Abstract
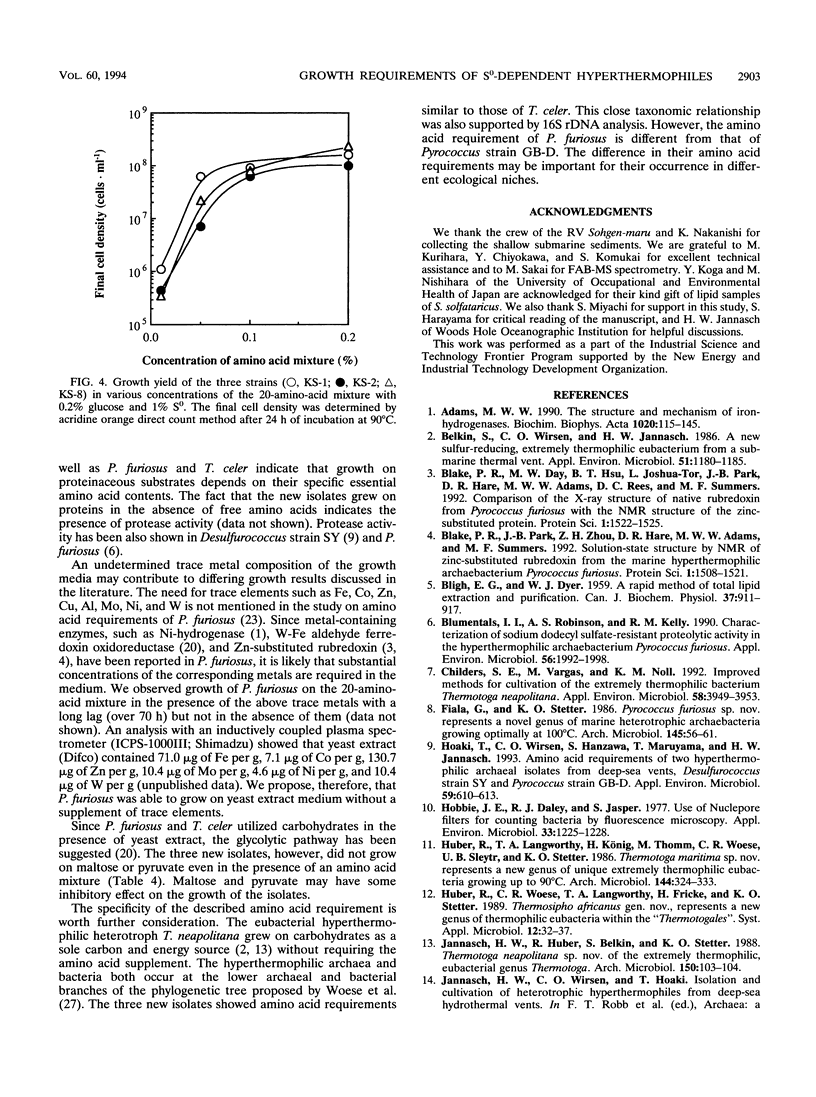
Three hyperthermophilic sulfur-dependent heterotrophs were isolated from a shallow submarine hydrothermal system at an inlet of Kodakara-jima island, Kagoshima, Japan. The isolates grew at 60 to 97 degrees C, with the optimum temperatures at 85 to 90 degrees C. Sensitivity to rifampin and the existence of ether lipids indicated that the isolates are hyperthermophilic archaea. Partial sequencing of the genes coding for 16S rRNA showed that the three isolates are closely related to the genus Thermococcus. They grew on proteinaceous mixtures, such as yeast extract, Casamino Acids, and purified proteins (e.g., casein and gelatin), but not on carbohydrates or organic acids as sole carbon and energy sources. Nine amino acids were essential for growth of isolate KS-1 (Thr, Leu, Ile, Val, Met, Phe, His, Tyr, and Arg). Isolate KS-2 required Lys in addition to the nine amino acids, and KS-8 required Lys instead of Tyr. In comparative studies, it was shown that Thermococcus celer DSM 2476 required 10 amino acids (Thr, Leu, Ile, Val, Met, Phe, Tyr, Trp, Lys, and Arg) while Pyrococcus furiosus DSM 3638 required only Ile and Val. The hyperthermophilic fermentative eubacterium Thermotoga neapolitana DSM 4359 did not require any amino acids for growth.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams M. W. The structure and mechanism of iron-hydrogenases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Nov 5;1020(2):115–145. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belkin S., Wirsen C. O., Jannasch H. W. A new sulfur-reducing, extremely thermophilic eubacterium from a submarine thermal vent. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1180–1185. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1180-1185.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. R., Day M. W., Hsu B. T., Joshua-Tor L., Park J. B., Hare D. R., Adams M. W., Rees D. C., Summers M. F. Comparison of the X-ray structure of native rubredoxin from Pyrococcus furiosus with the NMR structure of the zinc-substituted protein. Protein Sci. 1992 Nov;1(11):1522–1525. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560011113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. R., Park J. B., Zhou Z. H., Hare D. R., Adams M. W., Summers M. F. Solution-state structure by NMR of zinc-substituted rubredoxin from the marine hyperthermophilic archaebacterium Pyrococcus furiosus. Protein Sci. 1992 Nov;1(11):1508–1521. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560011112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumentals I. I., Robinson A. S., Kelly R. M. Characterization of sodium dodecyl sulfate-resistant proteolytic activity in the hyperthermophilic archaebacterium Pyrococcus furiosus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):1992–1998. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.1992-1998.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childers S. E., Vargas M., Noll K. M. Improved Methods for Cultivation of the Extremely Thermophilic Bacterium Thermotoga neapolitana. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Dec;58(12):3949–3953. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.12.3949-3953.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoaki T., Wirsen C. O., Hanzawa S., Maruyama T., Jannasch H. W. Amino Acid Requirements of Two Hyperthermophilic Archaeal Isolates from Deep-Sea Vents, Desulfurococcus Strain SY and Pyrococcus Strain GB-D. