Abstract
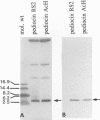
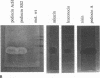
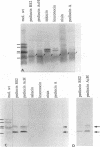
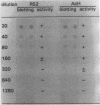
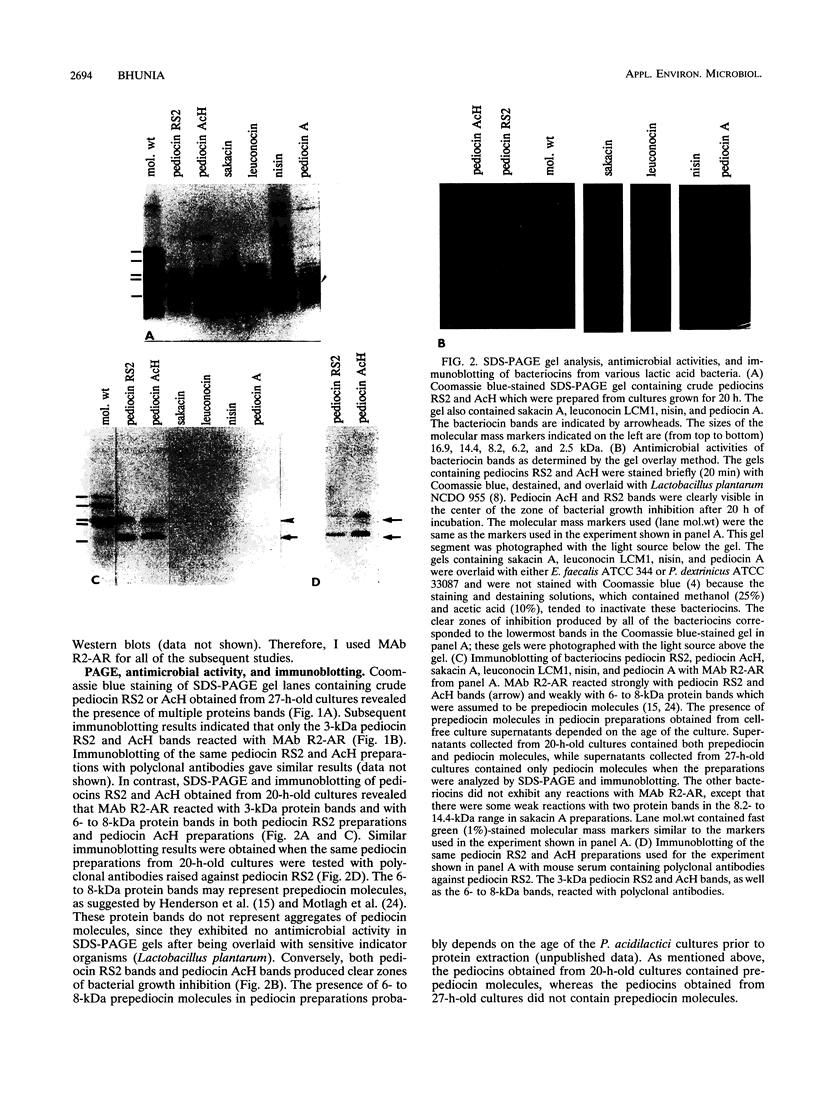
Monoclonal antibody (MAb) R2-AR against pediocin RS2 was developed. Mice were immunized for 12 weeks with pediocin RS2 conjugated to a polyacrylamide gel. Two hybridoma fusions yielded an MAb that in Western blots (immunoblots) reacted only with pediocins RS2 and AcH (3 kDa) from Pediococcus acidilactici RS2 and H, respectively, and did not react with any other bacteriocin, including sakacin A from Lactobacillus sake Lb 706, leuconocin LCM1 from Leuconostoc carnosum LM1, nisin from Lactococcus lactis ATCC 11454, and pediocin A from Pediococcus pentosaceus FBB61. Each of the bacteriocin bands on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gels was confirmed to be biologically active by a gel overlay test performed with sensitive indicator organisms. In dot immunoblot assays, the MAb could detect a minimum of 32,000 arbitrary units of pediocin RS2 or AcH per ml. In colony immunoblot assays, the MAb was used successfully to differentiate bac+ and bac- variants of P. acidilactici RS2 strains.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhunia A. K., Ball P. H., Fuad A. T., Kurz B. W., Emerson J. W., Johnson M. G. Development and characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria innocua. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3176–3184. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3176-3184.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhunia A. K., Johnson M. C., Ray B., Belden E. L. Antigenic property of pediocin AcH produced by Pediococcus acidilactici H. J Appl Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;69(2):211–215. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1990.tb01511.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhunia A. K., Johnson M. C., Ray B. Purification, characterization and antimicrobial spectrum of a bacteriocin produced by Pediococcus acidilactici. J Appl Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;65(4):261–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1988.tb01893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhunia A. K., Johnson M. G. Monoclonal antibody-colony immunoblot method specific for isolation of Pediococcus acidilactici from foods and correlation with pediocin (bacteriocin) production. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jul;58(7):2315–2320. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.7.2315-2320.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikindas M. L., García-Garcerá M. J., Driessen A. J., Ledeboer A. M., Nissen-Meyer J., Nes I. F., Abee T., Konings W. N., Venema G. Pediocin PA-1, a bacteriocin from Pediococcus acidilactici PAC1.0, forms hydrophilic pores in the cytoplasmic membrane of target cells. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Nov;59(11):3577–3584. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.11.3577-3584.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen D. P., Hutkins R. W. Collapse of the proton motive force in Listeria monocytogenes caused by a bacteriocin produced by Pediococcus acidilactici. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Oct;58(10):3312–3315. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.10.3312-3315.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daeschel M. A., Klaenhammer T. R. Association of a 13.6-Megadalton Plasmid in Pediococcus pentosaceus with Bacteriocin Activity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Dec;50(6):1538–1541. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.6.1538-1541.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings J. W., Sailer M., Johnson K., Roy K. L., Vederas J. C., Stiles M. E. Characterization of leucocin A-UAL 187 and cloning of the bacteriocin gene from Leuconostoc gelidum. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7491–7500. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7491-7500.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson J. T., Chopko A. L., van Wassenaar P. D. Purification and primary structure of pediocin PA-1 produced by Pediococcus acidilactici PAC-1.0. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 May 15;295(1):5–12. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90480-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holck A., Axelsson L., Birkeland S. E., Aukrust T., Blom H. Purification and amino acid sequence of sakacin A, a bacteriocin from Lactobacillus sake Lb706. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Dec;138(12):2715–2720. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-12-2715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G., Galabru J., Rivière Y., Montagnier L. Efficiency of poly(A).poly(U) as an adjuvant. Immunol Today. 1988 Jun;9(6):161–162. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91288-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaenhammer T. R. Genetics of bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1993 Sep;12(1-3):39–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1993.tb00012.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marugg J. D., Gonzalez C. F., Kunka B. S., Ledeboer A. M., Pucci M. J., Toonen M. Y., Walker S. A., Zoetmulder L. C., Vandenbergh P. A. Cloning, expression, and nucleotide sequence of genes involved in production of pediocin PA-1, and bacteriocin from Pediococcus acidilactici PAC1.0. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Aug;58(8):2360–2367. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.8.2360-2367.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motlagh A. M., Bhunia A. K., Szostek F., Hansen T. R., Johnson M. C., Ray B. Nucleotide and amino acid sequence of pap-gene (pediocin AcH production) in Pediococcus acidilactici H. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1992 Aug;15(2):45–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765x.1992.tb00721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto Lozano J. C., Meyer J. N., Sletten K., Peláz C., Nes I. F. Purification and amino acid sequence of a bacteriocin produced by Pediococcus acidilactici. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Sep;138(9):1985–1990. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-9-1985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schved F., Lalazar A., Henis Y., Juven B. J. Purification, partial characterization and plasmid-linkage of pediocin SJ-1, a bacteriocin produced by Pediococcus acidilactici. J Appl Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;74(1):67–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1993.tb02998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang R., Johnson M. C., Ray B. Novel method to extract large amounts of bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Oct;58(10):3355–3359. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.10.3355-3359.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]