Abstract
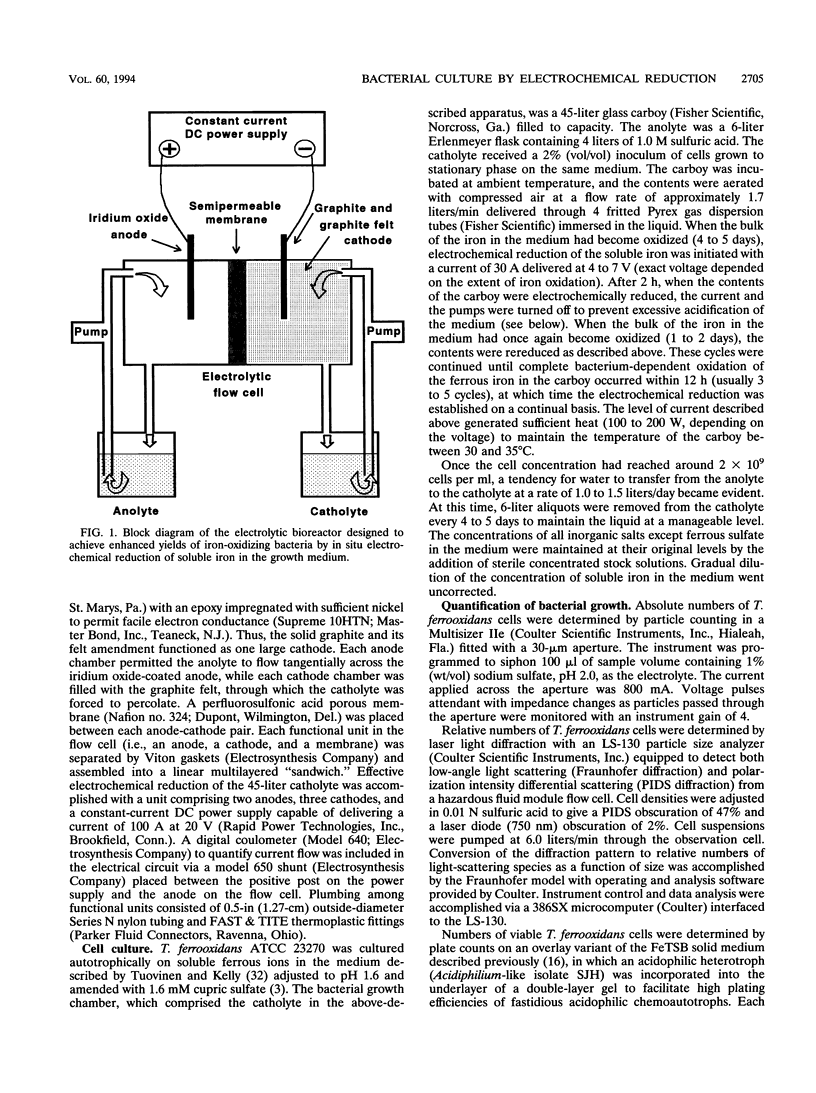
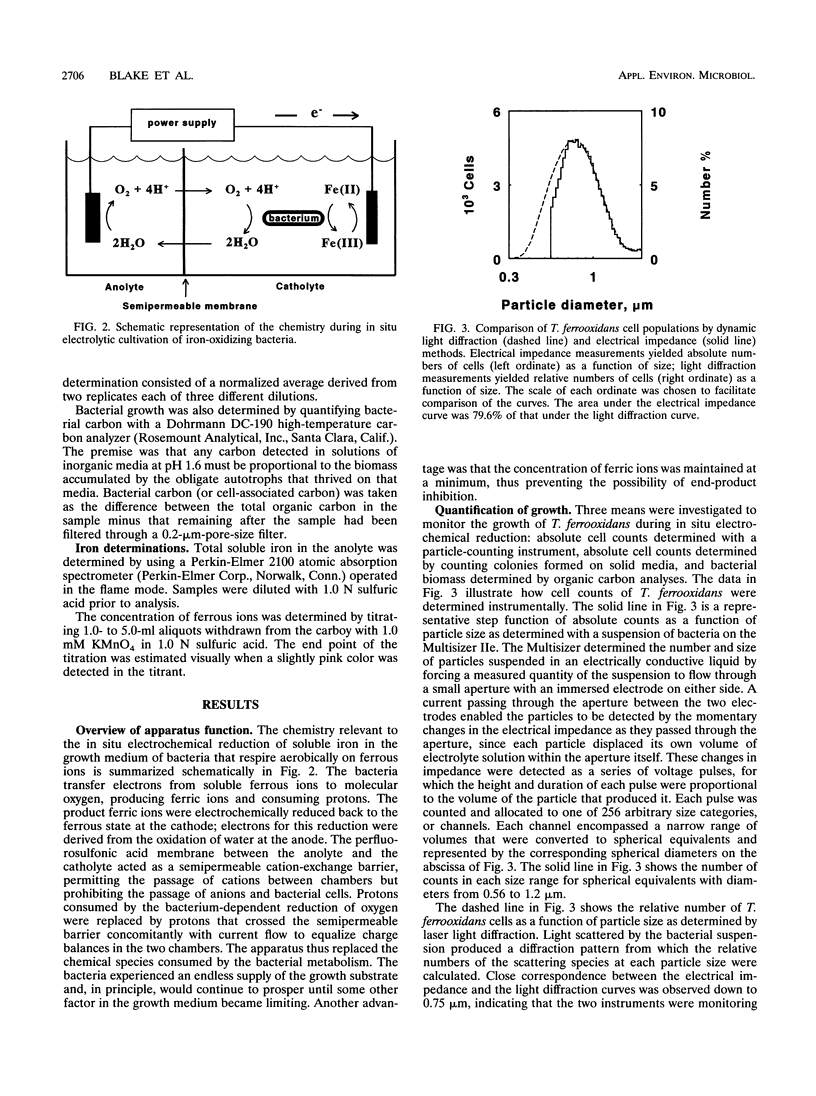
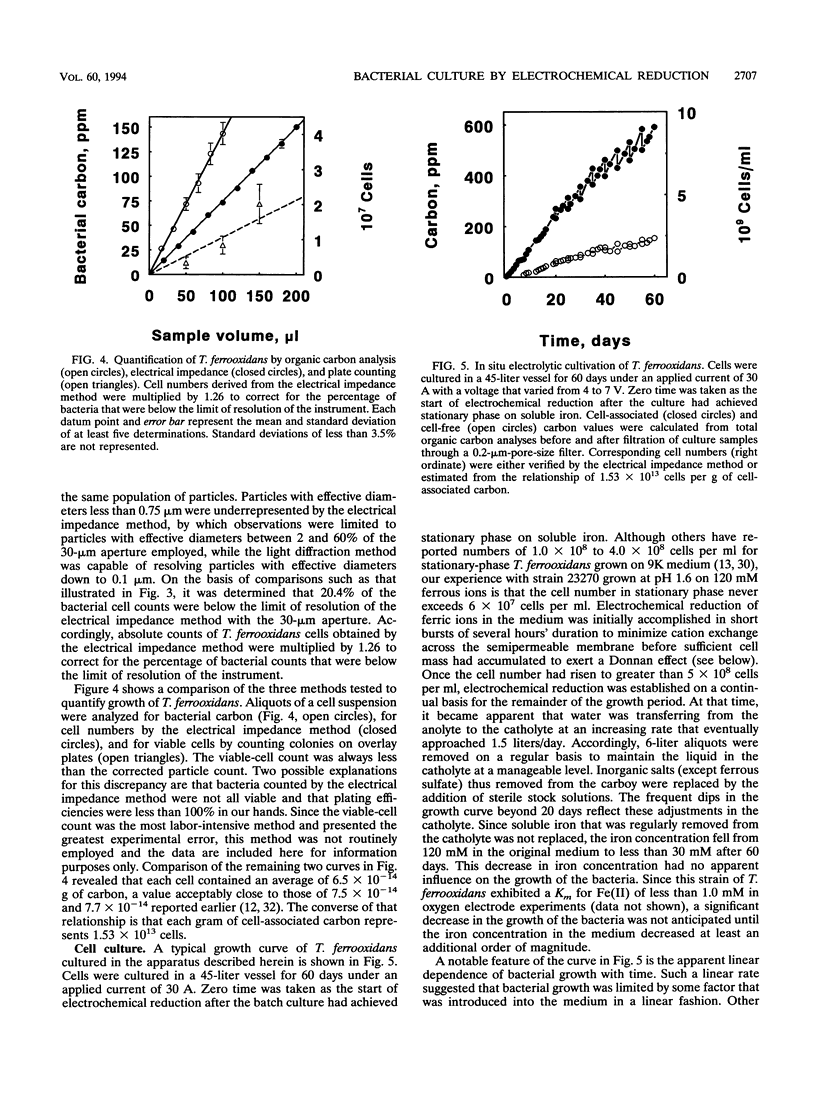
An electrochemical apparatus for culturing chemolithotrophic bacteria that respire aerobically on ferrous ions is described. Enhanced yields of the bacteria were achieved by the in situ electrochemical reduction of soluble iron in the growth medium. When subjected to a direct current of 30 A for 60 days, a 45-liter culture of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans grew from 6 × 107 to 9.5 × 109 cells per ml. Growth of the bacterium within the electrolytic bioreactor was linear with time. A final cell density corresponding to 4.7 g of wet cell paste per liter was achieved, and a total of 320 g of wet cell paste was harvested from one culture. The apparatus was designed to deliver protons concomitantly with electrons; therefore, the pH of the culture remained stable at 1.6 ± 0.1 for the duration of growth. This laboratory-scale apparatus may be readily adapted to pilot or production scale. It is thus anticipated that abundant numbers of iron-oxidizing bacteria may be obtained for both fundamental and applied studies.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake R. C., 2nd, Shute E. A., Greenwood M. M., Spencer G. H., Ingledew W. J. Enzymes of aerobic respiration on iron. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1993 Jul;11(1-3):9–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.1993.tb00261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake R. C., 2nd, Shute E. A. Respiratory enzymes of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. A kinetic study of electron transfer between iron and rusticyanin in sulfate media. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):14983–14989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colmer A. R., Hinkle M. E. The Role of Microorganisms in Acid Mine Drainage: A Preliminary Report. Science. 1947 Sep 19;106(2751):253–256. doi: 10.1126/science.106.2751.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denisov G. V., Kovrov B. G., Trubachev I. N., Gribovskaia I. V., Stepen' A. A. Sostav pitatel'noi sredy dlia nepreryvnogo kul'tivirovaniia Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Mikrobiologiia. 1980 May-Jun;49(3):473–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djebli A., Proctor P., Blake R. C., 2nd, Shoham M. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic studies of rusticyanin from Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 20;227(2):581–582. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90912-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsel N. A., Umbreit W. W. Method for electrolysis of culture medium to increase growth of the sulfur-oxidizing iron bacterium Ferrobacillus sulfooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1964 May;87(5):1243–1244. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.5.1243-1244.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovrov B. G., Denisov G. V., Sekacheva L. G. Zavisimost' skorosti okisleniia zakisnogo zheleza kul'turoi Thiobacillus ferrooxidans ot ego kontsentratsii. Mikrobiologiia. 1978 May-Jun;47(3):400–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R. Dissimilatory Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jun;55(2):259–287. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.2.259-287.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHNAITMAN C., LUNDGREN D. G. ORGANIC COMPOUNDS IN THE SPENT MEDIUM OF FERROBACILLUS FERROOXIDANS. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Feb;11:23–27. doi: 10.1139/m65-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERMAN M. P., LUNDGREN D. G. Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. I. An improved medium and a harvesting procedure for securing high cell yields. J Bacteriol. 1959 May;77(5):642–647. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.5.642-647.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi H., Silver M. Microbiological leaching of a chalcopyrite concentrate by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1976 Aug;18(8):1091–1101. doi: 10.1002/bit.260180806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuovinen O. H., Kelly D. P. Studies on the growth of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. I. Use of membrane filters and ferrous iron agar to determine viable numbers, and comparison with 14 CO 2 -fixation and iron oxidation as measures of growth. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973;88(4):285–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttle J. H., Dugan P. R., Apel W. A. Leakage of cellular material from Thiobacillus ferrooxidans in the presence of organic acids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):459–469. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.459-469.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttle J. H., Dugan P. R. Inhibition of growth, iron, and sulfur oxidation in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans by simple organic compounds. Can J Microbiol. 1976 May;22(5):719–730. doi: 10.1139/m76-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