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Feb;59(2):610–613. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.2.610-613.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbie J. E., Daley R. J., Jasper S. Use of nuclepore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1225–1228. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1225-1228.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannasch H. W., Wirsen C. O., Molyneaux S. J., Langworthy T. A. Comparative Physiological Studies on Hyperthermophilic Archaea Isolated from Deep-Sea Hot Vents with Emphasis on Pyrococcus Strain GB-D. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Nov;58(11):3472–3481. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.11.3472-3481.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jannasch H. W., Wirsen C. O., Molyneaux S. J., Langworthy T. A. Extremely thermophilic fermentative archaebacteria of the genus desulfurococcus from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 May;54(5):1203–1209. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.5.1203-1209.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol. 1980 Dec;16(2):111–120. doi: 10.1007/BF01731581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukund S., Adams M. W. The novel tungsten-iron-sulfur protein of the hyperthermophilic archaebacterium, Pyrococcus furiosus, is an aldehyde ferredoxin oxidoreductase. Evidence for its participation in a unique glycolytic pathway. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14208–14216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishihara M., Koga Y. Hydroxyarchaetidylserine and hydroxyarchaetidyl-myo-inositol in Methanosarcina barkeri: polar lipids with a new ether core portion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 12;1082(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90196-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snowden L. J., Blumentals I. I., Kelly R. M. Regulation of Proteolytic Activity in the Hyperthermophile Pyrococcus furiosus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Apr;58(4):1134–1141. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.4.1134-1141.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voss T., Melchers K., Scheirle G., Schäfer K. P. Structural comparison of recombinant pulmonary surfactant protein SP-A derived from two human coding sequences: implications for the chain composition of natural human SP-A. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Jan;4(1):88–94. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/4.1.88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLIN E. A., WOLIN M. J., WOLFE R. S. FORMATION OF METHANE BY BACTERIAL EXTRACTS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2882–2886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Kandler O., Wheelis M. L. Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4576–4579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zillig W., Holz I., Janekovic D., Klenk H. P., Imsel E., Trent J., Wunderl S., Forjaz V. H., Coutinho R., Ferreira T. Hyperthermus butylicus, a hyperthermophilic sulfur-reducing archaebacterium that ferments peptides. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3959–3965. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3959-3965.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]