Abstract
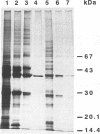
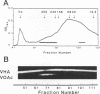
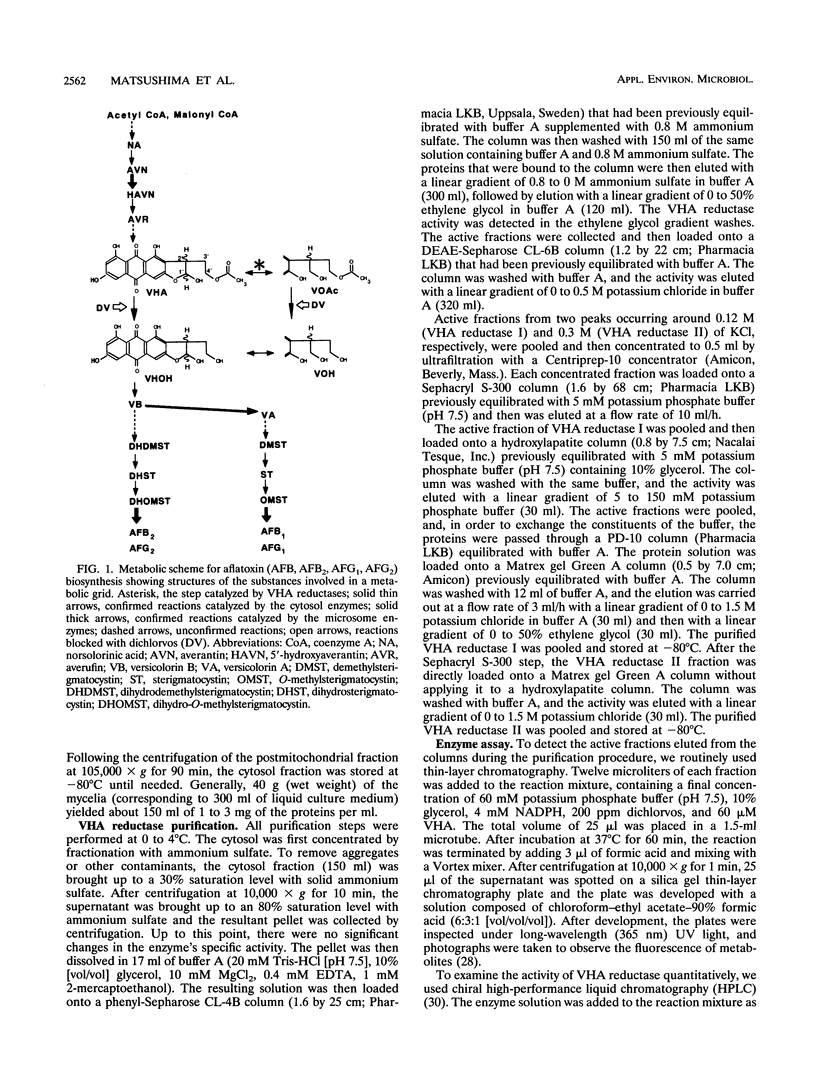
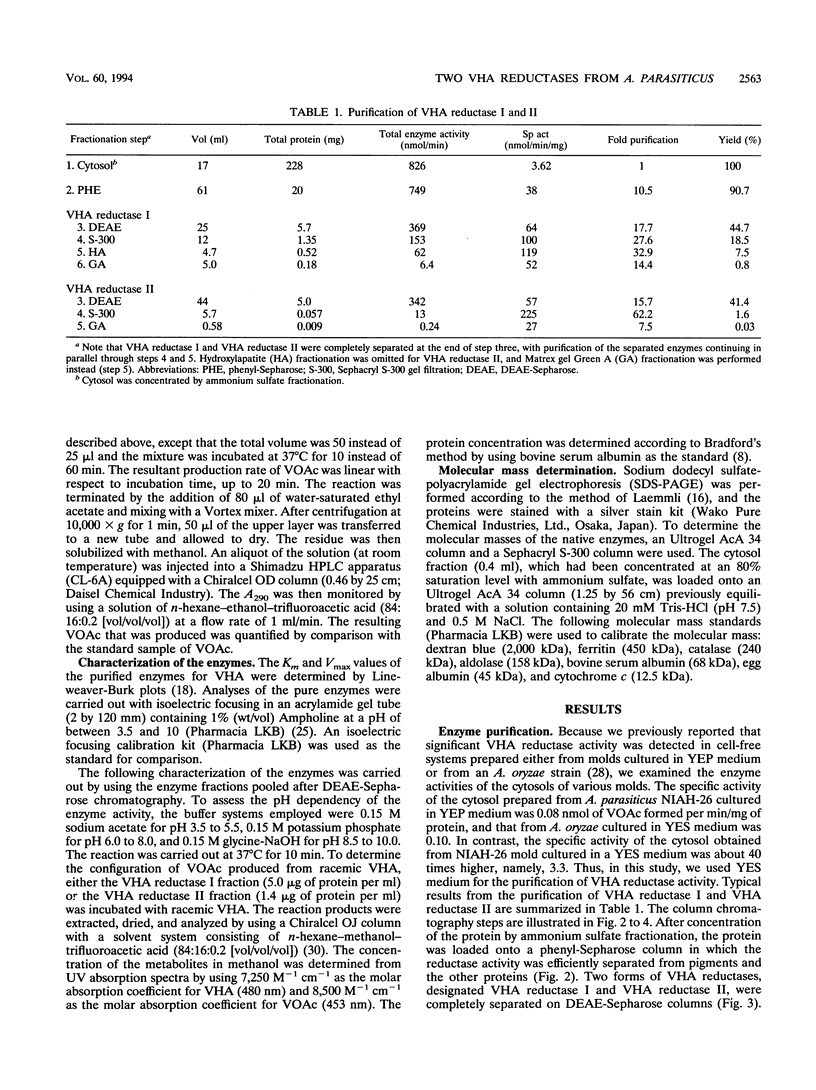
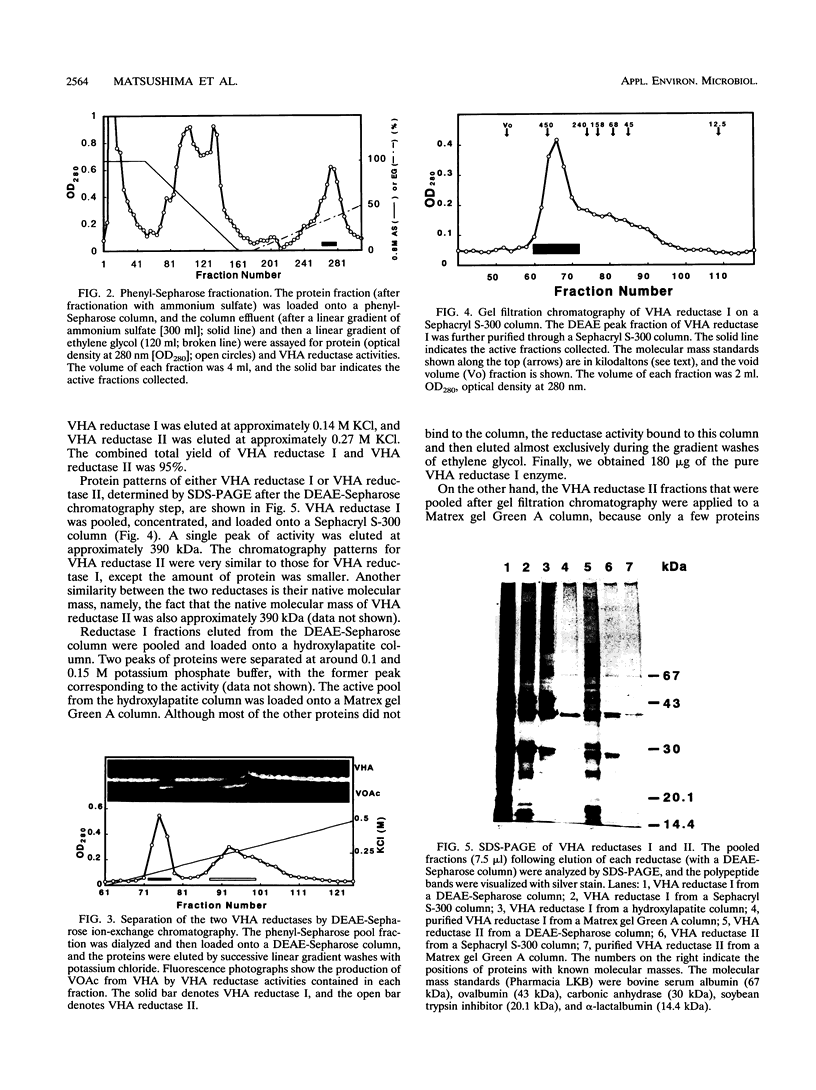
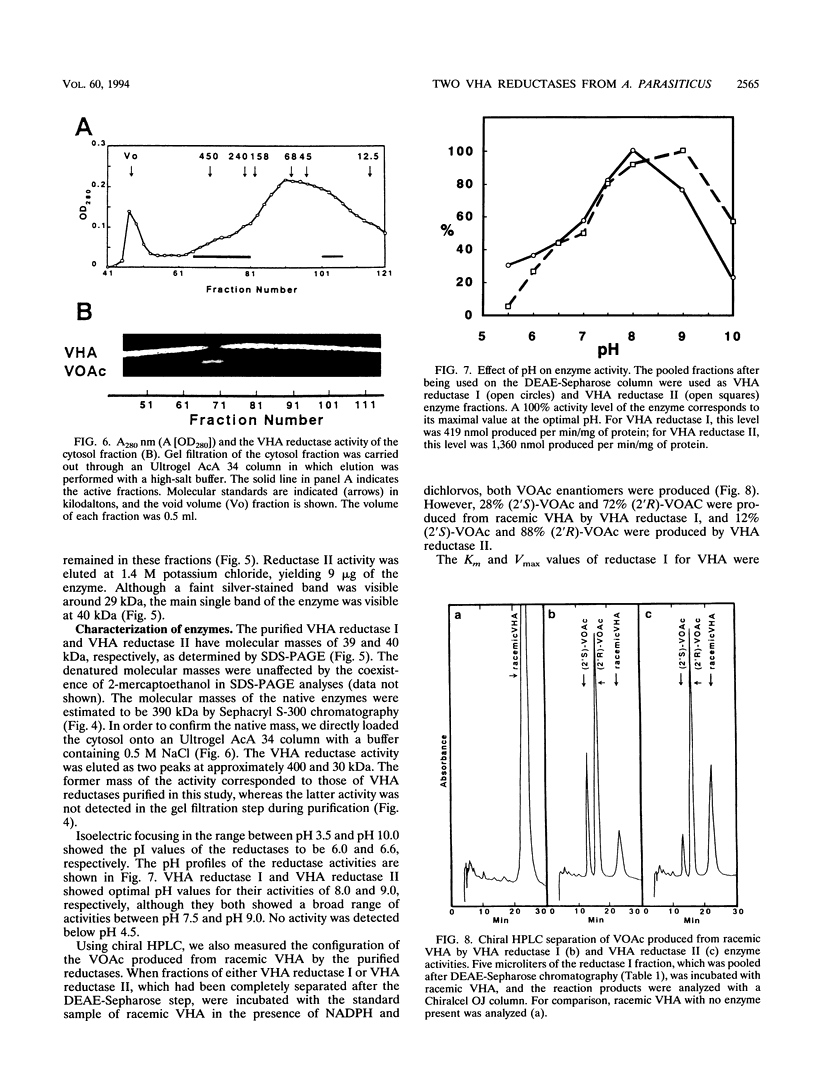
Two versiconal hemiacetal acetate (VHA) reductase activities (designated I and II), which catalyzed the reaction from VHA to versiconol acetate (VOAc) during aflatoxin biosynthesis, were purified to apparent homogeneity from the cytosol fraction of the mycelia of Aspergillus parasiticus mutant NIAH-26 through the following chromatography steps: first, fractionation with ammonium sulfate and then fractionation in succession with phenyl-Sepharose, DEAE-Sepharose, Sephacryl S-300, hydroxylapatite, and Matrex gel Green A chromatography. VHA reductase I and VHA reductase II were completely separated at the end of the DEAE-Sepharose step. The apparent molecular masses of reductase I and reductase II were estimated (by gel filtration) to be approximately 390 kDa; their denaturing molecular masses were 39- and 40-kDa, respectively (by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis). Their pI values were 6.6 and 6.0, respectively (as determined by isoelectric focusing), and the optimal pH values were 8.0 and 9.0, respectively, although both enzymes exhibited a broad optimal pH range of between 7.5 and 9.0. The Km values of reductase I and reductase II for VHA were 35.4 and 25.4 μM, respectively. On the other hand, in the cell-free experiments involving either VHA reductase fraction and high-performance liquid chromatography, both (2′S)- and (2′R)-VOAc enantiomers were formed from racemic VHA and more of the 2′R isomer than the 2′S isomer was produced, indicating that the VHA reductase fractions have very similar stereospecificities to the substrate.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J. W., Christensen S. B. New perspectives on aflatoxin biosynthesis. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1983;29:53–92. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70354-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar D., Cleveland T. E., Kingston D. G. Enzymological evidence for separate pathways for aflatoxin B1 and B2 biosynthesis. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 30;30(17):4343–4350. doi: 10.1021/bi00231a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar D., McCormick S. P., Lee L. S., Hill R. A. Identification of O-methylsterigmatocystin as an aflatoxin B1 and G1 precursor in Aspergillus parasiticus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1028–1033. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1028-1033.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar D., Ullah A. H., Cleveland T. E. Purification and characterization of a methyltransferase from Aspergillus parasiticus SRRC 163 involved in aflatoxin biosynthetic pathway. Prep Biochem. 1988;18(3):321–349. doi: 10.1080/00327488808062532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang P. K., Skory C. D., Linz J. E. Cloning of a gene associated with aflatoxin B1 biosynthesis in Aspergillus parasiticus. Curr Genet. 1992 Mar;21(3):231–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00336846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuturgoon A. A., Dutton M. F. The affinity purification and characterization of a dehydrogenase from Aspergillus parasiticus involved in aflatoxin B1 biosynthesis. Prep Biochem. 1991;21(2-3):125–140. doi: 10.1080/10826069108018008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland T. E., Bhatnagar D. Evidence for de novo synthesis of an aflatoxin pathway methyltransferase near the cessation of active growth and the onset of aflatoxin biosynthesis in Aspergillus parasiticus mycelia. Can J Microbiol. 1990 Jan;36(1):1–5. doi: 10.1139/m90-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton M. F. Enzymes and aflatoxin biosynthesis. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):274–295. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.274-295.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng G. H., Chu F. S., Leonard T. J. Molecular cloning of genes related to aflatoxin biosynthesis by differential screening. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):455–460. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.455-460.