheterogeneities were discovered in the rRNA operons of Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides (SC type), confirming the existence of two different rRNA operons. The 16S rRNA sequence of M. mycoides subsp. capri was identical to that of M. mycoides subsp. mycoides (type SC), except that no microheterogeneities were revealed. Furthermore, automated solid-phase DNA sequencing was used to identify a mycoplasmal contamination of a cell culture as Mycoplasma hyorhinis, which proved to be very difficult by conventional methods. The results suggest that the direct solid-phase DNA sequencing procedure is a powerful tool for identification of mycoplasmas and is also useful in taxonomic studies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brosius J., Palmer M. L., Kennedy P. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölske G., Mörner T. Isolation of a Mycoplasma sp. from three buzzards (Buteo spp.). Avian Dis. 1982 Apr-Jun;26(2):406–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölske G. Survey of Mycoplasma infections in cell cultures and a comparison of detection methods. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1988 Nov;269(3):331–340. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(88)80176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttger E. C. Rapid determination of bacterial ribosomal RNA sequences by direct sequencing of enzymatically amplified DNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Nov;53(1-2):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90386-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson S. J., Colwell R. R., McMeekin T. A., Franzmann P. D. Direct sequencing of the polymerase chain reaction-amplified 16S rRNA gene of Flavobacterium gondwanense sp. nov. and Flavobacterium salegens sp. nov., two new species from a hypersaline Antarctic lake. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;43(1):77–83. doi: 10.1099/00207713-43-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Wisotzkey J. D., Jurtshuk P., Jr How close is close: 16S rRNA sequence identity may not be sufficient to guarantee species identity. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;42(1):166–170. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-1-166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis N. F., Jensen P. T. Serological comparison of type strains of porcine, bovine, and ovine mycoplasmas with atypical colony morphology. Acta Vet Scand. 1984;25(1):29–35. doi: 10.1186/BF03547276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frydenberg J., Christiansen C. The sequence of 16S rRNA from Mycoplasma strain PG50. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):127–137. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W., Sankoff D., Cedergren R. J. On the evolutionary descent of organisms and organelles: a global phylogeny based on a highly conserved structural core in small subunit ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5837–5852. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultman T., Bergh S., Moks T., Uhlén M. Bidirectional solid-phase sequencing of in vitro-amplified plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1991 Jan;10(1):84–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultman T., Ståhl S., Hornes E., Uhlén M. Direct solid phase sequencing of genomic and plasmid DNA using magnetic beads as solid support. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):4937–4946. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.4937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwami M., Muto A., Yamao F., Osawa S. Nucleotide sequence of the rrnB 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Mycoplasma capricolum. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(2):317–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00328065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Pace B., Olsen G. J., Stahl D. A., Sogin M. L., Pace N. R. Rapid determination of 16S ribosomal RNA sequences for phylogenetic analyses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6955–6959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lea T., Vartdal F., Nustad K., Funderud S., Berge A., Ellingsen T., Schmid R., Stenstad P., Ugelstad J. Monosized, magnetic polymer particles: their use in separation of cells and subcellular components, and in the study of lymphocyte function in vitro. J Mol Recognit. 1988 Feb;1(1):9–18. doi: 10.1002/jmr.300010104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leitner T., Halapi E., Scarlatti G., Rossi P., Albert J., Fenyö E. M., Uhlén M. Analysis of heterogeneous viral populations by direct DNA sequencing. Biotechniques. 1993 Jul;15(1):120–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Overbeek R., Larsen N., Marsh T. L., McCaughey M. J., Maciukenas M. A., Kuan W. M., Macke T. J., Xing Y., Woese C. R. The Ribosomal Database Project. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20 (Suppl):2199–2200. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.suppl.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen G. J., Woese C. R. Ribosomal RNA: a key to phylogeny. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):113–123. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyle L. E., Taylor T., Finch L. R. Genomic maps of some strains within the Mycoplasma mycoides cluster. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7265–7268. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7265-7268.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Molecular biology and genetics of mycoplasmas (Mollicutes). Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):419–455. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.419-455.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemke G. W., Laigret F., Grau O., Bové J. M. Phylogenetic relationships of three porcine mycoplasmas, Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, Mycoplasma flocculare, and Mycoplasma hyorhinis, and complete 16S rRNA sequence of M. flocculare. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;42(2):220–225. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-2-220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taschke C., Ruland K., Herrmann R. Nucleotide sequence of the 16S rRNA of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 11;15(9):3918–3918. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.9.3918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlberg J., Holmberg A., Bergh S., Hultman T., Uhlén M. Automated magnetic preparation of DNA templates for solid phase sequencing. Electrophoresis. 1992 Aug;13(8):547–551. doi: 10.1002/elps.11501301112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Tully J. G., Rose D. L., Petzel J. P., Oyaizu H., Yang D., Mandelco L., Sechrest J., Lawrence T. G., Van Etten J. A phylogenetic analysis of the mycoplasmas: basis for their classification. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6455–6467. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6455-6467.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kuppeveld F. J., Johansson K. E., Galama J. M., Kissing J., Bölske G., van der Logt J. T., Melchers W. J. Detection of mycoplasma contamination in cell cultures by a mycoplasma group-specific PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Jan;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.1.149-152.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]