Abstract
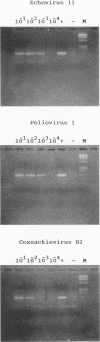
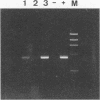
A procedure has been developed for the rapid detection of enteroviruses and adenoviruses in environmental samples. Several systems for virus concentration and extraction of nucleic acid were tested by adding adenovirus type 2 and poliovirus type 1 to different sewage samples. The most promising method for virus recovery involved the concentration of viruses by centrifugation and elution of the virus pellets by treatment with 0.25 N glycine buffer, pH 9.5. Nucleic acid extraction by adsorption of RNA and DNA to silica particles was the most efficient. One aliquot of the extracted nucleic acids was used for a nested two-step PCR, with specific primers for all adenoviruses; and another aliquot was used to synthesize cDNA for a nested two-step PCR with specific primers for further detection of seeded polioviruses or all enteroviruses in the river water and sewage samples. The specificity and sensitivity were evaluated, and 24 different enterovirus strains and the 47 human adenovirus serotypes were recognized by the primers used. The sensitivity was estimated to be between 1 and 10 virus particles for each of the species tested. Twenty-five samples of sewage and polluted river water were analyzed and showed a much higher number of positive isolates by nested PCR than by tissue culture analysis. The PCR-based detection of enteroviruses and adenoviruses shows good results as an indicator of possible viral contamination in environmental wastewater.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbaszadegan M., Huber M. S., Gerba C. P., Pepper I. L. Detection of enteroviruses in groundwater with the polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 May;59(5):1318–1324. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.5.1318-1324.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akusjärvi G., Aleström P., Pettersson M., Lager M., Jörnvall H., Pettersson U. The gene for the adenovirus 2 hexon polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13976–13979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allard A., Albinsson B., Wadell G. Detection of adenoviruses in stools from healthy persons and patients with diarrhea by two-step polymerase chain reaction. J Med Virol. 1992 Jun;37(2):149–157. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890370214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allard A., Girones R., Juto P., Wadell G. Polymerase chain reaction for detection of adenoviruses in stool samples. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Dec;28(12):2659–2667. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.12.2659-2667.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auvinen P., Stanway G., Hyypiä T. Genetic diversity of enterovirus subgroups. Arch Virol. 1989;104(3-4):175–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01315541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blacklow N. R., Greenberg H. B. Viral gastroenteritis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jul 25;325(4):252–264. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199107253250406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boom R., Sol C. J., Salimans M. M., Jansen C. L., Wertheim-van Dillen P. M., van der Noordaa J. Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):495–503. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.495-503.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman N. M., Tracy S., Gauntt C. J., Fortmueller U. Molecular detection and identification of enteroviruses using enzymatic amplification and nucleic acid hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):843–850. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.843-850.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz J. R., Cáceres P., Cano F., Flores J., Bartlett A., Torún B. Adenovirus types 40 and 41 and rotaviruses associated with diarrhea in children from Guatemala. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Aug;28(8):1780–1784. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.8.1780-1784.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty R. M., Phillips P. E., Gibson S., Young L. Restriction endonuclease digestion eliminates product contamination in reverse transcribed polymerase chain reaction. J Virol Methods. 1993 Feb;41(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(93)90130-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlich H. A., Gelfand D., Sninsky J. J. Recent advances in the polymerase chain reaction. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1643–1651. doi: 10.1126/science.2047872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gow J. W., Behan W. M., Clements G. B., Woodall C., Riding M., Behan P. O. Enteroviral RNA sequences detected by polymerase chain reaction in muscle of patients with postviral fatigue syndrome. BMJ. 1991 Mar 23;302(6778):692–696. doi: 10.1136/bmj.302.6778.692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havelaar A. H., van Olphen M., Drost Y. C. F-specific RNA bacteriophages are adequate model organisms for enteric viruses in fresh water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Sep;59(9):2956–2962. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.9.2956-2962.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst C. J., Benton W. H., McClellan K. A. Suppression of viral replication by guanidine: a comparison of human adenoviruses and enteroviruses. J Virol Methods. 1988 Oct;22(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(88)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyypiä T., Auvinen P., Maaronen M. Polymerase chain reaction for human picornaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3261–3268. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving L. G., Smith F. A. One-year survey of enteroviruses, adenoviruses, and reoviruses isolated from effluent at an activated-sludge purification plant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):51–59. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.51-59.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins O., Booth J. D., Minor P. D., Almond J. W. The complete nucleotide sequence of coxsackievirus B4 and its comparison to other members of the Picornaviridae. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jul;68(Pt 7):1835–1848. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-7-1835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopecka H., Dubrou S., Prevot J., Marechal J., López-Pila J. M. Detection of naturally occurring enteroviruses in waters by reverse transcription, polymerase chain reaction, and hybridization. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Apr;59(4):1213–1219. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.4.1213-1219.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikelis V., Spyrou N., Markoulatos P., Serie C. Seasonal distribution of enteroviruses and adenoviruses in domestic sewage. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Jan;31(1):24–25. doi: 10.1139/m85-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C. A., Flewett T. H., Bryden A. S., Davies H. Epidemic viral enteritis in a long-stay children's ward. Lancet. 1975 Jan 4;1(7897):4–5. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92370-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Bugawan T. L., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Analysis of enzymatically amplified beta-globin and HLA-DQ alpha DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):163–166. doi: 10.1038/324163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiemessen C. T., Wegerhoff F. O., Erasmus M. J., Kidd A. H. Infection by enteric adenoviruses, rotaviruses, and other agents in a rural African environment. J Med Virol. 1989 Jul;28(3):176–182. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890280313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhnoo I., Wadell G., Svensson L., Johansson M. E. Importance of enteric adenoviruses 40 and 41 in acute gastroenteritis in infants and young children. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Sep;20(3):365–372. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.3.365-372.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Shaffer J., Murphy R. F., Bonner J., Hirose T., Itakura K. Hybridization of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides to phi chi 174 DNA: the effect of single base pair mismatch. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3543–3557. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada O., Matsumoto T., Nakashima M., Hagari S., Kamahora T., Ueyama H., Kishi Y., Uemura H., Kurimura T. A new method for extracting DNA or RNA for polymerase chain reaction. J Virol Methods. 1990 Feb;27(2):203–209. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(90)90136-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]