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh D. P., Wan C. C., Billington J. A. A versiconal hemiacetal acetate converting enzyme in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Mycopathologia. 1989 Sep;107(2-3):121–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00707548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller N. P., Dischinger H. C., Jr, Bhatnagar D., Cleveland T. E., Ullah A. H. Purification of a 40-kilodalton methyltransferase active in the aflatoxin biosynthetic pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Feb;59(2):479–484. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.2.479-484.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin B. K., Anderson J. A. Purification and properties of versiconal cyclase from Aspergillus parasiticus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 Feb 14;293(1):67–70. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90366-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luchese R. H., Harrigan W. F. Biosynthesis of aflatoxin--the role of nutritional factors. J Appl Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;74(1):5–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1993.tb02989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G. A., Nystrom G. J., Bhatnagar D., Cleveland T. E., Woloshuk C. P. Cloning of the afl-2 gene involved in aflatoxin biosynthesis from Aspergillus flavus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jan;59(1):156–162. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.156-162.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skory C. D., Chang P. K., Cary J., Linz J. E. Isolation and characterization of a gene from Aspergillus parasiticus associated with the conversion of versicolorin A to sterigmatocystin in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Nov;58(11):3527–3537. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.11.3527-3537.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skory C. D., Chang P. K., Linz J. E. Regulated expression of the nor-1 and ver-1 genes associated with aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 May;59(5):1642–1646. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.5.1642-1646.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Ando Y., Hamasaki T. A metabolic grid among versiconal hemiacetal acetate, versiconol acetate, versiconol and versiconal during aflatoxin biosynthesis. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Oct;137(10):2469–2475. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-10-2469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Ando Y., Hamasaki T. Biosynthetic relationship among aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, and G2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):2101–2106. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.2101-2106.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Ando Y., Hashimoto J., Hamasaki T. Two distinct O-methyltransferases in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2172–2177. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2172-2177.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Hamasaki T. Stereochemistry during aflatoxin biosynthesis: cyclase reaction in the conversion of versiconal to versicolorin B and racemization of versiconal hemiacetal acetate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Aug;59(8):2493–2500. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.8.2493-2500.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Matsuyama Y., Ando Y., Nakajima H., Hamasaki T. Stereochemistry during aflatoxin biosynthesis: conversion of norsolorinic acid to averufin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Aug;59(8):2486–2492. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.8.2486-2492.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Nakamura H., Ando Y., Terakado N., Nakajima H., Hamasaki T. Isolation and characterization of Aspergillus parasiticus mutants with impaired aflatoxin production by a novel tip culture method. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):2096–2100. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.2096-2100.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yabe K., Nakamura Y., Nakajima H., Ando Y., Hamasaki T. Enzymatic conversion of norsolorinic acid to averufin in aflatoxin biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1340–1345. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1340-1345.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]